Our Environment (Part 2) Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What is the Environment? |

|
| Waste |

|
| Need to Manage Waste |

|
| Pollution |

|
| Greenhouse Effect |

|
| Global Warming |

|
What is the Environment?
- The environment is the natural space where living things grow, develop, and survive.
- The term "environ" means to surround, and it includes both living (plants and animals) and non-living (soil, water, and air) elements.
- The environment provides everything necessary for our survival, and all living things rely on each other and their surroundings.

- A clean environment is crucial for healthy living. If our surroundings are clean, it benefits us and other living beings. Damage to the environment, whether direct or indirect, affects everyone.
- Unfortunately, there has been a significant change in the environment recently. The extensive construction of towns and cities, the building of roads, and various other factors have contributed to environmental destruction. Many trees have been cut down to meet urban demands, and our activities, including the production of waste, are harming the environment.
- In simple terms, taking care of our environment is important for our well-being, and the actions we take, like cutting down trees or creating waste, have consequences for the world around us.
Waste
Generally, we discard many items that seem useless to us. Such useless and unwanted material that is discarded by humans is known as waste. Waste is produced in our homes, schools, offices, markets, industries and agricultural fields.
Types of waste

1. Biodegradable Waste
- The waste that easily decompose is called biodegradable waste.
- It consists of organic waste, which gets broken down into simpler particles (called degradation) by the action of decomposers.
- Examples: Vegetable peels, paper bits, dry leaves, tissues, egg shells, fruit peels, hairs, etc
2. Non-biodegradable Waste
- The waste that does not rot is called non-biodegradable waste.
- It consists of inorganic waste that cannot be broken down into simpler particles by the action of decomposers.
- Examples: Plastic and glass bottles, old cells, batteries, polythene bags, etc.
Need to Manage Waste
Proper management of waste, especially non-biodegradable waste, is very important. The generation of waste not only looks aesthetically unpleasant, but it is also harmful to our environment.
Management of Non-biodegradable Wastes
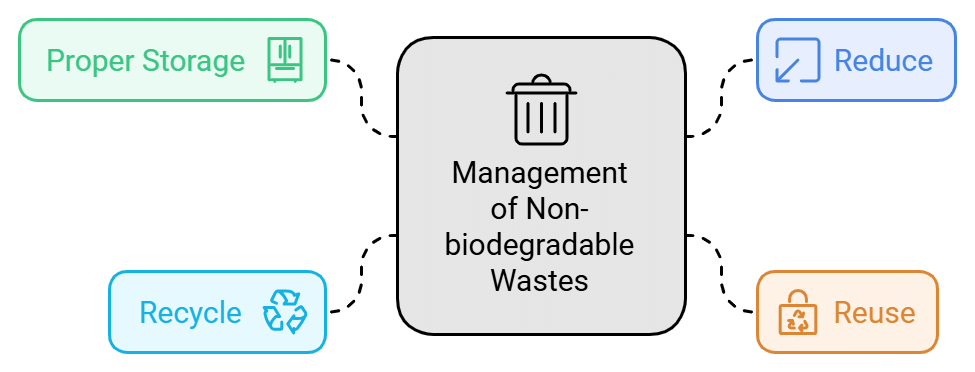 Management of Non-biodegradable Wastes
Management of Non-biodegradable Wastes
- Proper storage: To generate less waste, we should always store food items properly so that microorganisms cannot spoil them.
- Reduce: Reduce the production of wastes by consumption and low wastage. For example, avoid using plastic bags; carry your own cloth bags, use both sides of the paper, buy only what you need and avoid using disposable plastic items.
- Reuse: This explains the importance of utilizing things that we no longer require for different purposes. We can use empty jam containers to keep pickles, spices, etc. Also, we should choose to buy things like glass bottles for soft drinks and juices instead of metal cans.
- Recycle: This involves the production of new products from the old discarded products. Paper, glass, plastics and metals can be recycled repeatedly without any loss of quality.
Management of Biodegradable Waste
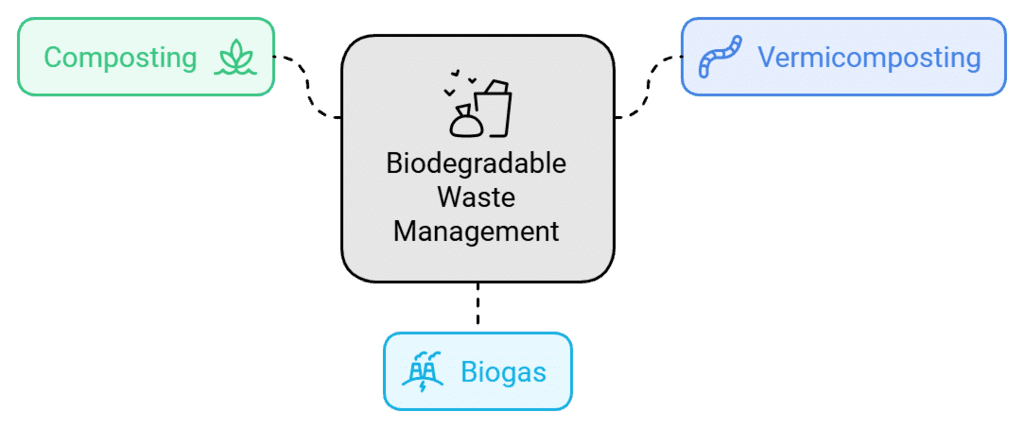 Management of Biodegradable Waste
Management of Biodegradable Waste
- Composting: Vegetable and fruit peels, egg shells, paper, jute products, hair, etc., are converted into compost in deep pits called compost pits. It is done by the action of decomposers like bacteria and fungi.
- Vermicomposting: Vermicomposting involves the use of red earthworms instead of fungi and bacteria. Earthworms are added to the waste and they breakdown the organic matter into soil like material, called vermicompost.
- Biogas: The biogas is produced in a biogas plant. Cow and buffalo dung along with agricultural remains get decomposed and produce biogas. The main constituent of this gas is methane. Methane gas acts as an excellent fuel.
Pollution
- The surroundings in which we live are our environment.
- Human beings have made several changes in the environment to suit their needs.
- The harmful changes brought into the environment by human activities are called pollution.
Types of Pollution
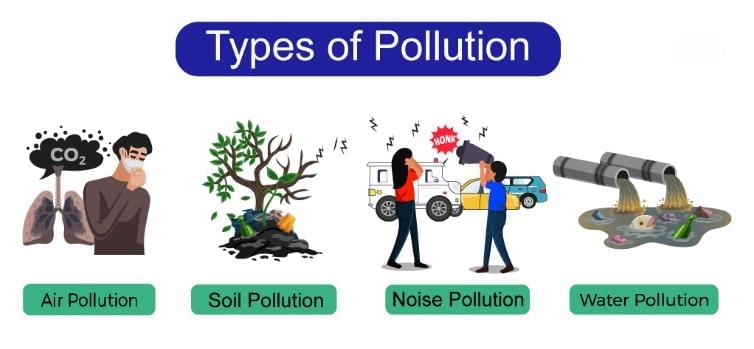 1. Air Pollution
1. Air Pollution
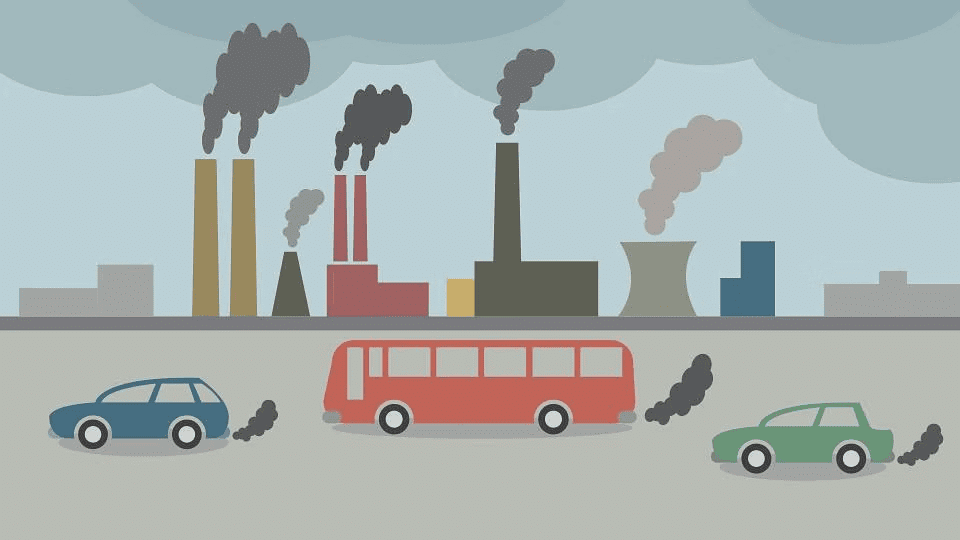
- It is caused by industries and vehicles.
- Air pollution refers to any physical, chemical or biological change in the air.
- It is the contamination of air by harmful gases, dust and smoke which affects plants, animals and humans drastically.
 Air Pollution
Air Pollution
2. Water Pollution
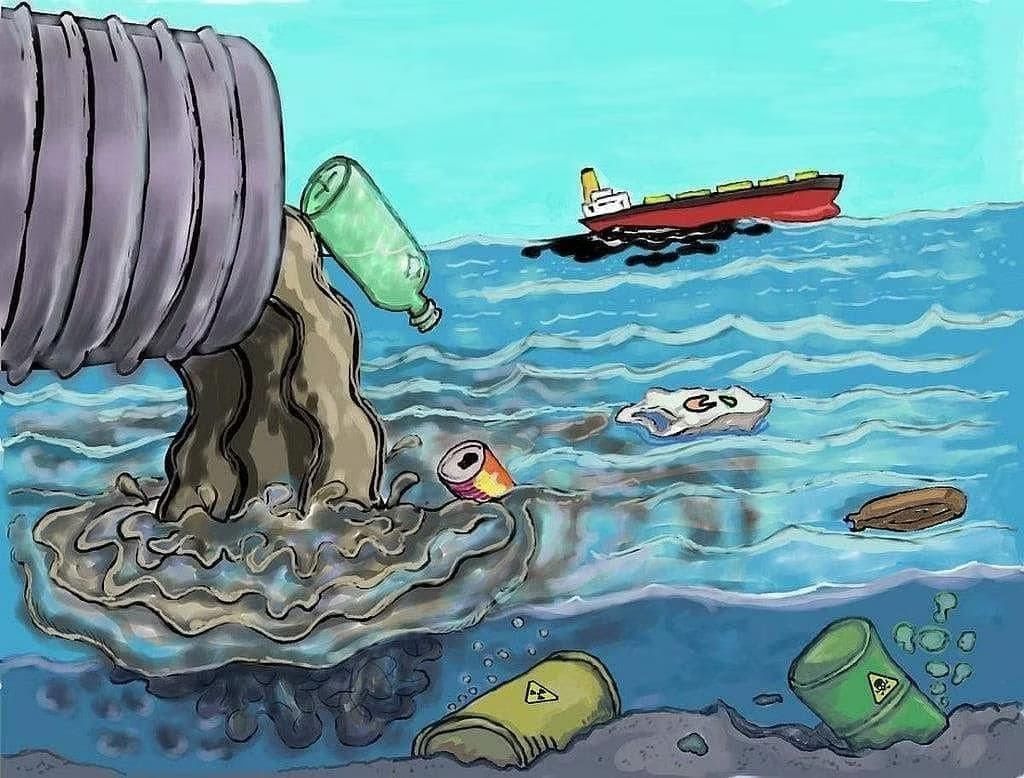
- It is caused by the release of household and industrial wastes into water bodies.
- Water pollution occurs when harmful substances—often chemicals or microorganisms—contaminate a stream, river, lake, ocean, aquifer, or other body of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to humans or the environment.
 Water Pollution
Water Pollution
3. Land Pollution
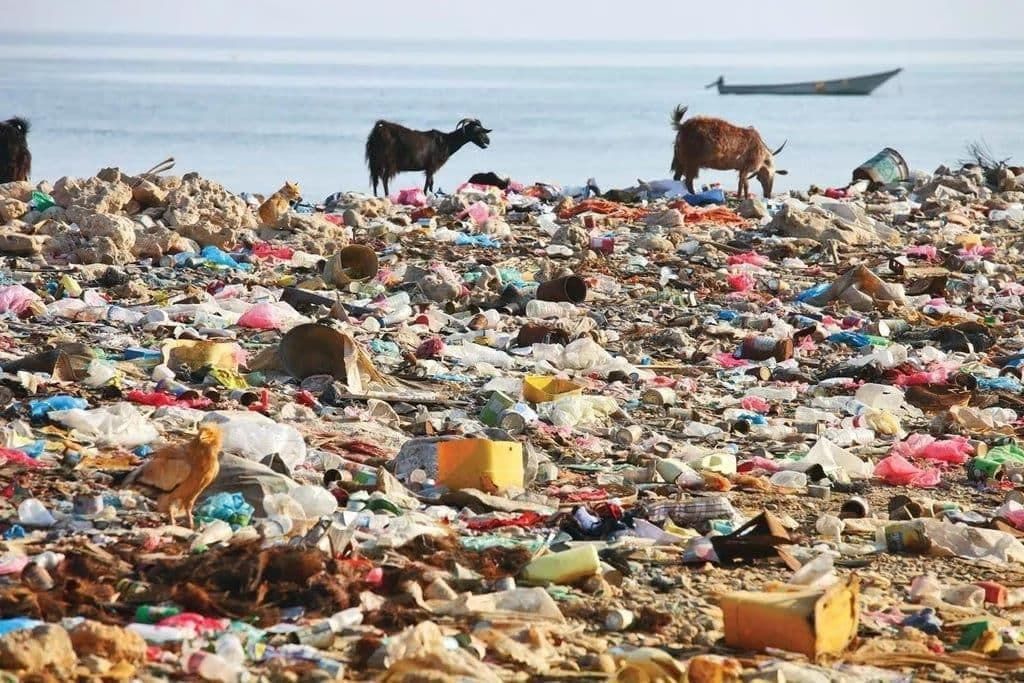
- It is caused by the dumping of solid wastes like polythene bags and glass bottles in the soil.
- Land pollution, the deposition of solid or liquid waste materials on land or underground in a manner that can contaminate the soil and groundwater, threaten public health, and cause unsightly conditions and nuisances.
 Land Pollution
Land Pollution
4. Noise Pollution
- It is caused by the loud noise of machines and vehicles.
- Noise is an unpleasant and undesirable sound which leads to discomfort in human beings.
- Due to increasing noise around the civilizations, noise pollution has become a matter of concern.
 Noise Pollution
Noise Pollution
Greenhouse Effect
- A greenhouse is a house made of glass that is used for growing plants in winter. The glass walls of a greenhouse allow sunlight to enter but do not allow heat to escape.
- Similarly, when the sunlight enters the atmosphere, some of the heat is trapped inside.
- The atmosphere consists of gases like carbon dioxide, water vapour, ozone and methane that have the property of trapping heat. Such gases are called greenhouse gases.
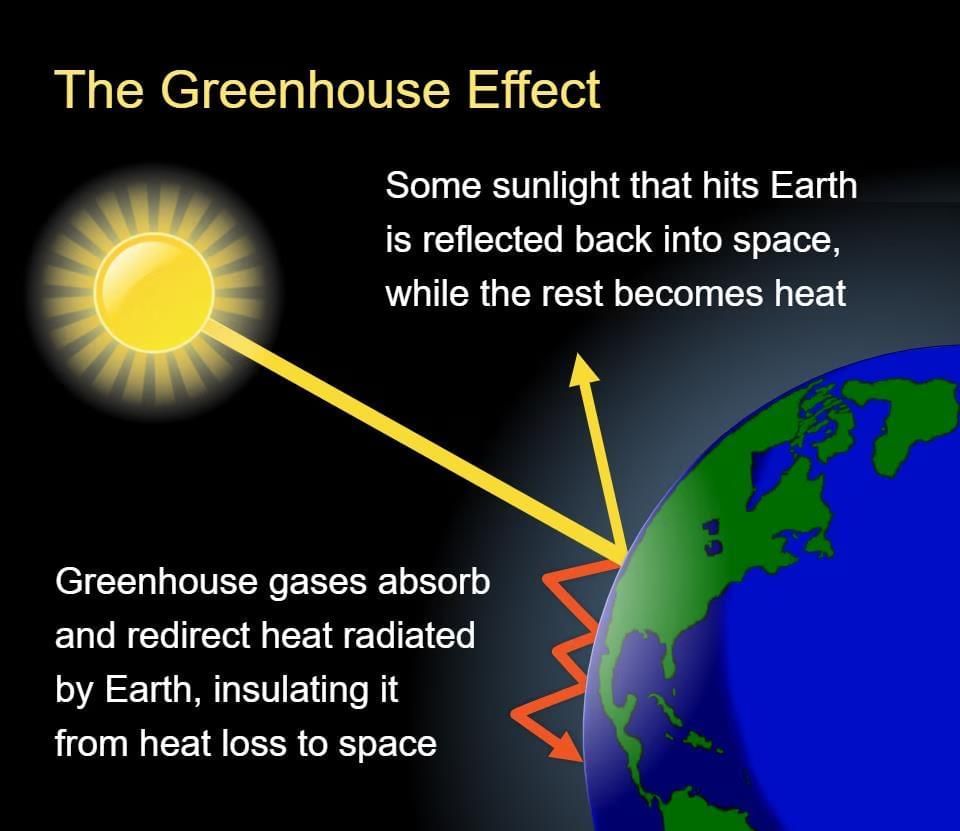
- These gases do not allow heat to escape into space thereby warming the atmosphere. This is called the greenhouse effect.
Global Warming
More greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap more heat. This has led to a steady rise in the Earth’s temperature. This is called global warming. Global Warming
Global Warming
Effects of Global Warming
- Global warming causes changes in climate on the Earth.
- Climate changes are leading to melting of polar ice caps, rise in sea levels and flooding of low-lying areas.
- There may be drastic changes due to global warming in the climate of a place leading to the extinction of some plants and animals in the long run.
Measures to Check Global Warming
- Reduce the use of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum.
- Use electricity wisely.
- Use public transport or car pooling.
- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle wastes.
- Plant more and more trees.
- Switch to clean energy sources like solar energy and wind energy.
|
8 videos|19 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Our Environment (Part 2) Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What is the environment and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What is waste and how does it affect our environment? |  |
| 3. Why do we need to manage waste effectively? |  |
| 4. What is pollution and what are its main types? |  |
| 5. What is the greenhouse effect and how does it relate to global warming? |  |





















