Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Computer for GCSE/IGCSE > Output Devices
Output Devices | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Actuators |

|
| Light projectors |

|
| Laser and Inkjet Printers |

|
| 3D Printers |

|
| Liquid Crystal Display screens |

|
| Organic light emitting diode (OLED) screen |

|
| Speakers |

|
Introduction
- Output devices present processed results in a format understandable to humans.
- Within a general-purpose computer system, the primary output device is the monitor or screen.
- Additional output devices encompass projectors, printers, speakers, and actuators.
Actuators
- Actuators work alongside motors to convert energy (such as electrical, air, or hydraulic) into physical movement of objects.
- They are manufactured in various sizes, each tailored for specific functions.
- Examples of applications include rotating a wheel, opening/closing doors, managing conveyor belts, operating machinery, controlling robotic arms, inducing vibrations, starting/stopping pumps, and regulating valves.
- Actuators are commonly paired with sensors. These sensors compare their input with preset values. If the input falls within a specific range, actuators are activated to move physical objects.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Question for Output Devices
Try yourself:
What is the primary output device in a general-purpose computer system?View Solution
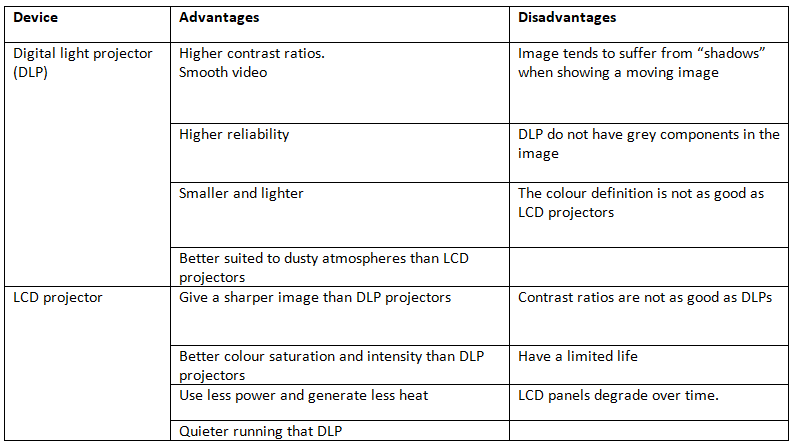
Light projectors
- Light projectors are devices used to display computer outputs on a large screen.
- They are commonly utilized for delivering presentations in various settings, including business and education.
- There exist two main types of light projectors: Digital Light Processing (DLP) and Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) projectors.
- DLP projectors employ millions of micro-mirrors on a microprocessor to manipulate light intensity through color filters.
- On the other hand, LCD projectors utilize three mirror filters to break down an image into red, green, and blue wavelengths, which are then combined to produce a full-color image.
Laser and Inkjet Printers
Both types of printers create physical copies of digital documents. This is essential when electronic devices are not available.
Laser Printers
- Are highly efficient for producing multiple copies quickly
- Suitable for high-volume print jobs like creating leaflets
- Offer cost-effective printing on a per-page basis
- Commonly utilized in business and educational environments
- Feature large toner cartridges and paper trays
- Utilize electrostatic charges to transfer and bond toner particles onto paper
Inkjet Printers
- Excel at producing high-quality images and graphics
- Ideal for low to moderate volume printing needs
- Can be more cost-efficient for color printing compared to laser printers
- Versatile and commonly found in home and small office settings
 |
Download the notes
Output Devices
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
3D Printers
- Creation of 3D Models: 3D printers build 3D objects by adding layers of material on top of each other based on a digital model. This process enables the production of precise objects.
- Medical Applications: These printers have significant medical uses such as crafting prosthetics and blood vessels with great precision to enhance healthcare.
- Rapid Prototyping: They are valuable for quickly creating prototype models for various industries, allowing for swift product development and testing.
- Global Accessibility: Models can be shared digitally and printed worldwide, showcasing the widespread reach and impact of this technology.
Question for Output Devices
Try yourself:
What are the two main types of light projectors?View Solution
Liquid Crystal Display screens
- LCD screens consist of numerous tiny liquid crystals.
- The display is structured with pixels organized in a matrix formation.
- Illumination from a backlight is necessary for the display.
- LCD screens find applications in TVs, monitors, tablets, and phones.
- These screens demonstrate low power consumption and operate at a cool temperature.
- They are not prone to image burn or flicker problems.
- LCD screens offer vivid images and colors.
- Production costs for LCD screens are lower compared to LED screens.
Organic light emitting diode (OLED) screen
- Much thinner and lighter than traditional LCD screens
- Use organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs)
- They use organic carbon compound to create semiconductors
- No form of backlighting is required
- You can have very thin, flexible screens
Speakers
- Speakers are devices that convert digital audio signals into sound waves that are audible to humans. This transformation is achieved by passing the digital data through a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), which converts the data into an electric current.
- The electric current is then amplified to a level that can drive the loudspeaker effectively. This amplification process ensures that the sound produced is of sufficient volume for listening.
- Once the amplified current reaches the loudspeaker, it is converted back into sound waves, which are then emitted into the surrounding environment, allowing us to hear the audio content.
- Common applications of speakers include listening to music, watching videos with sound, making phone calls, and receiving alerts or alarms for notifications.
Question for Output Devices
Try yourself:
Which type of screen requires a backlight for illumination?View Solution
The document Output Devices | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Computer for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
92 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Output Devices - Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are some examples of output devices? |  |
| 2. How do output devices work in a computer system? |  |
Ans. Output devices receive data from the computer and convert it into a form that is understandable and usable by humans, such as displaying images on a screen or printing text on paper.
| 3. What is the difference between liquid crystal display (LCD) screens and organic light emitting diode (OLED) screens? |  |
Ans. LCD screens use a backlight to illuminate the display, while OLED screens emit their own light, resulting in better contrast and energy efficiency.
| 4. How do speakers function as output devices? |  |
Ans. Speakers receive electrical signals from the computer and convert them into sound waves that we can hear, allowing us to listen to music, videos, and other audio content.
| 5. Can output devices be connected to multiple devices at once? |  |
Ans. Yes, many output devices can be connected to multiple devices simultaneously, allowing for greater flexibility and versatility in how they are used.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















