PH Measurements | Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
pH Measurements
In many process operations, pure and neutral water (i.e., not acidic or alkaline) is required for cleaning or diluting other chemicals. Water contains both hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. When these ions are in the correct ratio, the water is neutral, but an excess of hydrogen ions causes the water to be acidic, and an excess of hydroxyl ions causes the water to be alkaline [9].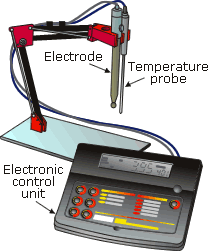
➢ pH Introduction
The pH (i.e., power of hydrogen) of the water is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. Neutral water has a pH value of 7 at 77°F (25°C). When water becomes acidic, the pH value decreases. Conversely, when the water becomes alkaline, the pH value increases. pH values use a base 10 log scale. That is, a change of 1 pH unit means that the concentration of hydrogen ions has increased (or decreased) by a factor of 10, and a change of 2 pH units means the concentration has changed by a factor of 100.
The pH value is given by:
pH = log10 [1/hydrogen ion concentration]....(12.16)
The pH value of a liquid can range from 0 to 14. The hydrogen ion concentration is in grams per liter. That is, a pH of 4 means that the hydrogen ion concentration is 0.0001 g/L at 25°C.
Strong hydrochloric or sulfuric acids will have a pH of 0 to 1.
- 4% caustic soda: pH =14;
- Lemon and orange juice: pH = 2 to 3;
- Ammonia: pH is approximately 11.
➢ pH Measuring Devices
The pH is normally measured by chemical indicators or by pH meters. The final color of chemical indicators depends on the hydrogen ion concentration, and their accuracy is only from 0.1 to 0.2 pH units. For indication of acid, alkali, or neutral water, litmus paper is used, which turns pink if acidic, turns blue if alkaline, and remains white if neutral.
A pH sensor normally consists of a sensing electrode and a reference electrode immersed in the test solution, which forms an electrolytic cell, as shown in Figure 12.9. One electrode contains a saturated potassium chloride (alkaline) solution to act as a reference. The electrode is electrically connected to the test solution via the liquid junction. The other electrode contains a buffer, which sets the electrode in contact with the liquid sample. The electrodes are connected to a differential amplifier, which amplifies the voltage difference between the electrodes, giving an output voltage that is proportional to the pH of the solution. A temperature sensor in the liquid is used by the signal conditioning electronics to correct the output signal for changes in pH caused by changes in temperature.
|
26 videos|28 docs|29 tests
|





















