RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Exam > RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Notes > Course for RPSC RAS Preparation > Palaeolithic or Old-Stone Age
Palaeolithic or Old-Stone Age | Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) PDF Download
Overview
Man is said to have appeared in the early Pleistocene in Africa about 3 million ( 30 lakh) years ago. In India, based on recent evidence, man is said to have appeared 1.4 million (14 lakh) years back at Bori, Maharashtra. This man had no knowledge of cultivation and house building till 9000 years B.C.
From there first appearance to beginning of 3000 BC man used tools & implements only made up of stone and so early phase of human existence has been called as Stone-Age. Based on nature of stone tools and nature of change in climate the stone age is divided into Palaeolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic age period to study history till 1000B.c.
The Palaeolithic age has been further divided into 3 sub-ages namely:
- Upto 1,00,000 BC: Lower Palaeolithic or Early Old Stone Ag
- 1,00,000 BC – 40,000 BC: Middle Palaeolithic or Middle Old Stone Age
- 40,000 BC – 10,000 BC: Upper Palaeolithic or Later Old Stone Age
1. Lower Palaeolithic or Early Old Stone Age (Upto 1,00,000 BC)
- Special characteristic stone tools – handaxe and cleaver.
- Raw materials used for making stone tools included – quartzite, quartz and basalt.
- The sites of early stone age discovered in Rajasthan have been identified as belonging to Acheulian culture, named after French site of St. Acheul who was the first effective colonization of the Indian subcontinent.
- The Acheulian culture was a hunter-gatherer culture.
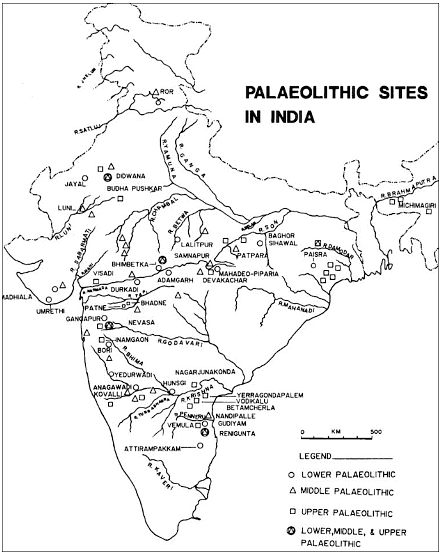
- Sites of lower-palaeolithic age are located in Belan valley in Uttar Pradesh, Barkhera, Bhimbetka and Putlikarar in Raisen district of Madhya Pradesh, Nevasa / Patne (Kolhapur district) in Maharshtra.
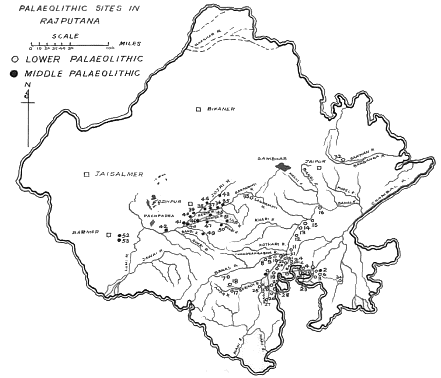
Lower Palaeolithic sites in Rajasthan
- In Rajasthan the discoveries of Lower Palaeolithic sites are largely confined to southern and central Rajasthan and partly to the western Rajasthan.
- Important sites include Didwana in Luni Valley, Jayal, Jaisalmer-Pokaran Road, Berach complex, Chambal complex (Allchin etal. 1978)
2. Middle Palaeolithic or Middle Old Stone Age (1,00,000 BC – 40,000 BC)
- The Acheulian culture of old stone age was slowly transformed into the middle Palaeolithic by giving some of the tool types and by developing new tools & technology.
- Special characteristic of stone tools – Flakes.
- In comparison to the lower Palaeolithic era, the tools in middle Palaeolithic became smaller, thinner and lighter.
- New raw materials used for making stone tools included fine-grained siliceous rocks like chert and jasper.
Middle Palaeolithic sites in Rajasthan
- In Rajasthan, Middle Palaeolithic sites are largely confined to central Rajasthan and partly in southern and western Rajasthan.
- Important Middle Palaeolithic age sites are located at Luni valley, around Didwana, Budha Pushkar.
 |
Download the notes
Palaeolithic or Old-Stone Age
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
3. Upper Palaeolithic or Later Old Stone Age (40,000 BC – 10,000 BC)
- The tools of Upper Palaeolithic Era are further refined upon the lower and middle periods and show a marked regional diversity with respect to the refinement of techniques and standardization of finished tool forms.
- Special characteristic of stone tools of Upper Palaeolithic age – Flakes and blades.
- One important discovery is of the Ostrich egg shells at over 40 sites in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra, which shows that ostrich, a bird adapted to arid climate.
- The upper Palaeolithic settlements also show a distinct trend of being associated with permanent sources of waters.
- Society was ‘Band Society‘ – small communities, usually consisting of less than 100 people. They were nomadic to some extent moving fro one place to another.
- The earliest form of art by humans also belongs to upper Palaeolithic period in the form of rock paintings (Bhimbetka).
Upper Palaeolithic sites in Rajasthan
- In Rajasthan, Upper Palaeolithic sites are largely confined to central Rajasthan and are partly found in western and northeastern Rajasthan.
- Major sites include Chittorgarh, Kota and basins of rivers Wagon, kadamli, Sabarmati & Mahi.
Map of Old Stone Age sites in Rajasthan
Map of Old Stone Age Sites in India
The document Palaeolithic or Old-Stone Age | Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) is a part of the RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) Course Course for RPSC RAS Preparation.
All you need of RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) at this link: RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
FAQs on Palaeolithic or Old-Stone Age - Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
| 1. What is the Palaeolithic period? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Palaeolithic period in Punjab? |  |
Ans. The Palaeolithic period in Punjab holds immense importance as it provides evidence of early human habitation in the region. Archaeological findings of stone tools and artifacts from this period shed light on the lifestyle, hunting practices, and cultural activities of our ancient ancestors in Punjab.
| 3. What are the key features of the Palaeolithic period in Punjab? |  |
Ans. The key features of the Palaeolithic period in Punjab include the existence of stone tools such as handaxes, scrapers, and blades. These tools were used for various purposes, including hunting, butchering, and preparing food. The period also witnessed the presence of early human settlements near rivers or water sources.
| 4. How do archaeologists determine the age of Palaeolithic artifacts in Punjab? |  |
Ans. Archaeologists determine the age of Palaeolithic artifacts in Punjab through various methods, such as radiocarbon dating, thermoluminescence dating, and stratigraphy. These techniques analyze the age of organic materials or the layers of soil and sediment in which the artifacts are found, providing valuable insights into their chronology.
| 5. What are the major archaeological sites in Punjab associated with the Palaeolithic period? |  |
Ans. Punjab is home to several significant archaeological sites associated with the Palaeolithic period. Some notable sites include Ropar, Sanghol, Lehra Gaga, and Dholbaha. These sites have yielded a vast array of stone tools and artifacts, contributing to our understanding of early human history in the region.
Related Searches


















