Parthenogenesis & Its Types | Biology for Grade 12 PDF Download

What is Parthenogenesis?
Parthenogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction involving the development of female gametes without any fertilization is called parthenogenesis.
- The animals which are formed by unfertilized eggs are called parthenotes.
- The discovery of parthenogenesis was done by Charles Bonnet in the eggs of sea-urchins.
 Whiptail Species reproduces by Parthenogenesis
Whiptail Species reproduces by Parthenogenesis
- Animals such as bees, aphids, wasps, ants have no sex chromosomes. These organisms reproduce by parthenogenesis. A few plants, reptiles and fish are also capable of reproducing in this manner.
Types of Parthenogenesis
- Natural Parthenogenesis
- Artificial Parthenogenesis
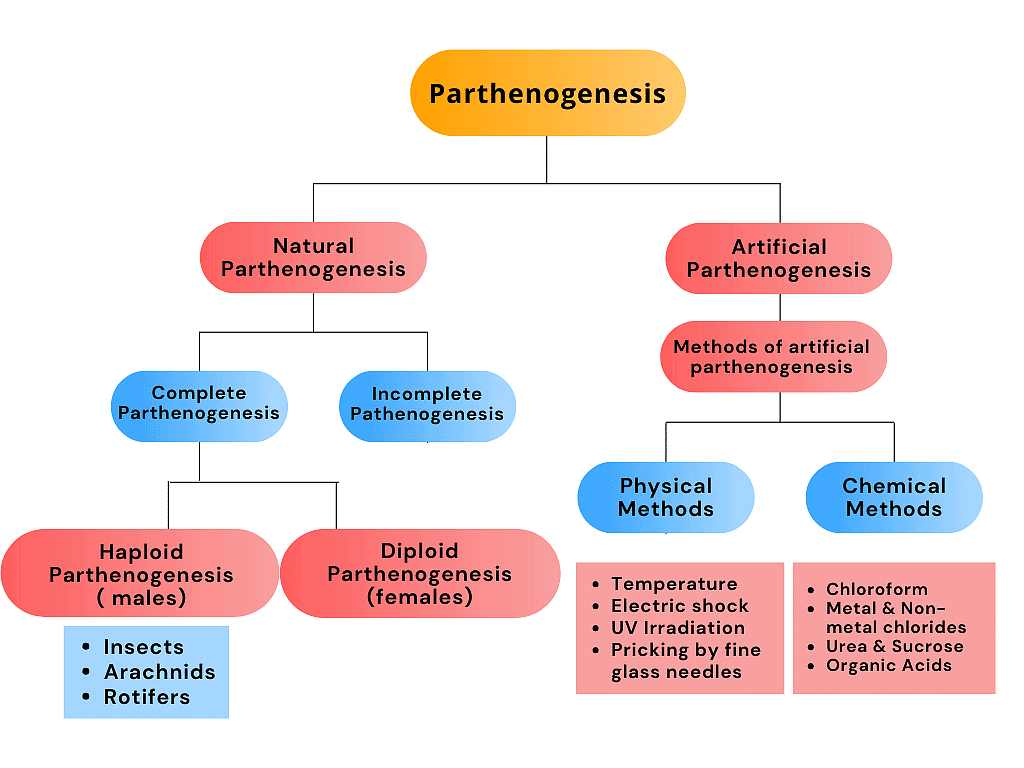
1. Natural Parthenogenesis
In certain animals, parthenogenesis occurs regularly, constantly and naturally in their life cycles and is known as natural parthenogenesis.
Natural parthenogenesis is of two types:
(i) Complete Parthenogenesis: Certain insects have no sexual phase and no males. They depend exclusively on parthenogenesis for self-reproduction. This type of parthenogenesis is known as complete parthenogenesis or obligatory parthenogenesis.
(ii) Incomplete Parthenogenesis: The life cycle of certain insects includes two generations, the sexual generation and parthenogenetic generation, both of which alternate to each other. In such cases, the diploid eggs produce females and the unfertilised eggs produce males. This type of parthenogenesis is known as partial or incomplete or cyclic parthenogenesis.
Two Complete or Incomplete Types of Natural Parthenogenesis:
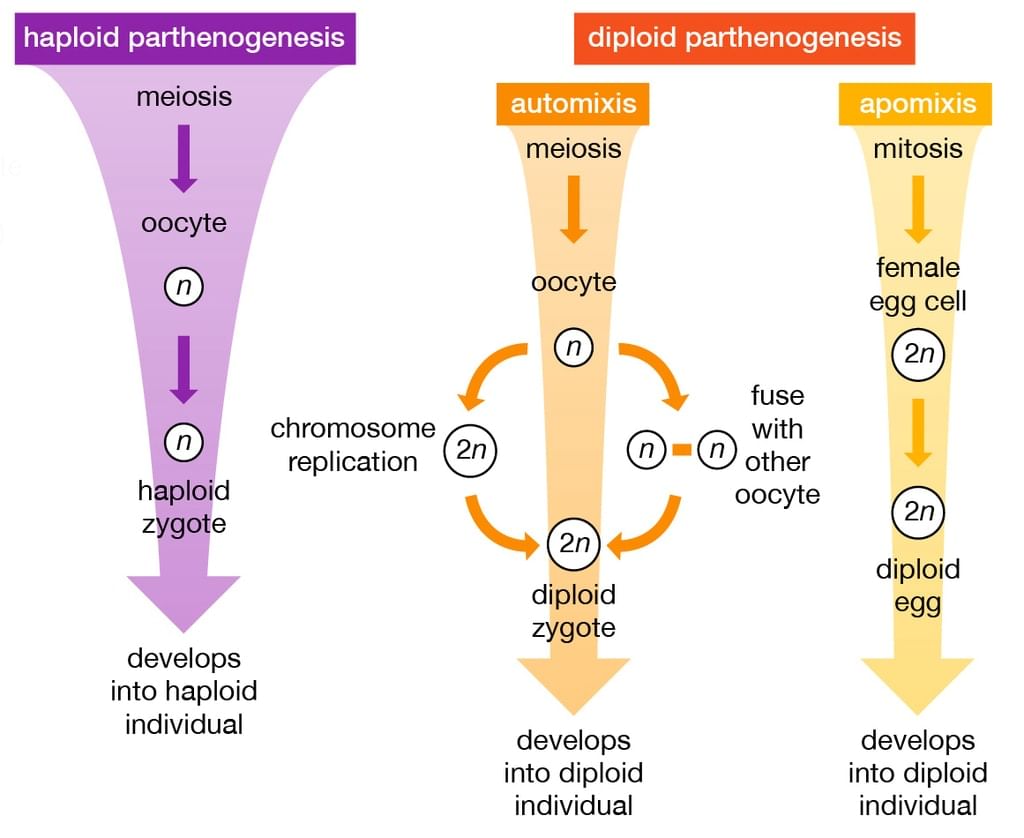
a) Haploid or Arrhenotokous Parthenogenesis
- In this case, eggs are formed by meiosis. Eggs are haploid, they have the power of fertilization; sometimes male animals are developed by unfertilized eggs.
- In Honeybees, unfertilized eggs develop into males (drones), and fertilized eggs develop into queens and soldiers. Thus male honey bees are always haploid and queens along with soldiers are always diploid.
b) Diploid or Thelytokous Parthenogenesis
- In this case, eggs are formed without meiosis division.
- Eggs are diploid; they do not have the power of fertilization.
- Diploid eggs give rise to the female generation only. Male members are absent in these species.
Examples: Lacerta Saxicola Armeniaca (lizard), Carassius auratus gibelio (Fish). Haploid and Diploid parthenogenesis
Haploid and Diploid parthenogenesis
2. Artificial Parthenogenesis
- This type of parthenogenesis is done by artificial methods. Artificial parthenogenesis is done by putting eggs in different atmospheres or by giving special stimulus to the eggs.
- The fertilised eggs might sometimes develop parthenogenetically by various chemical and physical means.
Physical Means
- Temperature induces parthenogenesis in eggs. For example, parthenogenesis is induced if an egg is transferred from -30 to -10°C.
- Parthenogenesis is caused by ultraviolet light.
- Electrical shocks cause parthenogenesis.
- When an egg is pricked by a needle, the development occurs parthenogenetically.
Chemical Means
The chemicals that are responsible for the parthenogenesis of eggs are:
- Chloroform
- Urea and Sucrose
- Strychnine
- Fat solvents
- Acids
- Chlorides
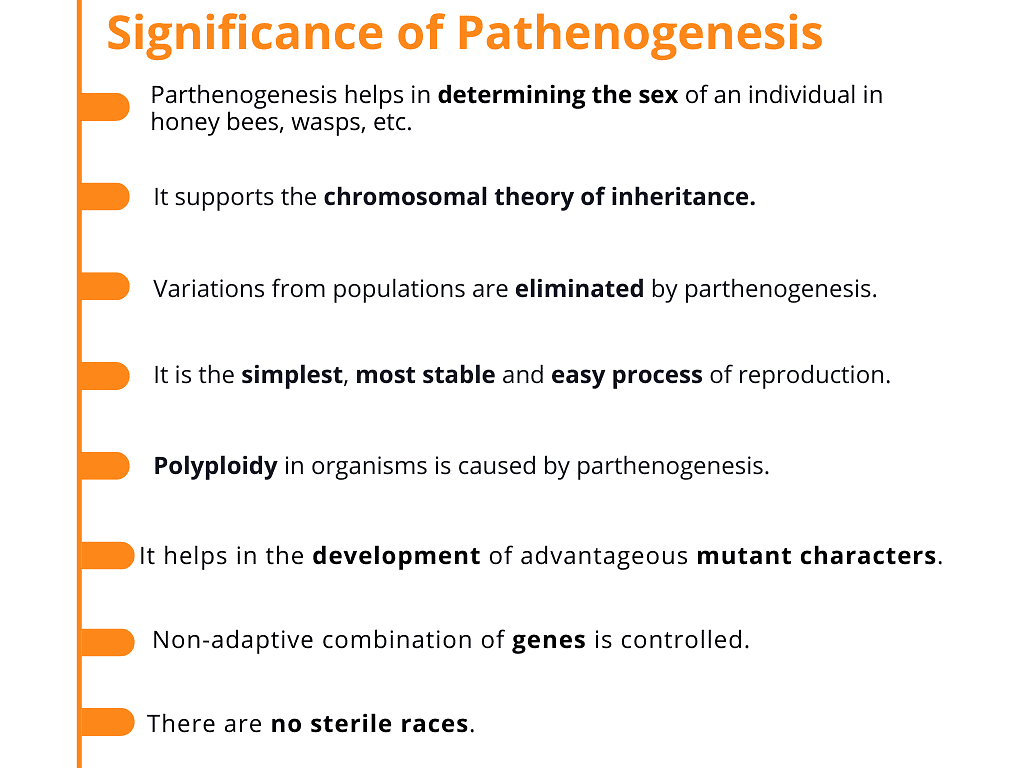
Parthenogenesis is important for the following reasons:
However, the organisms produced by parthenogenesis cannot survive for long due to no recombination of genetic material.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1. What is meant by Parthenogenesis?
Ans: Parthenogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which the development of mostly a female gamete takes place without fertilization. This type of reproduction is mostly shown by lower plants, some reptiles, and fishes, who do not possess sex chromosomes. It can be considered as an incomplete sexual reproduction since the resultant offspring develops from the gametes.
Q.2. What is the significance of Parthenogenesis?
Ans: Significance of Parthenogenesis is as follows:
- Parthenogenesis is a type of adaptive strategy to reproduce when environmental conditions are not proper and sexual reproduction is not possible.
- It allows the species to continue thriving and multiplying in some environments where the male population is scarce or none.
- Many offspring are produced by this method without costing much of parental energy or time. It enables sex determination in some organisms like wasps, bees.
- It is a simple, easy, and stable process of reproduction. It supports the chromosomal theory of inheritance which proves that chromosomes are the vehicles of genetic heredity.
- Parthenogenesis allows the cells of organisms to have more than two sets of chromosomes, called polyploidy.
- Advantageous mutant characters may develop by this method of reproduction.
- No chances of sterile races and a non-adaptive combination of genes is limited.
|
124 videos|210 docs|207 tests
|
FAQs on Parthenogenesis & Its Types - Biology for Grade 12
| 1. What is parthenogenesis and how does it occur? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of parthenogenesis? |  |
| 3. Which organisms commonly exhibit parthenogenesis? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of parthenogenesis? |  |
| 5. How does parthenogenesis differ from sexual reproduction? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 12 exam
|

|