Parts of Speech | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
What are Parts of Speech?
- Words are the fundamental building blocks of a sentence, and each word carries its own meaning.
- Words can be classified into different types based on how they are used in a sentence. These types are known as parts of speech.
- A single word can function as different parts of speech depending on its usage in a sentence.
- Understanding the parts of speech helps to clarify the exact meaning of words in context.
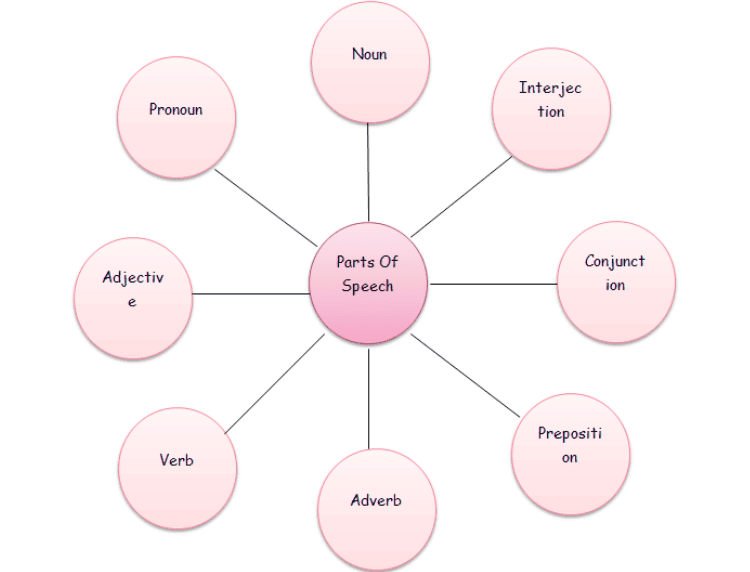
There are eight parts of speech in English:
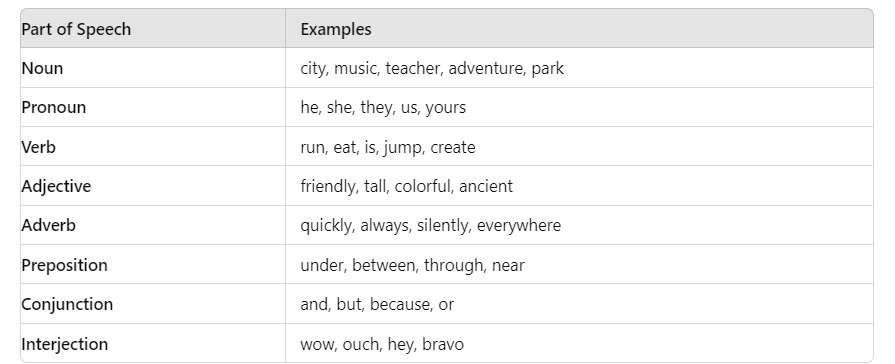
- Noun:. word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Pronoun:. word that takes the place of a noun.
- Verb:. word that expresses an action or state of being.
- Adjective:. word that describes a noun or pronoun.
- Adverb:. word that modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb.
- Preposition:. word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence.
- Conjunction:. word that connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Interjection:. word that expresses strong emotion.
- Determiner:. word that introduces a noun and indicates its reference.
1. The Noun
- Nouns are words used to name and identify people, places, animals, things, and ideas. They are the basic building blocks of sentences because they tell us what or who we are talking about.
- For example, in the sentences "The dog barks," "The book is on the table," and "Happiness is important," "dog," "book," and "happiness" are all nouns.
Sample Sentences:
- Amanda lives in Paris.
- John uses a fountain pen for writing.
- Lisa is very talented.
- Marcus is looking very dashing.
- Today is Emma’s birthday.
- My sister is moving to Tokyo.
Types of Nouns
- Proper Nouns: These are the names of specific people, places, or organizations, such as "John," "Paris," or "Microsoft." Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter.
- Common Nouns: These are general names for a person, place, or thing, like "city," "woman," or "car." They do not require a capital letter unless they start a sentence.
- Collective Nouns: These nouns refer to a group of individuals or items considered as a single unit, such as "team" (a group of players) or "flock" (a group of birds).
- Abstract Nouns: These nouns represent ideas, qualities, or conditions that cannot be seen or touched, like "love," "bravery," or "happiness."
2. The Pronoun
- Pronouns are words used to replace nouns in a sentence.
- They help avoid the repetition of nouns, making sentences clearer and more concise.
- A pronoun typically refers to a specific noun called its antecedent.
- Examples of pronouns include: I, you, he, she, we, ours, mine, yours, his, her, him, hers, they, them, theirs, it, etc.
Sample Sentences:
- Kevin is a very diligent student. He always works hard.
- The biggest portion is yours.
- They are Canadian.
- The coach gave all of us instructions.
- Sarah gave her notebook to Maya.
- His house is bigger than ours.
3. The Adjective
- This part of speech refers to a word that modifies, describes, or gives more information about a noun or pronoun.
- Adjectives are describing words and normally come before the nouns.
- Example: fast, quiet, useful, much, pretty, old, blue, smart, beautiful, big, sad, red, young, fun, crazy, three, etc.
Sample Sentences:
- The tiny girl had a red kite.
- The diligent worker received "A" grade.
- I have three bikes.
- Wow! That pizza is amazing.
- She is a young teacher.
- Max is a clever boy.
4. The Verb
- This part of speech refers to a word that tells us what the subject does, or what happens to it, or what state it is in, or what possesses.
- Examples: am, is, was, are, were, have, has, had, do, does, did, be, am, is, are, was, were, being, been, should, could, will, would, might, can, may, must, shall, ought (to), go, speak, run, eat, play, live, walk, like, etc.
Sample Sentences:
- They are always prepared for any situation.
- Nora is charming.
- Jake runs every day.
- I enjoy chocolate ice-cream.
- We had a nutritious meal.
- I believe that he is right.
5. The Adverb
- This part of speech refers to a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
- Adverbs tell us how, when, where, how often, and to what degree (extent) something happens or takes place. Adverbs often end in -ly.
- Examples: gently, quickly, extremely, carefully, well, slowly, quietly, very, always, never, too, tomorrow, here, etc.
Types of Adverbs:
- Adverbs of Manner: gently, quickly, carefully, beautifully, well, slowly, quietly
- Adverbs of Time: tomorrow, always, never
- Adverbs of Place: here
- Adverbs of Frequency: too
- Adverbs of Degree: very
Sample Sentences:
- He ate his cake quickly.
- The chef carefully prepared the dish.
- Liam was extremely happy about his new toy.
- She danced beautifully.
- We are leaving tomorrow.
- He looked everywhere for his glasses.
6. The Preposition
- This part of speech refers to a word or a group of words that shows its relation with another noun or pronoun or a verb.
- Therefore, it can also be called a ‘relation’ word and comes before a noun or a pronoun in a sentence.
- They are used to indicate time, place, direction, or relationship.
- Example: in, on, into, at, by, upon, across, beside, between, of, out of, for, above, below, throughout, outside, before, near, etc.
Sample Sentences:
- Mia’s cat is lying under the chair.
- She placed her bag on the desk.
- He sat on the rug.
- They will meet at 3 o’clock in the afternoon.
- Look behind the couch.
7. The Conjunction (Connectors or Linking Words)
This part of speech refers to a word that joins two or more words, phrases, or clauses. There are three kinds of conjunctions:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These are the words that join words, phrases, and clauses of equal grammatical importance in the sentence. Example: and, but, or, so, nor, for, yet.
- Correlative Conjunctions: These are the words that join equally important ideas, but they work in pairs. Example: either...or, both...and, not only...but also, neither…nor, whether…or, either…or.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: These are the words that join words, phrases, and clauses that are not equal. Example: because, although, while, since, after, as, as if, before, even if, even though, if, so that, though, unless, until, when, whenever, where, wherever, whether.
Sample Sentences:
- He wants to leave, but he cannot.
- She is kind and diligent.
- Would you prefer a cup of coffee or tea?
- He didn’t pass the exam because he wasn’t ready.
- We were thirsty, so we ordered lemonade.
- I was tired but I still finished my project.
8. The Interjection
- This part of speech refers to a word or phrase that expresses strong, sudden emotions.
- It expresses strong feelings of joy, sadness, surprise, appreciation, condemnation, etc.
- Since interjections are commonly used to convey strong emotions, they are usually followed by an exclamation mark but in case of mild interjections, a comma is placed after the interjection.
- Example: Ouch!, Alas!, Oh!, Bravo!, Fantastic!, Gorgeous!, Wow!, Hurrah!, Pooh!, Pshaw!, Fie!, Gosh!
Sample Sentences:
- Ouch! I hurt my foot.
- Hurray! Next week is a vacation.
- Hey! You made a mistake.
- Oh, we’re late for the meeting.
- Oh! I’m late for my appointment.
- Wow! I passed the driving test.
Note 1: Articles and determiners like a, an, the, some, any, etc., are also adjectives but they are studied separately due to their importance in modifying the meaning of the word they qualify.
Note 2: Same Word – Several Parts of Speech
There are words that can be used in more than one way. This implies that a word can function as several different parts of speech. The function of a word in a sentence decides to which part of speech it belongs.
Note the highlighted words in the following sentences:
- She likes to watch plays on TV. (noun)
- He plays basketball during his free time. (verb)
- I would like a drink. (noun)
- They drink too much soda. (verb)
- Alex bought a new sofa for his living room. (noun)
- She is planning to buy a sofa bed for her guest room. (adjective)
Parts of Speech With Examples
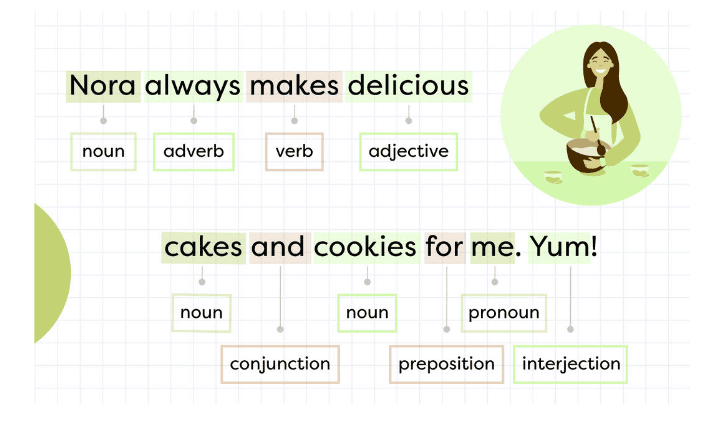
Sentences with All Parts of Speech
The (article) friendly (adjective) grey (adjective) cat (noun) sleeps (verb) under (preposition) the (article) big (adjective) tree (noun).
He (pronoun) cheerfully (adverb) sings (verb) the (article) song (noun) every (adjective) night (noun) in (preposition) the (article) moonlight (noun).
The (article) young (adjective) woman (noun) shares (verb) her (pronoun) knowledge (noun) with (preposition) the (article) students (noun).
Our (pronoun) cousin (noun) rarely (adverb) cooks (verb) delicious (adjective) meals (noun) in (preposition) his (pronoun) free (adjective) time (noun).
Before (preposition) the (article) movie (noun), they (pronoun) ate (verb) at (preposition) the (article) restaurant (noun) and (conjunction) enjoyed (verb) a (article) dessert (noun).
She (pronoun) was (verb) extremely (adverb) excited (adjective) when (conjunction) she (pronoun) found (verb) the (article) rare (adjective) book (noun).
We (pronoun) carefully (adverb) packed (verb) our (pronoun) bags (noun) with (preposition) warm (adjective) clothes (noun) for (preposition) the (article) trip (noun).
The (article) experienced (adjective) chef (noun) demonstrated (verb) the (article) intricate (adjective) recipe (noun) to (preposition) the (article) cooks (noun) patiently (adverb).
At (preposition) the (article) park (noun), they (pronoun) usually (adverb) have (verb) a (article) picnic (noun) near (preposition) the (article) lake (noun).
I (pronoun) have (verb) always (adverb) admired (verb) such (adjective) a (article) stunning (adjective) sculpture (noun) in (preposition) our (pronoun) gallery (noun).
|
49 videos|349 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Parts of Speech - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What is the function of a noun in a sentence? |  |
| 2. Can you provide an example of a pronoun and explain its purpose? |  |
| 3. How do adjectives enhance the meaning of a noun in a sentence? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an adverb and an adjective? |  |
| 5. How do conjunctions help connect different parts of a sentence or ideas? |  |






















