Past Year Questions: Flood Routing and Flood Control | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A flood control structure having an expected life of n years is designed by considering a flood of return period T years. When T= n, and n→∞, the structure's hydrologic risk of failure in percentage is . (round off to one decimal place) [2022, Set-2]
Ans: (63 to 63.5)
Sol:
Risk of failure = 1 − qn = 1 − ( 1 − p ) n = 1 − ( 1 − 1/T )n
For T= n → ∞
Risk of failure = 1 − 1/e = 0.632
% risk of failure = 0.632 x 100 = 63.2%
Q1: Super passage is a canal cross-drainage structure in which [2020, Set-2]
(a) natural stream water flows with free surface below a canal
(b) natural stream water flows under pressure below a canal
(c) canal water flows with free surface below a natural stream
(d) canal water flows under pressure below a natural stream
Ans: (c)
Sol:
Cross-section of a super passage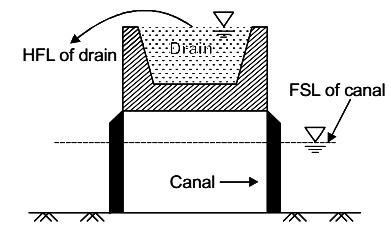
Q2: Muskingum method is used in [2020, Set-2]
(a) hydrologic reservoir routing
(b) hydrologic channel routing
(c) hydraulic channel routing
(d) hydraulic reservoir routing
Ans: (b)
Sol: Muskingum method is used in hydrological channel routing
Q3: In a homogeneous unconfined aquifer of area 3.00 km2 , the water table was at an elevation of 102.00 m. After a natural recharge of volume 0.90 million cubic meter ( Mm2 ), the water table rose to 103.20 m. After this recharge, ground water pumping took place and the water table dropped down to 101.020 m. The volume of ground water pumped after the natural recharge, expressed (in Mm2 and round off to two decimal places), is ______.
Ans: (1.4 to 1.6)
Sol:
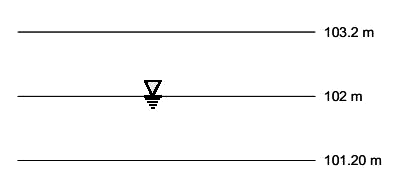
VR = 0.9Mm3
V = 3 x (103.2 - 102)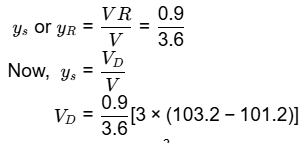 VD= 1.5 Mm3
VD= 1.5 Mm3
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Flood Routing and Flood Control - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is flood routing and why is it important in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. What are the different methods of flood routing used in civil engineering? |  |
| 3. How does flood control infrastructure mitigate flood risks? |  |
| 4. What role does hydrology play in flood routing and control? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in flood routing and control projects? |  |





















