Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics & Flow Measurements | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A 500 m long water distribution pipeline P with diameter 1.0 m, is used to convey 0.1 m3 /s of flow. A new pipeline Q, with the same length and flow rate, is to replace P. The friction factors for P and Q are 0.04 and 0.01 , respectively. The diameter of the pipeline Q (in meters) is _____(rounded off to 2 decimal places) [2024, Set-II]
Ans: 0.7 to 0.8
Initially, we have,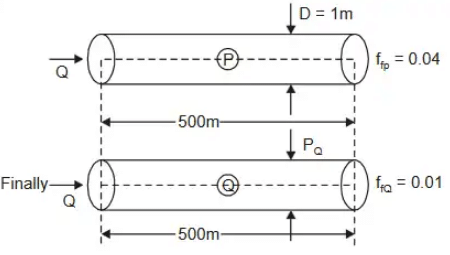
To replace the pipe, head loss has to be same
hfp = hfQ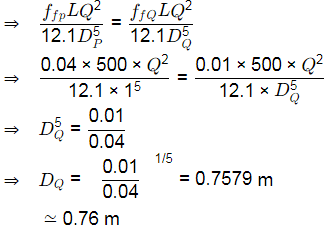
Q2: Match Column X with Column Y: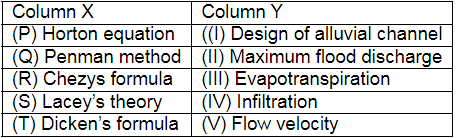
Which one of the following combinations is correct? [2022, Set-II]
(a) (P)-(IV), (Q)-(III), (R)-(V), (S)-(I), (T)-(II)
(b) (P)-(III), (Q)-(IV), (R)-(V), (S)-(I), (T)-(II)
(c) (P)-(IV), (Q)-(III), (R)-(II), (S)-(I), (T)-(V)
(d) (P)-(III), (Q)-(IV), (R)-(I), (S)-(V), (T)-(II)
Ans: (a)
Q3: Two reservoirs are connected by two parallel pipes of equal length and of diameters 20 cm and 10 cm, as shown in the figure (not drawn to scale). When the difference in the water levels of the reservoirs is 5 m, the ratio of discharge in the larger diameter pipe to the discharge in the smaller diameter pipe is ____________. (round off to two decimal places)
(Consider only loss due to friction and neglect all other losses. Assume the friction factor to be the same for both the pipes) [2022, Set-I]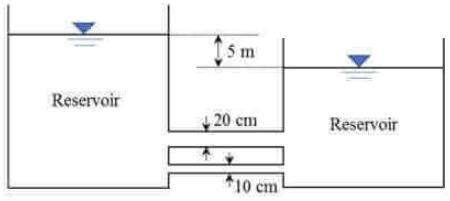 (a) 2.25
(a) 2.25
(b) 6.32
(c) 4.22
(d) 5.66
Ans: (d)
hf1 = hf2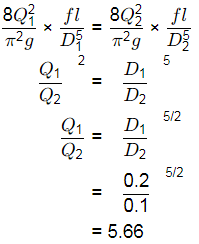
Q4: The ratio of the momentum correction factor to the energy correction factor for a laminar flow in a pipe is [2021, Set-II]
(a) 1/2
(b) 2/3
(c) 1
(d) 3/2
Ans: (b)
For laminar flow through pipe.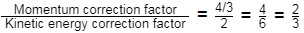
Q5: Two water reservoirs are connected by a siphon (running full) of total length 5000 m and diameter of 0.10m, as shown below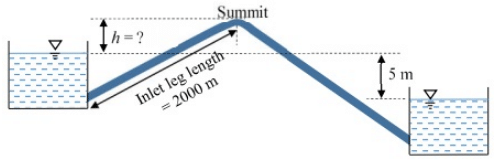 The inlet leg length of the siphon to its summit is 2000m. The difference in the water surface levels of the two reservoirs is 5 m. Assume the permissible minimum absolute pressure at the summit of siphon to be 2.5 m of water when running full.
The inlet leg length of the siphon to its summit is 2000m. The difference in the water surface levels of the two reservoirs is 5 m. Assume the permissible minimum absolute pressure at the summit of siphon to be 2.5 m of water when running full.
Given:
friction factor f = 0.02 throughout,
atmospheric pressure = 10.3 m of water, and
acceleration due to gravity g= 9.81 m/s2.
Considering only major loss using Darcy-Weisbach equation, the maximum height of the summit of siphon from the water level of upper reservoir, h (in m, round off to 1 decimal place) is _____ [2019, Set-I]
(a) 2.8
(b) 6.9
(c) 7.8
(d) 5.8
Ans: (d)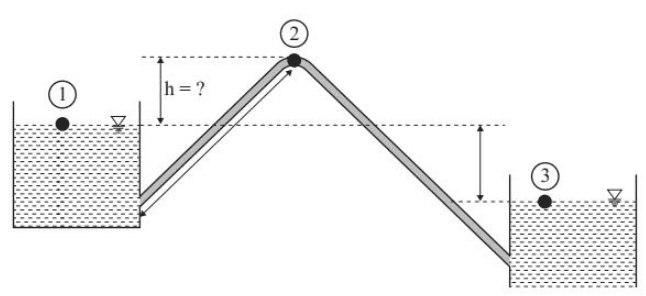 Applying Bernoulli's equation between 1 & 3
Applying Bernoulli's equation between 1 & 3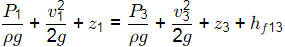
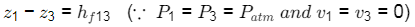
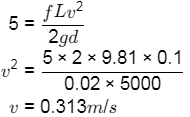
Applying Bernoulli's equation between 1 & 2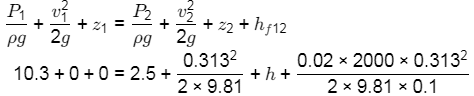
h = 5.798m
Q6: A circular duct carrying water gradually contracts from a diameter of 30 cm to 15 cm. The figure (not drawn to scale) shows the arrangement of differential manometer attached to the duct.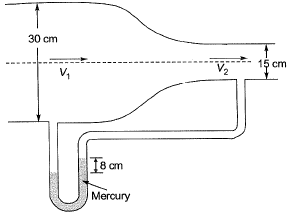 When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s, round off to 3 decimal places) through the duct is _______. [2019 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
When the water flows, the differential manometer shows a deflection of 8 cm of mercury (Hg). The values of specific gravity of mercury and water are 13.6 and 1.0, respectively. Consider the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81 m/s2. Assuming frictionless flow, the flow rate (in m3/s, round off to 3 decimal places) through the duct is _______. [2019 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
Ans:
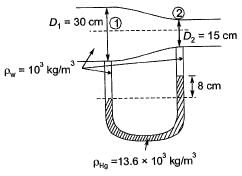
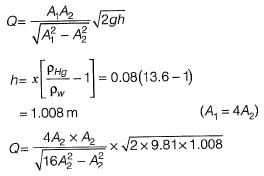
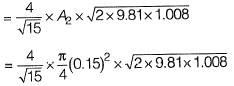
Q= 0.081 m3/s (round off to 3 decimal place)
Q7: Bernoulli’s equation is applicable for [2018 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) viscous and compressible fluid flow
(b) inviscid and compressible fluid flow
(c) inviscid and incompressible fluid flow
(d) viscous and incompressible fluid flow
Ans: (c)
Bernoulli’s equation is application for:
1. Flow along a stream line
2. When the effect of viscosity is negligible i.e., invisid flow
3. Incompressible flow condition
4. Steady flow condition
Note: Even if flow is rotational, Bernoulli’s equation can be applied between two points on the same stream line
Q8: Water flows through a 90° bend in a horizontal plane as depicted in the figure.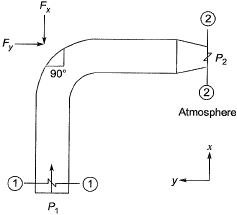 A pressure of 140 kPa is measured at section 1-1. The inlet diameter marked at section 1-1 is
A pressure of 140 kPa is measured at section 1-1. The inlet diameter marked at section 1-1 is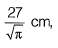 while the nozzle diameter marked at section 2-2 is
while the nozzle diameter marked at section 2-2 is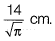 Assume the following:
Assume the following:
(i) Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m/s2
(ii) Weights of both the bent pipe segment as well as water are negligible
(iii) Friction across the bend is negligible.
The magnitude of the force (in kN, up to two decimal places) that would be required to hold the pipe section is _________. [2017 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans:
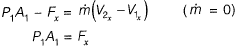
Or 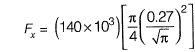
=2551.5 N
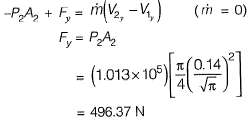
Resultant force

Q9: A venturimeter having a throat diameter of 0.1 m is used to estimate the flow rate of a horizontal pipe having a diameter of 0.2 m. For an observed pressure difference of 2 m of water head and coefficient of discharge equal to unity, assuming that the energy losses are negligible, the flow rate (in m3/s) through the pipe is approximately equal to [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
(a) 0.500
(b) 0.150
(c) 0.050
(d) 0.015
Ans: (c)
Diameter of throat,
D2 = 0.1 m
Diameter of pipe,
D1= 0.2 m
Pressure difference
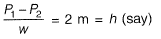
Since it is given that losses are negligible. Take coefficient of discharge as,
CD= 1
Discharge,
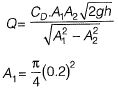
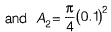
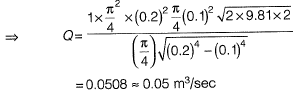
Q10: A venturimeter, having a diameter of 7.5 cm at the throat and 15 cm at the enlarged end, is installed in a horizontal pipeline of 15 cm diameter. The pipe carries an incompressible fluid at a steady rate of 30 litres per second. The difference of pressure head measured in terms of the moving fluid in between the enlarged and the throat of the venturimeter is observed to be 2.45 m. Taking the acceleration due to gravity as 9.81 m/s2, the coefficient of discharge of the venturimeter (correct up to two places of decimal) is ____. [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans:
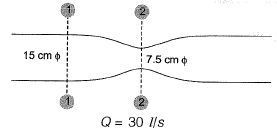
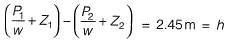
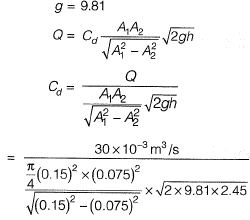
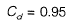
Q11: Group-I lists a few devices while Group-ll provides information about their uses. Match the devices with their corresponding use.
Group-i
P. Anemometer
Q. Hygrometer
R. Pitot Tube
S. Tensiometer
Group-ll
1. Capillary potential of soil water
2. Fluid velocity at a specific point in the flow stream
3. Water vapour content of air
4. Wind speed [2014:1 Mark, Set-II
Ans: (d)
Hygrometer: A hygrometer is an instrument used for measuring the amount of humidity and water vapour in the atmosphere, in soil or in confined spaces.
Tensiometer: It is used to measure capillary potential of soil water.
Q12: Match List-I (Devices) with List-ll (Uses) and select the answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
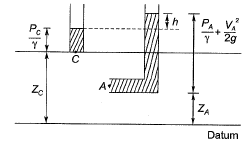
A. Pitot tube
B. Manometer
C. Venturimeter
D. Anemometer
List-ll
1. Measuring pressure in a pipe
2. Measuring velocity of flow in a pipe
3. Measuring air and gas velocity
4. Measuring discharge in a pipe
Codes: [2010 : 1 Mark]
Ans: (c)
Pitot tube: It is used to measure velocity of fluid. Difference in the readings of pitot tube and piezometer (h), indicates the velocity head. This is with the assumption that pierometric head at A and C is same
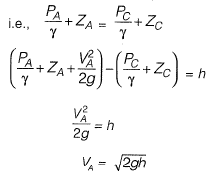
Manometer: Measureiy pressure in a pipe.
Venturimeter: Measuring discharge in a pipe.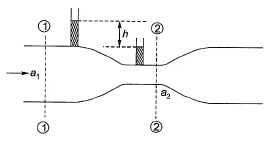
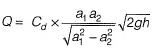
Anemometer: Used to measure air velocity.
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Fluid Dynamics & Flow Measurements - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the basic principles of fluid dynamics? |  |
| 2. How do flow measurements work in fluid dynamics? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between laminar and turbulent flow? |  |
| 4. What role do viscosity and density play in fluid dynamics? |  |
| 5. How is the Reynolds number used in fluid dynamics analysis? |  |
















