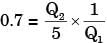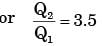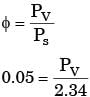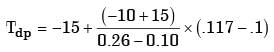GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Pumps & Cycles | Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: In a vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the refrigerant enters the compressor in saturated vapour state at evaporator pressure, with specific enthalpy equal to 250 kJ/kg. The exit of the compressor is superheated at condenser pressure with specific enthalpy equal to 300 kJ/kg. At the condenser exit, the refrigerant is throttled to the evaporator pressure. The coefficient of performance (COP) of the cycle is 3. If the specific enthalpy of the saturated liquid at evaporator pressure is 50 kJ/kg, then the dryness fraction of the refrigerant at entry to evaporator is ____ [GATE ME 2022 SET-2]
(a) 0.2
(b) 0.25
(c) 0.3
(d) 0.35
Ans: (b)
Given data,
Saturated vapour refrigerant enters to compressor COP = 3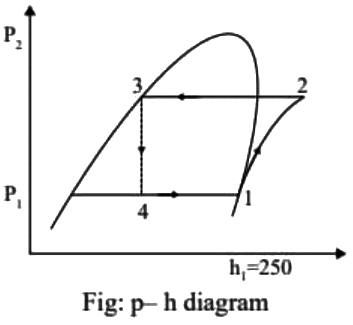 Specific liquid enthalpy of refrigerant corresponding to evaporator pressure
Specific liquid enthalpy of refrigerant corresponding to evaporator pressure 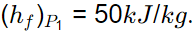
Dryness fraction of refrigerant of entry to evaporator (x4) = ?
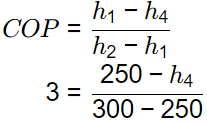
h4 = 100 kJ/kg
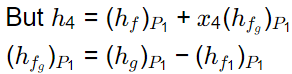
⇒ hfg = 250 - 50 = 200 kJ/kg
100 = 50 + x4 x 200
⇒ x4 = 0.25
Q1: Superheated steam at 1500 kPa, has a specific volume of 2.75 m3/kmol and compressibility factor (Z) of 0.95. The temperature of steam is ºC (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2021 SET-1]
(a) 522
(b) 471
(c) 249
(d) 198
Ans: (c)
P = 1500 kPa
V = 2.75 m3/k−mol
Z = 0.95
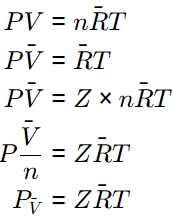
1500 KPa x 2.75 m3/K - mol = 0.95 x 8.314 kJ/K - molK x T
T = 522.26 K
T = 522.26 - 273 = 249.26ºC
[1997]
[2003]
[2005]
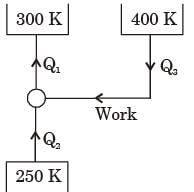
[2015]
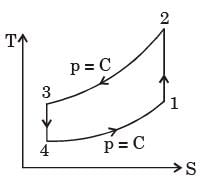
[2004]
[2006]
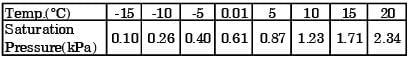
Neglecting the heat transfer between the water and the ground, the water temperature in the field after phase equilibrium is reached equals
|
29 videos|152 docs|36 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Heat Pumps & Cycles - Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is a heat pump and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the main applications of heat pumps in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner? |  |
| 4. What are the key performance indicators for heat pumps? |  |
| 5. What factors should be considered when selecting a heat pump for a specific application? |  |



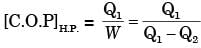
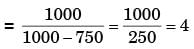
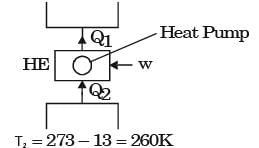
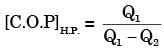 for actual heat pump
for actual heat pump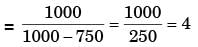
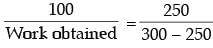
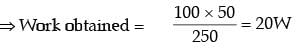

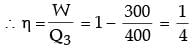
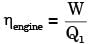 ...(i)
...(i)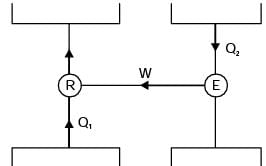
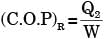
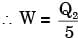 ...(ii)
...(ii)