Past Year Questions: Water Treatment - 2 | Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: A water treatment plant of capacity, 1 m3/s has filter boxes of dimensions 6m x 10m. Loading rate to the filters is 120 m3/day/m2. When two of the filters are out of service for back washing, the loading rate (in m3 / day / m2) is ______ . [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 144 m3/day/m2
Sol: Total water filtered in a day
= 60 x 60 x 24 = 86400 m3/day
Total surface area of filter required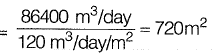
Area of one filter = 6 x 10 = 60 m2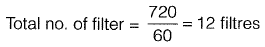
As two filters are out of service, number of filters
working = 1 2 - 2 = 10
Total surface area of filter
= 60 x 10 = 600 m2
The new loading rate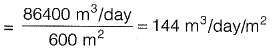
Q2: Consider a primary sedimentation tank (PST) in a water treatment plant with Surface Overflow Rate (SOR) of 40 m3/m2/d. The diameter of the spherical particle which will have 90 percent theoretical removal efficiency in this tank is ______ μm. Assume that settling velocity of the particles in water is described by Stoke’s Law. Given: Density of water = 1000 kg/m3; Density of particle = 2650 kg/m3; g= 9.81 m/s2; Kinematic viscosity of water (v) = 1.10 x 10-6 m2/s. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Ans: 22.576 μm
Sol:

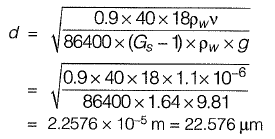
Q1: An effluent at a flow rate of 2670 m3/d from a sewage treatment plant is to be disinfected. The laboratory data of disinfection studies with a chlorine dosage of 15 mg/l yield the model Nt =Noe-0.145t where Nt = number of micro- organisms surviving at time t (in min.) and N0 = number of micro-organisms present initially (at t = 0). The volume of disinfection unit (in m3) required to achieve a 98% kill of micro-organisms is ____ [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 50.0244 m3
Sol: Q = 2670 m3/d
Nt = No. e-0.145t
Let x be the no. of microorganisms (M.O.) present initially.
98% kill of M.O. imlies that at time ‘t’ 2% of M.O. are still surviving
∴ M .O . surviving at time 't' 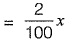
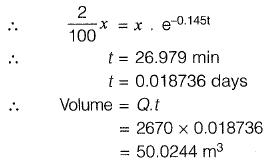
Q2: A surface water treatment plant operates round the clock with a flow rate of 35 m3/min. The water temperature is 15 °C and jar testing indicated an alum dosage of 25 mg/l with flocculation at a Gt value of 4 x 104 producing optimal results. The alum quantity required for 30 days (in kg) of operation of the plant i s ______ . [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 37,800 kg
Sol: Given data
Flow rate, Q = 35 m3/min
Gt = 4 x 104
Alum dosage = 25 mg/lit.
Alum quantity (kg) required for 30 days
= 35 x 103 x 60 x 24 x 30 x 25 x 10-6
= 37,800 kg
Q3: A suspension of sand like particles in water with particles of diameter 0.10 mm and below is flowing into a settling tank at 0.10 m3/s. Assume g = 9.81 m/s2, specific gravity of particles = 2.65, and kinematic viscosity of water =1.0105 x 10-2 cm2/s. The minimum surface area (in m2) required for this settling tank to remove particles of size 0.06 mm and above with 100% efficiency is ___ . [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Ans: 31.214 m2
Sol: For particles of size 0.06 mm,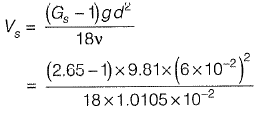
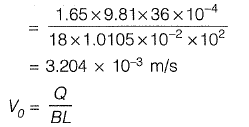
For 100% efficient removal of 0.06 mm size particles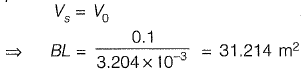
Q4: The potable water is prepared from turbid surface water by adopting the following treatment sequence. [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
(a) Turbid surface water -> Coagulation -» Flocculation -> Sedimentation -> Filtration Disinfection -> Storage & Supply
(b) Turbid surface water -> Disinfection -> Flocculation -» Sedimentation -> Filtration Coagulation Storage & Supply
(c) Turbid surface water -> Filtration -» Sedimentation - » Disinfection -» Flocculation -» Coagulation -» Storage & Supply
(d) Turbid surface water Sedimentation -» Flocculation -> Coagulation -> Disinfection Filtration -> Storage & Supply
Ans: (a)
Q5: 16 MLD of water is flowing through a 2.5 km long pipe of diameter 45 cm. The chlorine at the rate of 32 kg/d is applied at the entry of this pipe so that disinfected water is obtained at the exit. There is a proposal to increase the flow through this pipe to 22 MLD from 16 MLD. Assume the dilution coefficient, n = 1. The minimum amount of chlorine (in kg per day) to be applied to achieve the same degree of disinfection for the enhanced flow is [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-1]
(a) 60.50
(b) 44.00
(c) 38.00
(d) 23.27
Ans: (a)
Sol: In the disinfection process we have the relationship,
tCn = K
where
t = time required to kill all organism
c = concentration of disinfectant
n = dilution coefficient
k = constant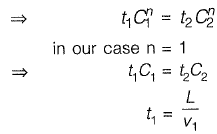
L = length of pipe ; v1, = velocity of flow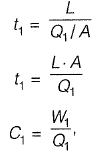
where W1 = weight of disinfectant per day;
Q1 = discharge per day,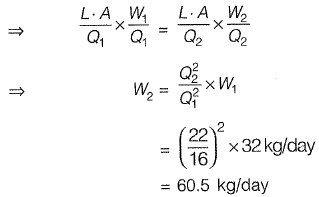
Q1: A settling tank is designed for a surface overflow rate of 30 m3/day.m2. Assuming specific gravity of sediment particles = 2.65. Density of water, γw = 1000 kg/m3, dynamic viscosity of water mwater = 0.001 Ns/m2 and stokes law is valid. The approximate minimum size of particles which can be completely removed is [2013 : 2 Marks]
(a) 0.01 mm
(b) 0.02 mm
(c) 0.03 mm
(d) 0.04 mm
Ans: (b)
Sol: To calculate minimum size of particles equating settling velocity to overflow rate, we get,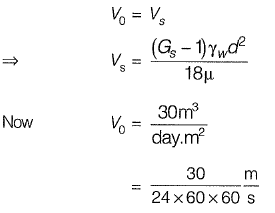
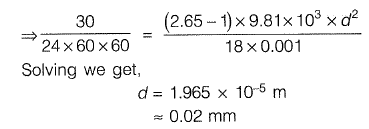
Q2: A water treatment plant, having discharge 1 m3/sec, has 14 filters to treat the water. Each filter is having 50 m2 area, but due to backwashing activity 2 filters are non operational. Calculate hydraulic loading rate in m3/day.m2. [2013 : 1 Mark]
Ans: 144m3/day.m2
Sol: Q= 1 m3/sec
No. of working filters = 12
S.A. of each filter = 50 m2
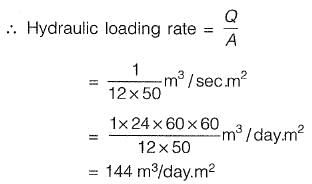
Q1: A town is required to treat 4.2 m3/min of raw water for daily domestic supply. Flocculating particles are to be produced by chemical coagulation. A column analysis indicated that an overflow rate of 0.2 mm/s will produce satisfactory particle removal in a settling basin at a depth of 3.5 m. The required surface area (in m2) for settling is [2012 : 2 Marks]
(a) 210
(b) 350
(c) 1728
(d) 21000
Ans: (b)
Sol: Overflow rate, V0 = 0.2 x 10-3 m/s Water required to treat raw water,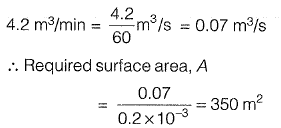
Q1: Chlorine gas (8 mg/L as Cl2) was added to a drinking water sample. If the free chlorine residual and pH was measured to be 2 mg/L (as Cl2) and 7.5, respectively, what is the concentration of residual OCl- ions in the water? Assume that the chlorine gas added to the water is completely converted to HOCI and OCh Atomic Weight of Cl: 35.5 [2011 : 2 Marks]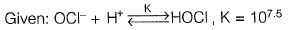
(a) 1.408 x 1CL5 moles/L
(b) 2.817 x 10-5 moles/L
(c) 5.634 x 10 6 moles/L
(d) 1.127 x 10-4 moles/L
Ans: (a)
Sol:
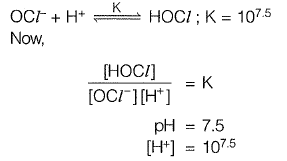
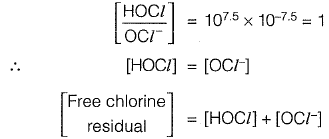
Free chlorine residual = 2 mg/l
[Free chlorine residual]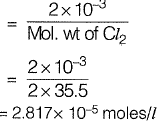
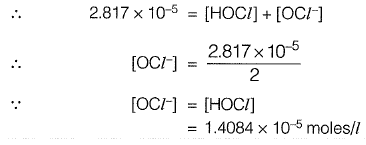
Q2: Consider the following unit processes commonly used in water treatment; rapid mixing (RM), flocculation (F), primary sedimentation (PS), secondary sedimentation (SS), chlorination (C) and rapid sand filtration (RSF), The order of these unit processes (first to last) in a conventional water treatment plant is [2011 : 1 Mark]
(a) P S -R SF-F-R M -S S-C
(b) PS -F-R M -R S F-S S -C
(c) PS F SS RSF - RM - C
(d) P S -R M -F-SS -R SF-C
Ans: (d)
Sol: Rapid mixing is the process done to disperse the coagulant into the entire mass of water after that flocculation occurs. Flocculated particles are then removed in secondary sedimentation tank followed by rapid sand filter. Water is than chlorinated and sent for supply.
|
14 videos|99 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Water Treatment - 2 - Environmental Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the main stages of water treatment in municipal systems? |  |
| 2. How does sedimentation contribute to water treatment? |  |
| 3. What are common disinfection methods used in water treatment? |  |
| 4. Why is water quality testing crucial in the treatment process? |  |
| 5. What role do filtration systems play in water treatment? |  |





















