Peptides: Definition, Types and Applications | Chemistry for ACT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Peptides |

|
| Types & Classes of Peptides |

|
| Molecular Biology |

|
| Applications of Peptides |

|
Peptides
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and when two or more amino acids are joined together, they form a peptide. Peptides can range in length from just a few amino acids to several dozen.
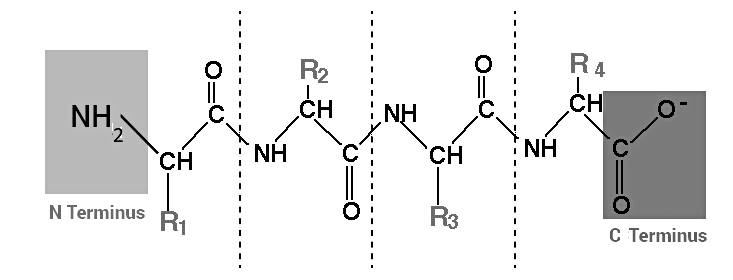
Peptides are distinguished from proteins based on their size, as they typically consist of shorter chains of amino acids. In contrast, proteins are composed of multiple polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional manner.
Peptides encompass a wide variety of types, including di-peptides, which are the shortest peptides comprising only two amino acids linked by a single peptide bond. On the other hand, a polypeptide represents a longer, uninterrupted chain of amino acids. Hence, it can be affirmed that peptides are part of a broad classification of biological polymers and oligomers.
Types & Classes of Peptides
Peptides are classified into various categories based on their origins and production methods.
- Milk Peptides: Milk peptides are generated when the digestive system breaks down a milk protein called Casein. They can also be produced through proteinases released by lactobacilli during milk fermentation.
- Peptones: Peptones are produced through the proteolysis of animal milk or meat. In some cases, they may also form from vitamins, fats, metals, and certain salts. Peptones find utility in cultivating fungi and bacteria for nutrient media.
- Ribosomal Peptides: Ribosomal peptides are created through translation, a process where cellular ribosomes synthesize proteins from mRNA. They often undergo proteolysis to attain their mature form. Certain microorganisms, such as microcins, produce peptides as antibiotics. These peptides undergo post-translational modifications like hydroxylation, phosphorylation, sulfonation, and glycosylation.
- Non-ribosomal Peptides: Non-ribosomal peptides are synthesized by unique enzymes specific to each peptide, rather than through ribosomes. Glutathione is an example of a common non-ribosomal peptide. These peptides possess intricate and often cyclic structures.
- Peptide Fragments: Peptide fragments refer to segments of proteins that are utilized for quantification or identification of the protein's source. They serve as markers or indicators in various analytical techniques.
Molecular Biology
Peptides hold a significant position in molecular biology for several compelling reasons. One primary purpose is their role in the generation of peptide antibodies in animals. These antibodies are produced in mice or rabbits to target specific proteins. Peptides are also employed in the exploration of protein function and structure, as well as in mass spectrometry techniques. Additionally, there exist peptide hormones, which consist of hormone molecules with peptide structures. These peptide hormones play crucial roles in various physiological processes.
Applications of Peptides
- Anti-Ageing Skincare: Various types of peptides are utilized in anti-ageing creams. Commonly sourced from ocean plants like sea jasmine, sea fennel, and sea beet, these peptides contribute to the formulation's effectiveness in reducing signs of ageing.
- Anti-Microbial Treatments: Antimicrobial peptides have emerged as valuable agents in treating skin conditions resulting from injuries, sun damage, or acne lesions. They have shown efficacy in combating drug-resistant bacteria, opening up new possibilities in medical applications.
- Body Imaging: In body imaging procedures, dyes are injected into the bloodstream to highlight specific tissues. Peptides are involved in these dyes, which fluoresce upon contact with targeted tissues. This enables doctors to detect life-threatening cancers in their early stages.
- Aspartame: Aspartame, an artificial sweetener found in many low-calorie or diet foods, is a synthesized peptide. Produced in laboratories, it is approximately 200 times sweeter than sugar and offers a zero-calorie alternative for sweetening products.
|
110 videos|125 docs|115 tests
|














