Permittivity & Relative Permittivity for Coulomb's Law | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Relative Permittivity? |

|
| What is Dielectric Constant? |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Every material has a characteristic that quantifies the resistance it provides to the development of an electric field. The Greek letter ε is used to represent it. It reveals how many charges are necessary to produce one unit of electric flux in the specified material. Formula for Permittivity is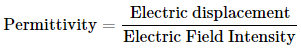
Permittivity of Free Space
Vacuum permittivity is another name for the permittivity of free space. Permittivity of open space is given as:
ε0 ≈ 8.854187817620 × 10−12F/m
Farad/meter is the SI unit for permittivity, often known as permittivity of open space. The dimensional symbol for the permittivity or permittivity of free space is [M−1L−3T4I2]
Absolute Permittivity
The attribute of the medium that specifies a specific electric field intensity at a place in the field creates how much flux density at that location is known as the absolute permittivity, or simply permittivity, of a medium. The product of two quantities, absolute permittivity of the vacuum and relative permittivity of the medium, can be used to express the absolute permittivity of any medium. This is done to make calculations based on permittivity simpler. The base value of the permittivity is assumed to be the absolute permittivity of vacuum. The ratio of a medium's permittivity to vacuum's absolute permittivity is the relative permittivity of the medium.
What is Relative Permittivity?
The permittivity of a substance relative to the permittivity of vacuum is referred to as relative permittivity. The Coulomb force between charged sites of a substance is described by a property of a material called permittivity. The electric field (between two charged sites) is reduced in relation to the vacuum as a result of this component.
Relative Permittivity of Free Space
The vacuum embodies permittivity at its lowest level. This is also known as the electric constant or the permittivity of free space. Denoted by ε0 and has the value 8.85 x 10-12 Farad/meter. Dielectrics exhibit the same resistance to the development of electric field lines. The relative permittivity of a dielectric, also known as a dielectric's permittivity, is defined as the ratio of the dielectric's absolute permittivity to the electric constant. It is described as an dimensionless quantity and is given as:
εr = ε/ε0
Where, ε0 is the electric constant, εr is the relative permittivity and ε is the absolute permittivity of that material.
Relative Permittivity for Coulomb’s Law
Using Coulomb’s law, the magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance r in free space can be calculated using relative permittivity (εr). By taking “the ratio of electrostatic force (Fa) between two point charges separated by a certain distance in air or vacuum to the electrostatic force (Fm) between the same two point charges separated by the same distance in a medium.” It is written as:
What is Dielectric Constant?
The property of an electrical insulating substance that is equal to the ratio of the material's capacitance to the capacitance of vacuum is known as the dielectric constant. Despite the fact that they have a few subtle distinctions, we most frequently use this phrase interchangeably with relative permittivity. "Dielectric" is a term used to describe an electrical insulator. The term "capacitance of material" in the definition of "dielectric constant" refers to the capacitance of a capacitor filled with the specific material. The capacitance of an identical capacitor devoid of dielectric material is used to calculate the capacitance of vacuum.
Dielectric Constant Formula
- Polarization: Polarization can be considered as an event that occurs when positive and negative charges align within the dielectric but there is no overall increase in the dielectric's charge. A vector quantity P called polarization describes the degree of polarization of a dielectric.
- Electron susceptibility: When an electric field is created in an air dielectric substance. It polarizes electrically as a result. In the majority of materials, polarization and electric field are inversely correlated, that is,
P ∝ E
⇒ P = XeE
Where Xe is constant, a property of a substance known as electrical susceptibility.
Xe = P/E
Dielectric constant and susceptibility are related as:
D = εo(E+P) -----(1)
Also,
D = εE and P = XeE
By changing these values, in equation (1),
It is mathematically expressed as
K = ε/ε0
Where, K is the dielectric constant, ε is the permittivity of the substance and ε0 is the permittivity of the free space.
It is a unitless, dimensionless quantity since it is the ratio of two like entities. The Greek letter kappa ‘K’ is used to represent the relative permittivity of a dielectric substance, which is also known as the dielectric constant.
Conclusion
The relationship between electric displacement and electric field intensity is governed by a constant called permittivity, also known as electric permittivity. A dielectric is a substance that has low electrical conductivity but can store electric charge through dielectric polarization. Capacitors, which store and release electrical energy, benefit from this property as they primarily exhibit displacement current. The dielectric constant of a substance is defined as the ratio of its permittivity to the permittivity of free space. Relative permittivity, on the other hand, describes the difference between the absolute permittivity of a medium and the absolute permittivity of vacuum. The dielectric constant and permittivity have significant impacts on various aspects of electrical and electronic technology. For example, in RF transmission lines and radio propagation, the relative permittivity of a medium can affect multiple aspects of electronics, radio, and other technological and scientific fields. It should be noted that the relative permittivity and dielectric constant are not only relevant to capacitors but have broader implications.
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
















