Placentation: Marginal, Axile, Parietal, Free Central & Basal | Biology for Grade 11 PDF Download
Placentation is defined as the arrangement of the placenta in the ovary of a flower. The placenta connects the ovules with the wall of the ovary.
The types of Placentation are
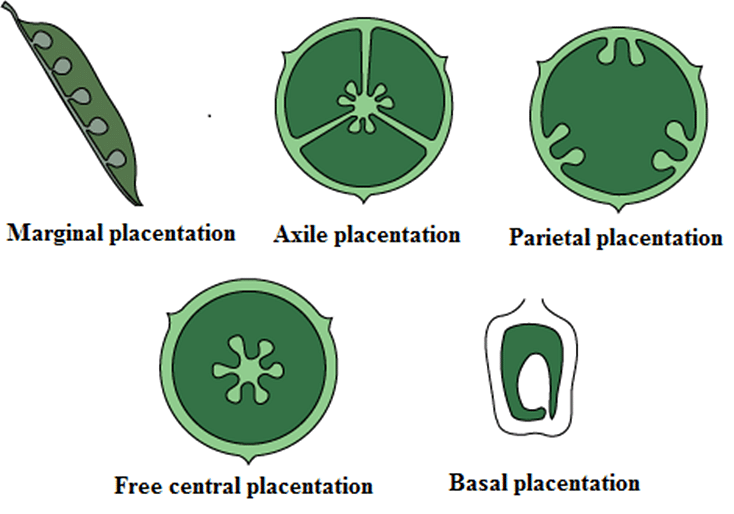
1. Marginal placentation: In marginal placentation, the placenta forms a ridge along the ventral suture of the ovary and the ovules develop on it making two separate rows. This type of placentation is found in pea plants.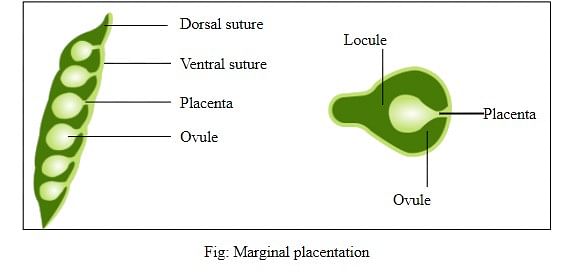
2. Parietal placentation: In parietal placentation, the ovules remain attached to the inner walls of the ovary. It is found in cucumber, etc.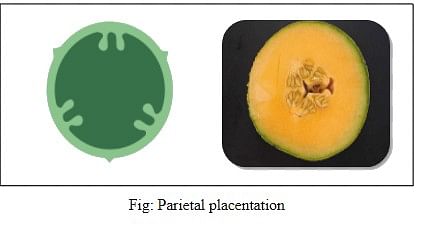
3. Axile placentation: In axile placentation, the placenta lies on a central axis and ovules are attached to it. The ovary is segmented by fibrous septa. It is found in China rose, lemon, and tomato.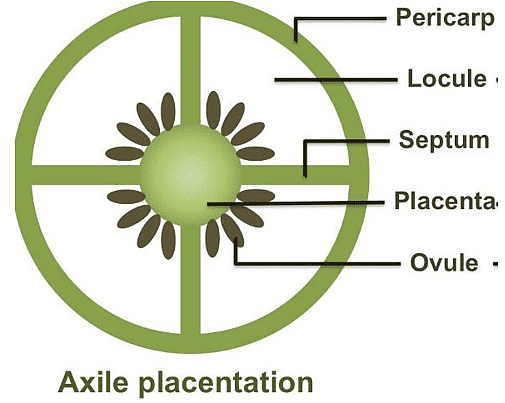
4. Basal placentation: In basal placentation, the placenta develops from its base and a single ovule is found attached to the base. It is found in the Asteraceae family that consists of marigold, sunflower, etc.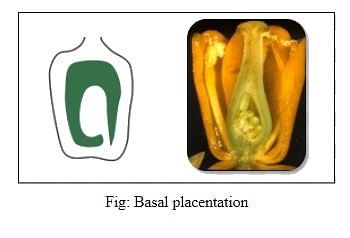
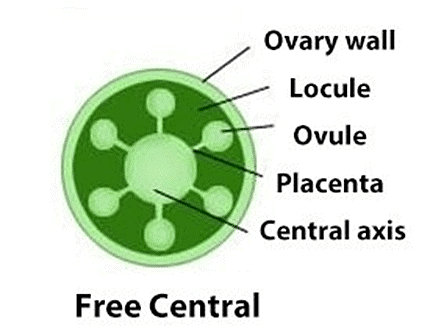
5. Free central placentation: In free central placentation, the ovules are present on the central axis. There is no formation of septa. This type of placentation is found in Dianthus and primrose.
Note:
- The ovules inside a flower's ovary are attached via funiculi, the plant part equivalent to an umbilical cord in human beings. The part of the ovary where the funiculus attaches is known as the placenta.
- Placentation is meant for the transfer of nutrients, respiratory gases, and water from maternal tissue to the growing embryo, and also for the removal of waste from the embryo.
- Some plants have a special type of placentation known as Superficial placentation where the ovules develop over the entire inner surface of the carpels. It generally occurs in a multicarpellary ovary, e.g., Nymphaea.
|
219 videos|306 docs|270 tests
|
FAQs on Placentation: Marginal, Axile, Parietal, Free Central & Basal - Biology for Grade 11
| 1. What is placentation? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between marginal and axile placentation? |  |
| 3. How does parietal placentation occur? |  |
| 4. What is free central placentation? |  |
| 5. What is basal placentation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|

















