Plant Kingdom and it's Classification | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Classification of the Plant Kingdom |

|
| Algae |

|
| Habitat |

|
| Plant Body |

|
| Green Algae |

|
| Reproduction in Algae and Gymnosperms |

|
| Gymnosperms |

|
| Reproduction |

|
Introduction
Whittaker’s classification system divides all living organisms into five kingdoms based on body complexity (unicellular vs. multicellular), cell structure (prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic), and nourishment mechanisms (autotrophs vs. heterotrophs).
Classification of the Plant Kingdom
Plant classification can be categorized into three main types:
Artificial System: This system uses a limited number of morphological traits for classification. Notable proponents include Theophrastus, Pliny, and Linnaeus, who used various fictional classification schemes.
Natural System: Classification is based on a broad range of interconnected characteristics, both external and internal. This approach was used by Bentham, Hooker, Adanson, and Candolle.
Phylogenetic System: Plants are classified according to their evolutionary relationships. This system was utilized by Eichler, Blessy, Whittaker, Engler, Prantl, and Hutchinson.
Other Classification Methods
- Numerical Taxonomy: Uses computer-based statistical techniques, giving equal weight to different characteristics.
- Cytotaxonomy: Based on cytological features such as chromosome number, form, and behavior.
- Chemotaxonomy: Relies on chemical components like protein composition, DNA sequencing, flavor, and aroma.
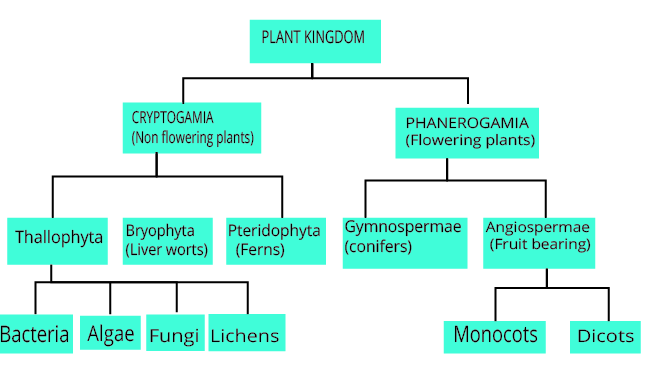
Plant Kingdom Classification
Phanerogamae: Flowering, seed-bearing plants.
Cryptogamae: Non-flowering, seedless plants, further divided into:
- Thallophyta: Plants with undifferentiated bodies resembling a thallus.
- Bryophyta: Plants with stem- and root-like structures but lacking vascular tissues.
- Pteridophyta: Plants with well-defined roots, stems, and leaves, containing vascular tissues.
Thallophytes are further divided into:
- Algae: Pigmented thallophytes.
- Fungi: Non-pigmented thallophytes.
- Lichens: Symbiotic associations between algae and fungi.
Phanerogamae are divided into:
- Gymnosperms: Naked seed plants.
Angiosperms: Covered seed plants, further divided into:
- Monocots: Single cotyledon, fibrous root system, parallel venation.
- Dicots: Two cotyledons, taproot system, reticulate venation.
Tracheophytes are the group that includes Gymnosperms, Angiosperms, and Pteridophytes because they have vascular tissue. The Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms are referred to as Embryophyta because of the presence of embryos.
Algae
Study of algae is known as phycology. Fritch is considered the father of phycology, while M.O. Iyengar is the father of Indian phycology.
Habitat
- Hydrophytes: Aquatic, e.g., Spirogyra (freshwater) and Sargassum (marine).
- Floating Algae: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra.
- Benthophytes: Attached to the substrate, e.g., Chara (stoneworts).
- Xerophytes: Desert habitat.
- Mesophytes: Medium moisture habitats.
- Epiphytes: Grow on plants, e.g., Cladophora.
- Epizoic: Grow on animals, e.g., Trichophillus.
- Lithophytes: Grow on rocks.
- Halophytes: Grow in saline areas.
- Terrestrials: Grow in moist soil, e.g., Fritschiella.
Plant Body
- Haploid Gametophyte: The vegetative plant body.
- Single-celled or Flagellated: e.g., Chlamydomonas.
Multiple Cells:
- Coenobium: Colony with a fixed number of cells, e.g., Volvox.
- Aggregation: Indefinite colony, e.g., Tetraspora.
- Filamentous Unbranched: e.g., Ulothrix.
- Filamentous Branched: e.g., Cladophora.
- Siphonous: Multinucleate, e.g., Vaucheria.
- Parenchymatous: e.g., Ulva.
- Branched Like Higher Plants: e.g., Sargassum, Chara.
Green Algae

Nutrition: Mostly autotrophic (photosynthetic), with rare parasitic forms like Cephaleuros.
Pigments:
- Chlorophylls: a, b, c, d.
- Carotenoids: Carotene, xanthophylls, fucoxanthin in brown algae.
- Phycobilins: Phycocyanin, phycoerythrin.
Reproduction in Algae and Gymnosperms
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction involves using vegetative parts of the plant for reproduction. The main types include:
- Fission: Division of a single organism into two or more parts.
- Fragmentation: Breaking of the plant body into fragments that regenerate into new individuals.
- Budding: Formation of a new organism from a bud or outgrowth on the parent.
- Tubers: Underground storage organs that can develop into new plants.
- Gemmae: Specialized reproductive structures that can form new individuals.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction occurs without the fusion of gametes and includes:
- Zoospores: Motile spores that develop within sporangia.
- Aplanospores: Non-motile spores.
- Akinete: A type of thick-walled spore adapted for survival.
- Hypnospores: Dormant spores.
- Endospore: A spore formed within the parent cell.
- Exospore: A spore formed outside the parent cell.
- Monospore: A single spore.
- Auxospore: A spore that develops into a new individual.
Palmella Stage
In the Palmella stage, spores cluster together and appear similar to the algae Palmella. Examples include Ulothrix and Chlamydomonas.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes and can be categorized into:
- Homogametes: Gametes that are similar in morphology and physiology.
- Heterogametes: Gametes that differ in morphology or physiology.
Types of sexual reproduction include:
- Isogamy: The fusion of similar gametes. Examples are Chlamydomonas (flagellated) and Spirogyra (non-flagellated).
- Anisogamy: The fusion of gametes with different morphologies or physiological profiles. Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra exhibit this type.
- Oogamy: The fusion of a large, non-motile female gamete with a small, motile male gamete. Examples include Fucus and Volvox.
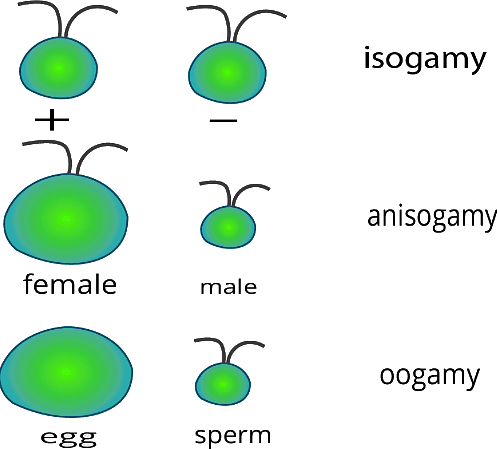
Sexual Reproduction in Chlamydomonas
- Exceptional Cases: Unicellular antheridium and oogonium are seen in Oedogonium.
Special Reproductive Structures:
- Conceptacles: Found in Sargassum.
- Globule (Antheridium) and Nucule (Oogonium): Seen in Chara.
In Spirogyra, conjugation, a unique form of sexual reproduction, occurs.
Gymnosperms
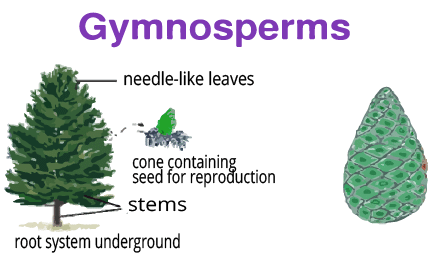
Gymnosperms are seed-producing plants with exposed ovules and no fruit covering. They include shrubs and medium to large trees and were prevalent during the Jurassic era. Key features include:
Reproduction
- Cones/Strobili: Groups of sporophylls form cones. Male cones (microsporophylls) produce microspores that develop into pollen grains. Female cones (megasporophylls) contain megaspores that develop into seeds.
- Pollen Tubes: Pollen grains create tubes to deliver male gametes to the ovules, resulting in fertilization and seed formation.
Economic Importance:
- Timbers: Used for furniture, pulpwood, and musical instruments.
- Resins and Turpentine: Produced by plants like Pinus.
- Edible Seeds: Found in Cycas, Pinus, and Ginkgo.
- Medicinal Uses: Ephedrine from Ephedra for respiratory issues and Taxol from Taxus for cancer treatment.
Common Gymnosperms:
- Maidenhair Tree: Ginkgo.
- Sago Palm: Cycas.
- Largest Gymnosperm: Sequoia.
- Smallest Gymnosperm: Zamia.
- Gymnosperm with Xylem Vessels: Ephedra and Gnetum.
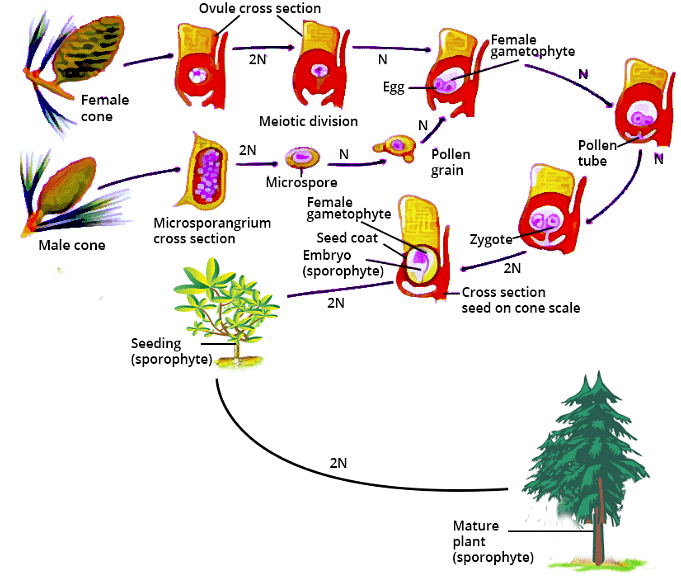
Alternation of Generations
Three types of life cycles are:
- Haplontic Life Cycle: Dominated by a haploid gametophyte that produces gametes. Examples include Chlamydomonas.
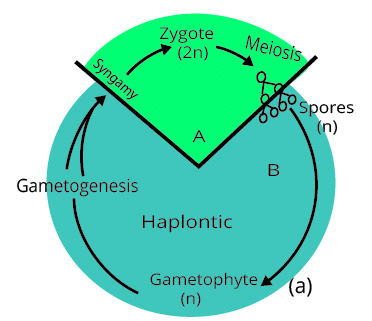
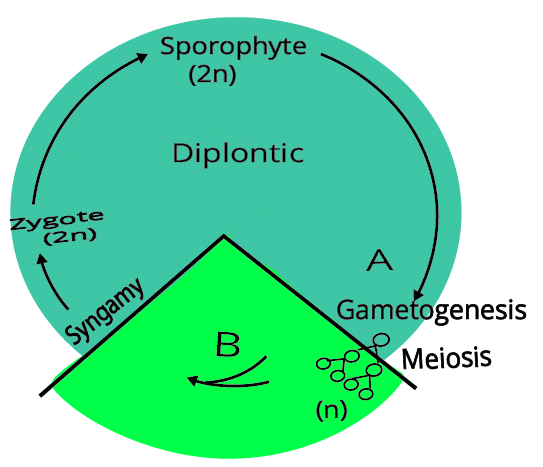
- Diplontic Life Cycle: Dominated by a diploid sporophyte. Examples include angiosperms and gymnosperms.
- Haplo-Diplontic Life Cycle: Features both haploid and diploid phases. Examples include bryophytes and pteridophytes.
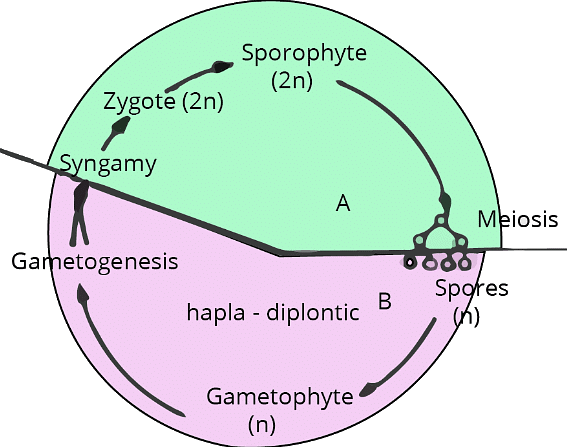
Most algae exhibit a haplontic life cycle, though some, like brown algae (Fucus), show a haplo-diplontic cycle.
|
528 videos|2113 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on Plant Kingdom and it's Classification - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main characteristics of algae in the plant kingdom? |  |
| 2. How do green algae differ from other types of algae? |  |
| 3. What is the habitat of algae in the plant kingdom? |  |
| 4. How do gymnosperms reproduce in the plant kingdom? |  |
| 5. How is the plant kingdom classified, and what are some examples of plants in each classification? |  |















