Plant Physiology | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Nutrition in Plants |

|
| Respiration in Plants |

|
| Transportation in Plants |

|
| Excretion in Plants |

|
| Mineral Nutrition in Plants |

|
| Plant Growth and Development |

|
Plants undergo various physio-chemical processes such as photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and transpiration, which contribute to their growth, development, and reproduction, thereby completing their life cycle.
Nutrition in Plants
Plant nutrition involves the study of essential chemical elements necessary for plant growth.
There are generally two types of nutrition in plants as mentioned below :
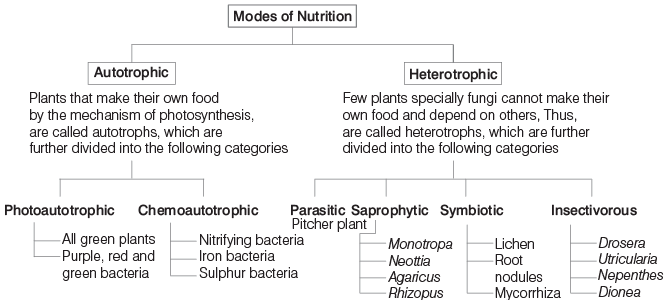
Photosynthesis
- This process enables plants to use CO2 and H2O to produce food (carbohydrates) in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
- During photosynthesis, chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light energy, which is then converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- CO2 is fixed into carbohydrates like glucose, storing potential energy.
Photosynthetic Pigments: Green plants can perform photosynthesis due to the presence of chlorophyll-a and b, along with other accessory pigments. These pigments convert light energy into chemical energy stored in organic compounds (carbohydrates).
Respiration in Plants
The food produced during photosynthesis is broken down in the mitochondria to release energy through cellular respiration.
Basic reaction of cellular respiration is as under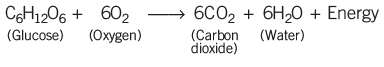
This energy is used by the plant to synthesize other necessary molecules.
The cell respiration is of following two types
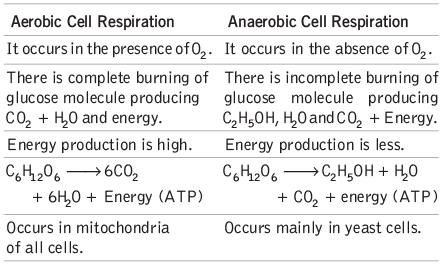
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): ATP serves as the energy currency of the cell. The hydrolysis of one ATP molecule releases about 7.6 kcal (31.8 kJ) of energy, which is used by plant cells for various functions.
Transportation in Plants
Leaves are responsible for food production, while roots absorb water. The plant transport system, consisting of xylem and phloem, moves these substances throughout the plant. Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves, and phloem distributes food to roots and other parts of the plant.
- Transport of Water: Xylem tissues in roots, stems, and leaves are interconnected. The process of photosynthesis and transpiration creates a water shortage in leaves, generating a demand for water and creating a pull that moves water from roots to leaves.
- Transport of Food: Phloem distributes photosynthetic products and other essential nutrients from leaves to the entire plant, particularly to storage organs such as roots and fruits.
Excretion in Plants
Plants excrete various waste products through different processes. Gaseous wastes (O2 and CO2) are expelled through stomata and lenticels, liquid wastes (excess water) through transpiration, and solid wastes (old leaves). Some excreted products, like essential oils, gums, and natural rubber, are useful to humans.
Transpiration in Plants
Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from plants, mainly through the stomata in leaves, with some water loss occurring through the general plant surface. Plants have developed adaptations to minimize excessive transpiration, particularly xerophytes in desert areas, which have features like thick waxy cuticles, modified leaves (thorns), or no leaves to reduce the rate of water loss.
Mineral Nutrition in Plants
Plants absorb minerals as ions from the soil and incorporate them into vital biomolecules.
Essential Elements: Some elements are absolutely necessary for the normal growth, development, and reproduction of plants and are irreplaceable. These elements are directly involved in the plant's metabolism, and without them, plants cannot complete their life cycle or produce seeds. These are known as essential elements, which are categorized into two groups:
- Macroelements: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Sulfur (S), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Magnesium (Mg), and Calcium (Ca).
- Microelements: Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl), and Molybdenum (Mo).
Following table gives a brief information about above mentioned nutrients
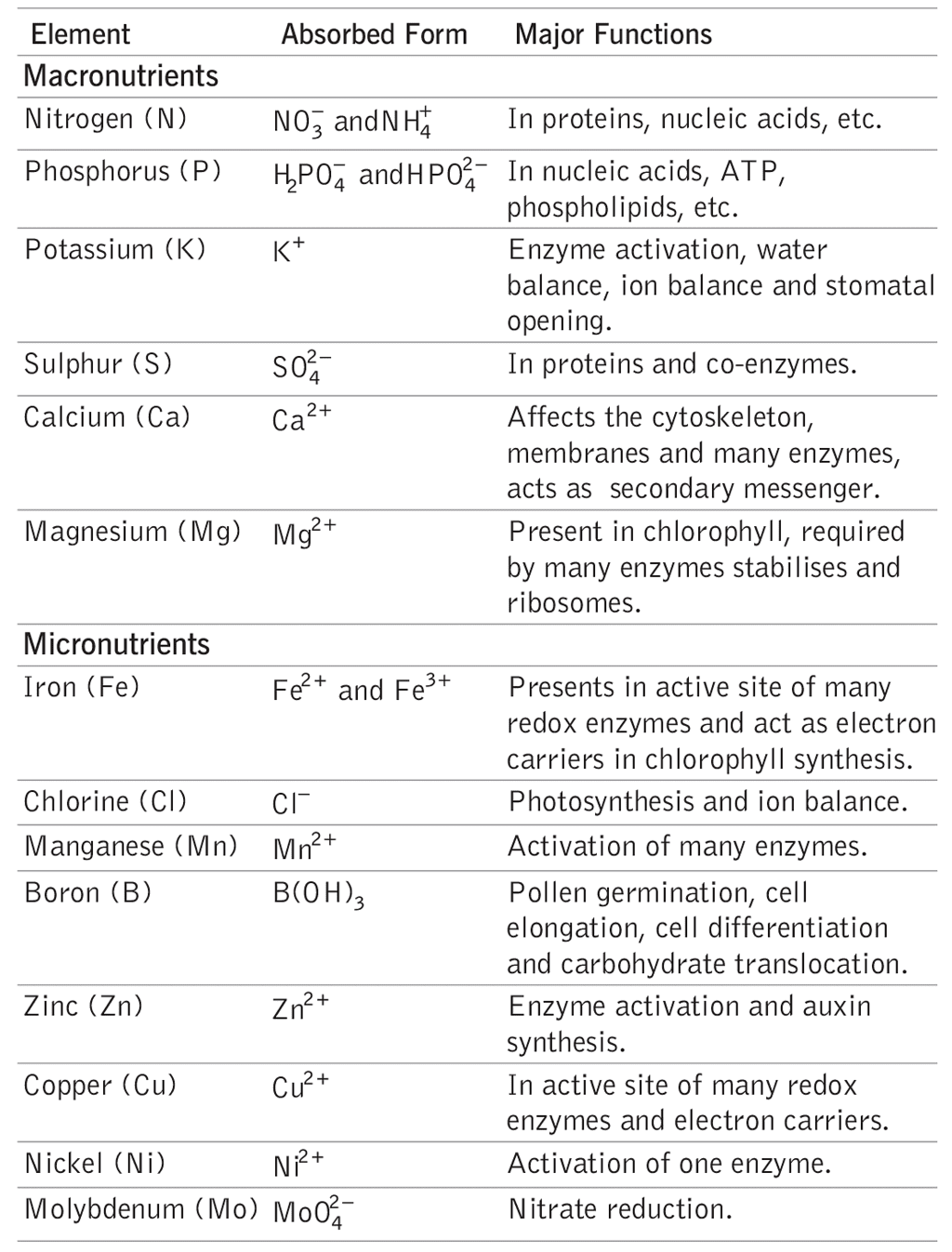
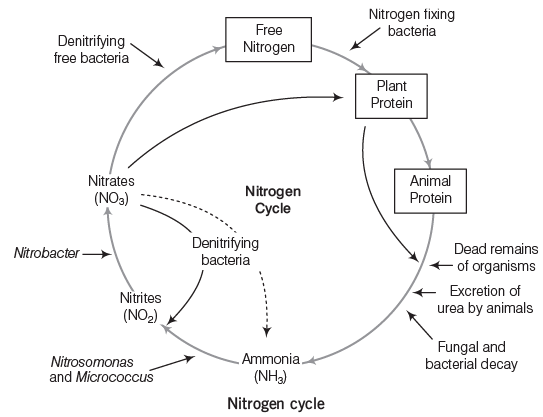
Nitrogen Metabolism: Nitrogen is a crucial macronutrient as it is a major component of proteins and nucleic acids. Biological nitrogen fixation, a key process in nitrogen metabolism, occurs in the roots of leguminous plants through a symbiotic relationship with Rhizobium bacteria. The steps involved in this process are:
- Ammonification: Decomposition of dead organic matter into ammonia by microbial activity.
- Nitrification: Conversion of ammonium (NH4+) to nitrates (NO3−) and nitrites (NO2−) by nitrifying bacteria like Nitrosomonas.
- Denitrification: Release of nitrogen back into the atmosphere by denitrifying bacteria such as Pseudomonas, which decompose dead organic matter and release nitrogen gas (N2).
Note: The burning of coal and other fossil fuels releases fixed nitrogen into the atmosphere as nitrogen-based trace gases like nitric oxide, which are then returned to the soil through the nitrogen cycle.
Plant Growth and Development
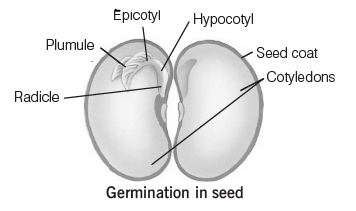
A new plant is formed by the germination of seed. This process is called seed germination. Until the seed start germinating it is kept in dormant stage. Seed germination can be easily understood by following diagram
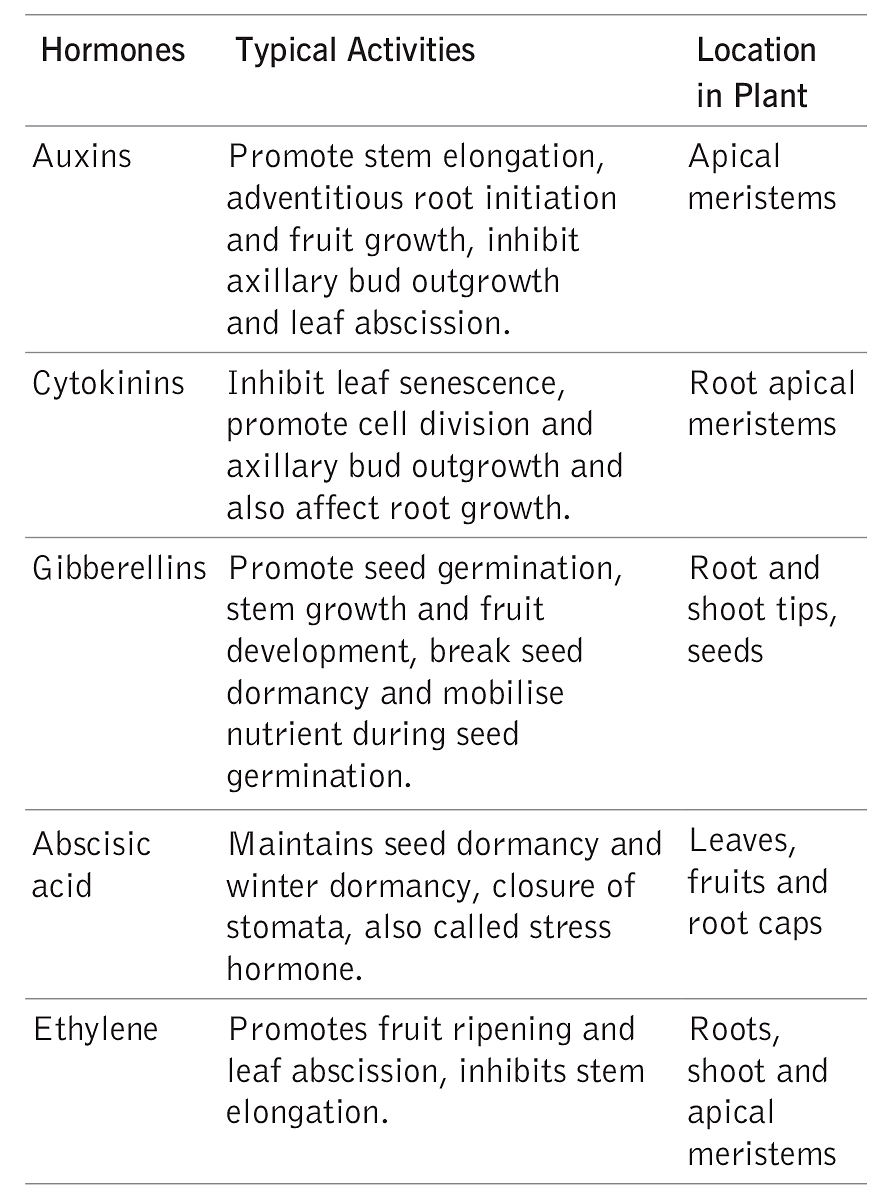
Growth is regarded as the irreversible permanent increase in the size and biomass of the plant. Plant hormones influence the growth and development of the plant.
Following table gives a brief idea of action of different plant hormones and their location.
Photoperiodism
The flowering of plants depends on their exposure to light, which is classified into the following categories:
- Long Day Plants (LDP): Plants requiring light exposure exceeding a well-defined critical duration, such as spinach and sugar beet.
- Short Day Plants (SDP): Plants needing light exposure less than a well-defined critical duration, like Xanthium and Dahlia.
- Day Neutral Plants (DNP): Plants whose flowering is not influenced by light duration, such as tomatoes and cotton.
- Vernalization: The process where flowering in some plants depends on exposure to low temperatures. For example, chilling treatment in certain wheat varieties reduces their vegetative growth period and induces early flowering.
|
478 videos|1421 docs|396 tests
|
FAQs on Plant Physiology - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the role of respiration in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants transport water and nutrients? |  |
| 3. How do plants excrete waste products? |  |
| 4. What are the essential minerals required for plant nutrition? |  |
| 5. How does plant growth and development occur? |  |




















