Plant Tissue Culture | Biology for Grade 12 PDF Download
PLANT TISSUE CULTURE
Tissue culture technique is based on totipotent nature of plant cell.

Plant tissue culture is the technique of maintaining and growing plant cells, tissues and organs in sterilized culture medium, under controlled aseptic conditions in vitro.
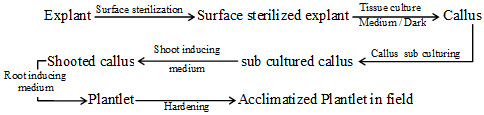
Ex-plant :
Plant part that is excised from its original location and used for initiating a culture. It may be root tip, shoot bud, anther, embryo, ovule etc. Normally undetermined cells of plant are used as explant.
Surface Sterilization :
The process of treatment of explant with specific antimicrobial chemicals like sodium hypochlorite, H2O2, C2H5OH, Mercuric chloride etc.
Autoclaving :
Sterilization of culture media, plastic ware and glass ware by moist heat (steam) at high pressure. It is performed at 120ºC for 15 psi pressure for 20 minute.
Culture medium or nutrient medium :
Medium, which provides nutrition to explants which is required for normal growth and development of explants.
Standard culture medium contains inorganic Salts, Vitamins, Sucrose (as a source of energy and carbon), growth regulators (2,4–D, Cytokinins, BAP-benzylaminopurine)
Growth regulators are required for cell division and organogenesis in explant.
Murashige and Skoog's culture medium is the most commonly used culture medium (MS medium).
Axenic culture :
Culturing of cell under complete aseptic condition is known as Axenic culture.
Callus : Group of undifferentiated or dedifferentiated cells, which are produced through invitro culture.
Types of Cultures –
(1) Callus culture & suspension culture.
(2) Meristem culture
(3) Embryo culture
(4) Anther culture
(5) Protoplast culture
(1) Callus & Suspension culture –
Callus culture – In callus culture when an explant is placed on a agar containing medium. Many of the cells become meristematic and begin to divide and giving rise to callus in 2-3 week. The agar medium contain growth regulator like auxin 2, 4 –D and cytokinin like BAP.
Suspension culture –In case of suspension culture a single cell or small group of cells placed on liquid medium. The medium normally contains the auxin 2, 4-D. These cells divide and form small groups of cells.
The suspension cultures are continuously agitated to break the cell mass in to smaller clumps and single cells and also maintain uniform distribution of cells and cell clumps in the medium.
It also allows gaseous exchange.
Suspension cultures grow much faster than callus culture.
With passage of time in a culture : -
(a) Cell tissue dry matter (biomass) 
(b) The level of nutrients in the medium 
(c) The medium volume declines due to evaporation.
The process of transferring the cell culture into a fresh culture medium is called Subculturing. It is normally done after 4-6 week when callus develops to its maximum. During subculture only a part of the culture from a vessel is transferred into the new culture vessel.
Haberlandt was first one who grow isolated leaf cells in plant tissue culture medium.
Totipotency : - The ability of a plant cell to regenerate into complete plant.
The concept of totipotency was given by ‘‘Haberlandt’’ and practical applications of totipotency was demonstrated by ‘‘Steward’’.
Steward developed a complete carrot plant from a single cell obtained from root of wild carrot.
Shoot and root formation :
The regeneration of root and shoot is controlled by two types of growth regulators.
The auxin NAA (Naphthaline Acetic Acid) promotes root regeneration whereas cytokinins BAP promotes shoot regeneration.
Callus is first kept on medium containing BAP, which initiates shoot formation from the callus.
When shoots become 2-3 cm. long, the culture is transferred to a medium containing auxin. Roots develop from the lower ends of these shoots and develop into young plant called plantlet.
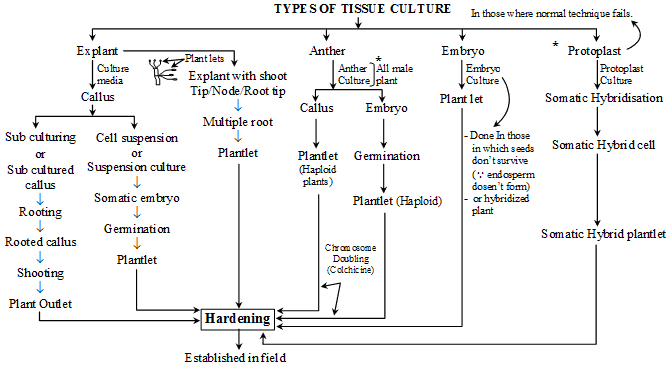
(2) Embryo culture : Culturing of immature young embryo in in-vitro medium.
Applications :-
Significance of Embryo Culture :
(i) In some inter-specific crosses or distant hybridization the endosperm of developing hybrid seeds degenerate very early or not formed so young hybrid embryo which gets devoid of nutrition also dies. In such cases the young hybrid embryo is excised and cultured in vitro to obtain hybrid seedling.
(ii) Seeds of some plants like orchid lack stored food. In such cases embryo culture allows seedling development from the embryos. This method is also used for rapid clonal propagation in orchid.
(iii) In some species seeds may remains dormant due to inhibitors present in the endosperms/seed coat. Embryo culture in such cases allows embryo development by eliminating the inhibitors responsible for dormancy
(3) Meristem Culture
Significance of Meristem Culture : -
- Rapid clonal multiplication.
- Production of virus free plant.
- Conservation of germplasm.
- Production of transgenic plant.
(4) Anther Culture
Significance of Anther Culture : -
(i) They have single set of chromosome, so even a very small change or mutation can be detected in haploids.
(ii) These haploids are used to produce homozygous diploids (by colchicine treatment) and these homozygous diploids are used as parents in crossing.s
(iii) Use of haploids in producing pure lines has reduced the period required for developing new varieties from 10 years to 5 years.
(5) Protoplast culture : -
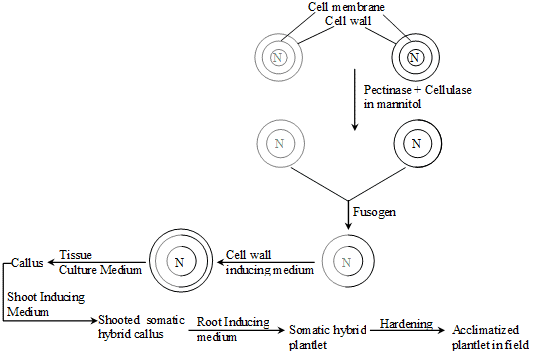
Somatic hybrid : A hybrid produced by fusion of somatic cells of two species or varieties.
The process of production of somatic hybrid is somatic hybridization.
Protoplast : Cell wall less plant cell is called protoplast.
STEPS OF SOMATIC HYBRIDIZATION
(A) Removal of cell wall → 2 method
(i) Mechanical method → Old method
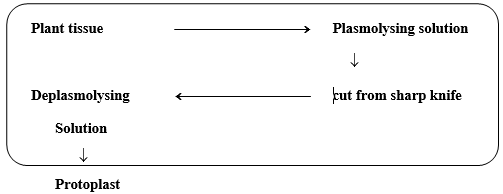
(ii) Enzymatic method → New method
Discovered by-Cocking.
In this method cell wall is digested by using pectinase & cellulase enzyme.
(B) Fusion between protoplast → 2 methods
(i) Spontaneous fusion : -
- During enzymatic treatment some protoplast fused together and form multi-nucleated structure which is called homokaryons or homokaryocytes.
- This is a intraspecific fusion.
- Not very useful in study.
(ii) Induced fusion : -
- Protoplast of two different species are fused together by induced fusion.
- Substance which induced the fusion of protoplast are called fusogen or fusogenic agent.
Fusogenic substance and condition : -
- By treatment of NaNO3
- By treatment of Ca+2 ions at high pH
- By treatment of polyethylene glycol [PEG]
- By high voltage electric shock
Culture of the fused protoplast : -
- Product of fused protoplast of two different species is called heterokaryon.
- Heterokaryons are mainly used in tissue culture.
- When the fused protoplasts are cultured on a suitable medium they regenerate cell wall and begin to divide ultimately to produce plantlets.
Importance of somatic hybridization :
(i) It allows the production of hybrids between different lines and species that can not be produced normally by sexual reproduction.
Pomato is a somatic hybrid between potato and tomato.
Bromato-Brinjal & tomato
(ii) Use of somatic hybrid :
For gene transfer.
Transfer of cytoplasm.
Production of useful allopolyploids.
SPECIAL POINTS
Somatic hybridization is also called parasexual hybridization.
First somatic hybrids were obtained between two species of tobacco Nicotiana gluca and N.langsdorfit by Carlson et. al.
|
124 videos|210 docs|207 tests
|
FAQs on Plant Tissue Culture - Biology for Grade 12
| 1. What is plant tissue culture and how is it relevant to the NEET exam? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of plant tissue culture? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of plant tissue culture? |  |
| 4. What are the steps involved in plant tissue culture? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced in plant tissue culture? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 12 exam
|

|


















