Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Year 9 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) > Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics | Year 9 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 9 PDF Download
Introduction to Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into several large and small plates that float and move on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them.
Evidence Supporting Plate Tectonics
- Fossil Similarities: Fossils of the same species found on continents now separated by oceans suggest they were once connected.
- Paleomagnetism: Magnetic minerals in rocks record the orientation of Earth's magnetic field at the time of their formation, showing past plate positions.
- Geological Fit: Matching coastlines of continents like South America and Africa provide evidence of their past proximity.
Question for Plate tectonicsTry yourself: Which evidence supporting plate tectonics involves the matching coastlines of continents?View Solution
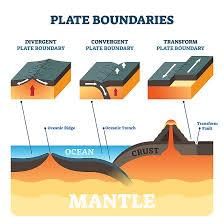
Types of Plate Boundaries
- Divergent Boundaries
- Plates move apart from each other.
- Example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge where new oceanic crust forms as plates diverge.
- Resulting features: Mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys (e.g., East African Rift).
- Convergent Boundaries
- Plates move towards each other.
- Subtypes:
- Oceanic-Continental: Oceanic plate subducts beneath continental plate.
- Oceanic-Oceanic: One oceanic plate subducts beneath another.
- Continental-Continental: Collision leads to mountain formation.
- Example: Andes Mountains formed by the convergence of the Nazca Plate and South American Plate.
- Transform Boundaries:
- Plates slide past each other horizontally.
- Example: San Andreas Fault in California.
- Resulting features: Earthquakes due to friction along faults.
Driving Forces of Plate Tectonics
Convection Currents: Heat-driven movements in the mantle cause plates to move.
- Hot mantle material rises at mid-ocean ridges, spreads horizontally, and sinks at subduction zones.
Impact of Plate Tectonics
- Volcanic Activity: Subduction zones and hot spots (e.g., Hawaii) lead to volcanic eruptions.
- Earthquakes: Transform boundaries and subduction zones generate seismic activity.
- Mountain Building: Collision of continental plates forms mountain ranges (e.g., Himalayas).
Measurement and Study of Plate Movement
- GPS Satellites: Track precise movements of Earth's surface points over time.
- Seismic Monitoring: Records earthquakes and their locations to understand plate interactions.
Conclusion
Plate tectonics is crucial for shaping Earth's surface and plays a significant role in geological processes such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and mountain formation. Understanding these processes helps scientists predict geological hazards and study Earth's history and future changes.
The document Plate tectonics | Year 9 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Year 9 Science IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
2 videos|38 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Plate tectonics - Year 9 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 9
| 1. What are divergent boundaries in plate tectonics? |  |
Ans. Divergent boundaries are areas where tectonic plates are moving away from each other, causing new crust to form from magma rising to the Earth's surface.
| 2. How do divergent boundaries contribute to the process of plate tectonics? |  |
Ans. Divergent boundaries play a crucial role in the movement of tectonic plates, as they are responsible for the creation of new crust and the overall process of plate tectonics.
| 3. What are some examples of divergent boundaries around the world? |  |
Ans. Some examples of divergent boundaries include the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the East African Rift, and the Red Sea Rift.
| 4. How do scientists study divergent boundaries and their effects on plate tectonics? |  |
Ans. Scientists study divergent boundaries using various techniques such as seismology, GPS monitoring, and studying the magnetic properties of rocks to understand their impact on plate tectonics.
| 5. How do divergent boundaries compare and contrast with other types of plate boundaries, such as convergent and transform boundaries? |  |
Ans. Divergent boundaries involve plates moving away from each other, while convergent boundaries involve plates colliding and transform boundaries involve plates sliding past each other horizontally. Each type of boundary has unique geological features and contributes differently to the movement of tectonic plates.
Related Searches




















