Points to Remember: Quadrilaterals | Mathematics Class 8- New NCERT (Ganita Prakash) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Polygon |

|
| Concave polygons |

|
| Convex polygons |

|
| Regular and irregular polygons |

|
| Parallelogram |

|
| Rhombus |

|
| Rectangle |

|
| Square |

|
| Kite |

|
| Trapezium |

|
| Diagonal |

|
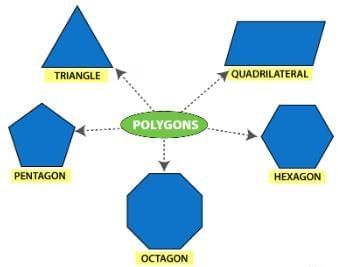
Polygon
A simple closed curve made up of only line segments is called a polygon.
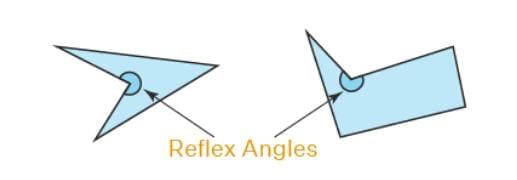
Concave polygons
Concave polygons are those polygons in which at least one interior angle is a reflex angle and it points inwards. They have a minimum of 4 sides
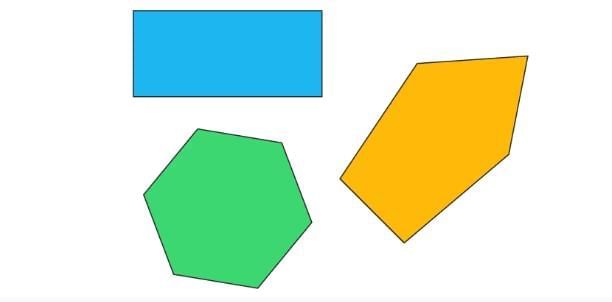
Convex polygons
A polygon is a two-dimensional shape that has a minimum of three sides and angles. A convex polygon is a shape in which all of its vertices point in the outward direction.
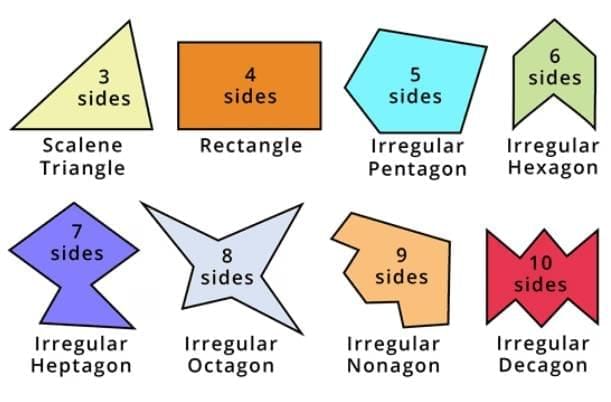
Regular and irregular polygons
A regular polygon is a two-dimensional shape having all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure.
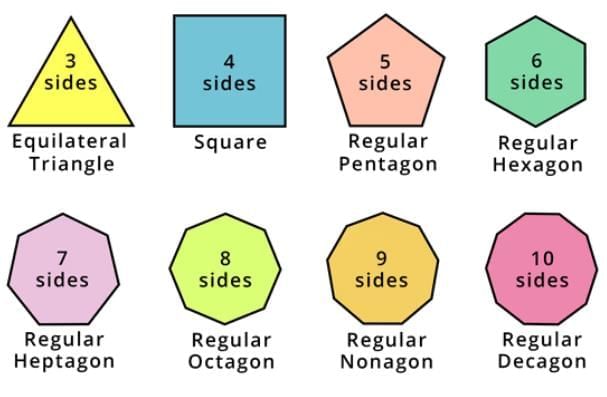
An irregular polygon, also known as non-regular polygon is a shape that does not have all sides of equal length and all angles of equal.
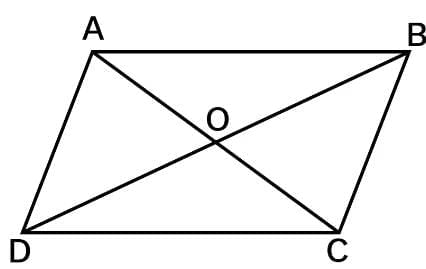
Parallelogram
A quadrilateral with each pair of opposite sides parallel.
- Opposite sides are equal.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Diagonals bisect one another.
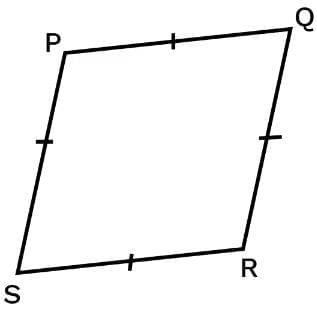
Rhombus
A parallelogram with sides of equal length.
- All the properties of a parallelogram.
- Diagonals are perpendicular to each other.
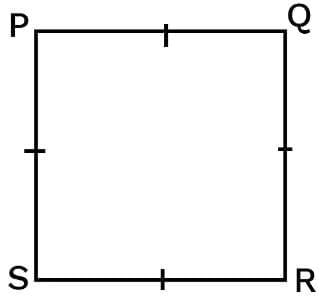
Rectangle
A parallelogram with a right angle.
- All the properties of a parallelogram.
- Each of the angles is a right angle.
- Diagonals are equal.

Square
- A rectangle with sides of equal length.
- All the properties of a parallelogram, rhombus, and a rectangle.
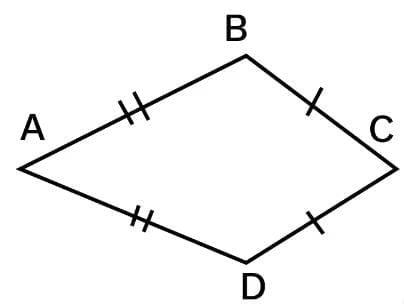
Kite
A quadrilateral with exactly two pairs of equal consecutive sides.
- The diagonals are perpendicular to one another.
- One of the diagonals bisects the other.
- From figure, m∠B=m∠D but m∠A≠m∠C
Trapezium
A quadrilateral having exactly one pair of parallel sides.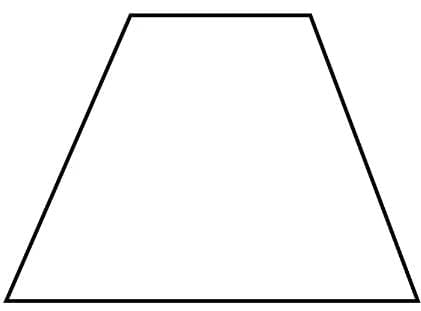
Diagonal
- A simple closed curve is made up of only line segments.
- A line segment connecting two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon is called diagonal.
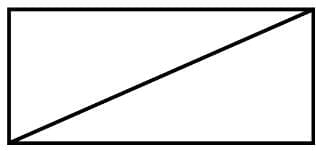
Convex: The measure of each angle is less than 180º .
Concave: The measure of at least one angle is more than 180º.
Quadrilateral: A polygon having four sides.
Element of quadrilateral:
(i) Sides: Line segments joining the points.
(ii) Vertices: Point of intersection of two consecutive sides.
(iii) Opposite sides: Two sides of a quadrilateral having no common endpoint.
(iv) Opposite Angles: Two angles of a quadrilateral not having a common arm.
(v) Diagonals: A line segment is obtained by joining the opposite vertices.
(vi) Adjacent Angles: Two angles of a quadrilateral having a common arm.
(vii) Adjacent Sides: Two sides of a quadrilateral having a common endpoint.
|
22 videos|133 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Quadrilaterals - Mathematics Class 8- New NCERT (Ganita Prakash)
| 1. What are the main characteristics that differentiate concave and convex polygons? |  |
| 2. How can you classify quadrilaterals, and what are the key properties of a parallelogram? |  |
| 3. What makes a shape a regular polygon, and can you provide examples of both regular and irregular polygons? |  |
| 4. What are the distinguishing features of a kite in geometry? |  |
| 5. How does a trapezium differ from other quadrilaterals, and what types of trapeziums exist? |  |















