Points to Remember: Triangles | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
Properties of Triangles
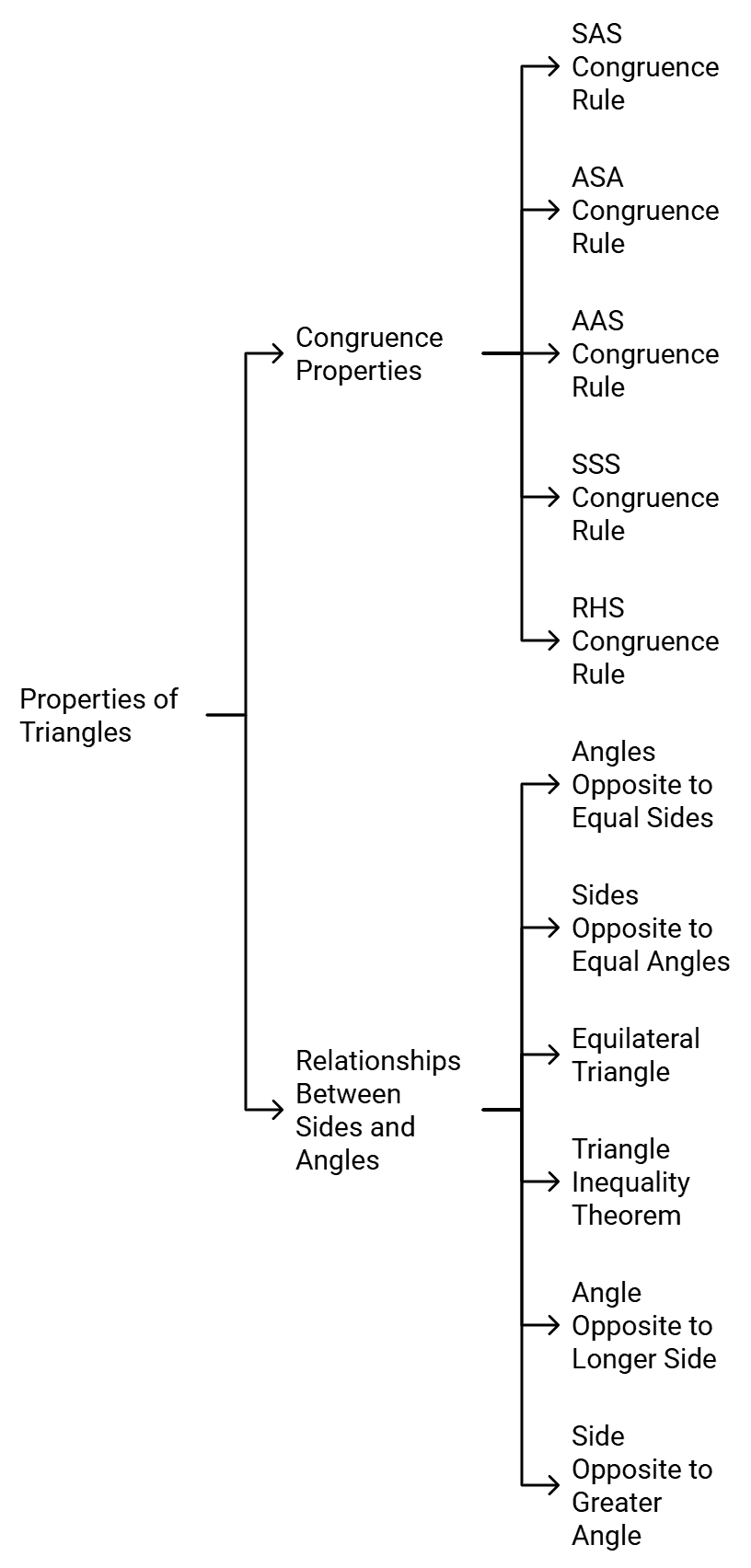 Properties of Triangle
Properties of Triangle
- Two congruent figures have exactly the same shape and size.
- If two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding parts are equal.
- If two sides and included angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the included angle of the other triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. [SAS congruence rule]
- If two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to two angles and included side of the other triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. [ASA congruence rule]
- If two angles and one side of a triangle are equal to two angles and the corresponding side of the other triangles, then the two triangles are congruent. [AAS congruence rule]
- If three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of other triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. [SSS congruence rule]
- If in two right triangles, hypotenuse and one side of a triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and one side of the other triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. [RHS congruence rule]
- Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal.
- Sides opposite to equal angles are equal.
- The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60º.
- In a triangle, the sum of any two sides is always greater than the third side.
- In a triangle, the angle opposite to the longer side is (greater) larger.
- In a triangle, the side opposite to the greater angle is longer.
Congruent Figures
If two geometrical figures have exactly the same shape and size then they are called congruent figures.
Note: (i) Two line segments are congruent only when their lengths are equal.
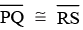

(ii) Two angles are congruent only when their degree measures are equal. ∠ABC ≌ ∠PQR
(iii) The symbol ‘≌’ is used to represent congruence.
Congruent Triangles
Two triangles are congruent if and only if one of them can be made to superimpose on the other, such as to cover it exactly.
In the figure, ΔABC ≌ ΔDEF.
Note: (i) When ΔABC ≌ ΔDEF, then sides of ΔDEF fall on corresponding equal sides of ΔABC, i.e.
DE covers AB or DE ↔ AB; EF covers BC or EF ↔ BC and FD covers CA or FD ↔ CA.
(ii) In case ΔABC ≌ ΔDEF,
∠D covers ∠A or ∠D ↔ ∠A.
∠E covers ∠B or ∠E ↔ ∠B.
∠F covers ∠C or ∠F ↔ ∠C.
(iii) In case ΔABC ≌ ΔDEF
D corresponds to A or D ↔ A.
E corresponds to B or E ↔ B.
F corresponds to C or F ↔ C.
(iv) In congruent triangles, corresponding parts are equal and we write in short ‘c.p.c.t.’ “for Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles”.
|
40 videos|471 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Points to Remember: Triangles - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What are the properties of congruent triangles? |  |
| 2. How can we prove that two triangles are congruent? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the congruence criteria in solving triangle problems? |  |
| 4. Can two triangles be congruent if they have the same angles but different side lengths? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of congruent triangles? |  |

















