Potentiometry & Potentiometric Titrations | Inorganic Chemistry PDF Download
What is Potentiometric Titration?
It is the procedure through which the quantity of the given test substance is determined by the measured addition of titrant until the entire test substance undergoes reaction. After the titration process, the potential difference between the two electrodes (namely the reference and indicator electrode) is measured in conditions where a thermodynamic equilibrium is maintained and the current passing through the electrodes does not disturb this equilibrium.
Potentiometric Titration Principle
Potentiometric titration is a laboratory method to determine the concentration of a given analyte. It is used in the characterization of acids. In this method, there is no use of a chemical indicator. Instead, the electric potential across the substance is measured.
Potentiometric Titration Method
Potentiometric Titration is done via the usage of two electrodes – an indicator electrode and a reference electrode (generally a hydrogen electrode or a silver chloride electrode). One half-cell is formed with the indicator electrode and the ions of the analyte, which is generally an electrolyte solution. The other half-cell is formed by the reference electrode.
The overall cell potential can be calculated using the formula given below.
Ecell = Eind – Eref + Esol
Where the potential drop between the indicator and reference electrodes over the electrolyte solution is given by Esol.
The overall cell potential, Ecell is calculated in every interval where the titrant is measured and added. Now, a graph is plotted with the Potential difference on the Y-axis and the volume on the X-axis as shown below.
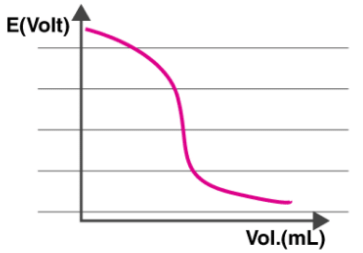
It can be observed from the graph that the electric potential of the cell is dependent on the concentration of ions which are in contact with the indicator electrode. Therefore, the Ecell is measured with each addition of the titrant.
Types of Potentiometric Titration
There are four types of titration that fall under the category of potentiometric titration, namely acid-base titration, redox titration, complexometric titration, and precipitation titration. A brief description of each of these types of titration is given below.
Acid-Base Titration: This type of potentiometric titration is used to determine the concentration of a given acid/base by neutralizing it exactly using a standard solution of base/acid whose concentration is known.
Redox Titration: This type of potentiometric titration involves an analyte and titrant that undergo a redox reaction. An example of this type of titration would be the treatment of an iodine solution with a reducing agent which produces iodide ion (a starch indicator is used to get the endpoint).
Complexometric Titration: This type of titration can also be referred to as chelatometry. In this method, a coloured complex is formed, indicating the end point of the titration. This method is used to determine a mixture of metal ions in a given solution.
Precipitation Titration: This type of titration involves a reaction between the given analyte and the titrant wherein an insoluble precipitate is formed. The end-point of this titration is noted when the addition of the titrant no longer forms a precipitate.
|
50 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Potentiometry & Potentiometric Titrations - Inorganic Chemistry
| 1. What is potentiometric titration? |  |
| 2. How does potentiometry work in potentiometric titration? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of potentiometric titration? |  |
| 4. How is potentiometric titration different from other titration methods? |  |
| 5. What are some applications of potentiometric titration? |  |





















