Practice Questions: Data Caselets - 2 | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
Direction for Questions (1 - 4):
Behala Players’ Corner is a registered club known for its grand public annual Durga Puja celebration held at Behala Chowrasta, Kolkata, under the patronage of the family of Mr Chandidas Ganguly, whose sons Mr Snehasis Ganguly and Mr Sourav Ganguly are notable members.
Mr Abhik Mishra, Mr Biplab Das, Mr Chinmoy Sen and Mr Dilip Palit, all of whom were very reputed and well-to-do local residents are actively involved every year as volunteers in collecting subscriptions on behalf of Behala Players’ Corner for the expenditure of Durga Puja celebrations. They are cumulatively entrusted with the responsibility of subscriptions from the four localities of Barisha, Bakultala, Sarsuna and Adarshapally, all areas being in the vicinity of Behala Players’ Corner.
The following partially filled table shows the subscriptions collected by each of them in the month of September 2021, a month before Durga Puja :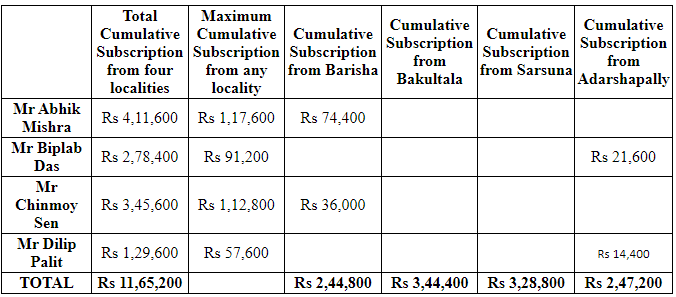
It was also known that :
a) Each volunteer collected the maximum cumulative subscription from distinct localities out of the four.
b) No volunteer collected equal subscriptions from any two localities.
c) Mr Biplab Das collected more subscriptions from Bakultala than Sarsuna.
d) The subscription collected by all four volunteers from each locality was a multiple of Rs 1,200.
Q1: What was the difference (in Rs) between the amounts collected as subscription by Mr Chinmoy Sen from Bakultala and Sarsuna ?
(a) 12,000
(b) 9,600
(c) 6,000
(d) Cannot be determined
Ans: (b)
Sol:
The final figures of all the subscriptions collected by the four volunteers from the four localities are : 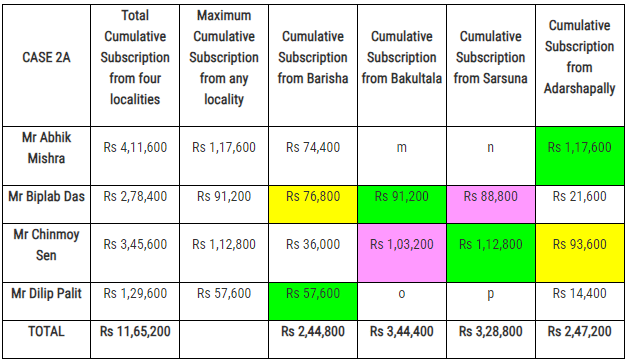 with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being :
with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being :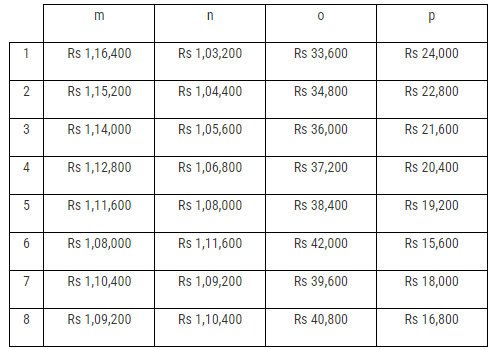 Hence, the difference (in Rs) between the amounts collected as subscription by Mr Chinmoy Sen from Bakultala and Sarsuna
Hence, the difference (in Rs) between the amounts collected as subscription by Mr Chinmoy Sen from Bakultala and Sarsuna
= 112800 – 103200
= Rs 9,600
Q2: Which of the following could be the summation of the subscriptions collected (in Rs) by Mr Abhik Mishra and Mr Dilip Palit from the locality of Bakultala ?
(a) 1,42,800
(b) 1,50,000
(c) 1,78,800
(d) All of the above
Ans: (b)
Sol:
The final figures of all the subscriptions collected by the four volunteers from the four localities are :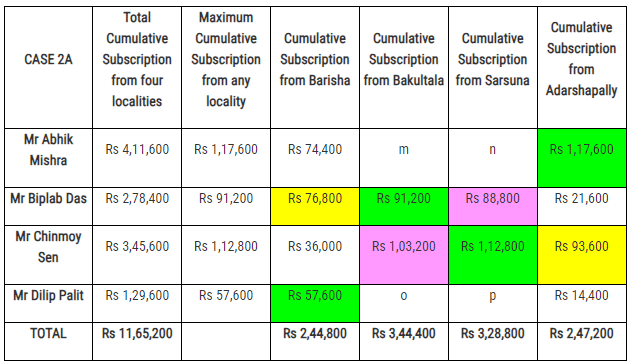
with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being :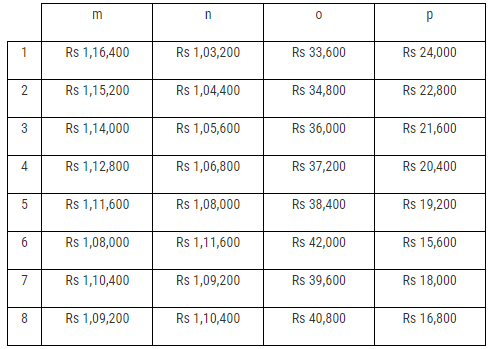 The summation of the subscriptions collected by Mr Abhik Mishra and Mr Dilip Palit from the locality of Bakultala would be denoted by m + o.
The summation of the subscriptions collected by Mr Abhik Mishra and Mr Dilip Palit from the locality of Bakultala would be denoted by m + o.
As calculated previously, m + o = Rs 1,50,000
Hence, the summation of the subscriptions collected (in Rs) by Mr Abhik Mishra and Mr Dilip Palit from the locality of Bakultala is Rs 1,50,000.
Q3: Which of the following (in Rs) cannot be the amount collected as subscription by Mr Abhik Mishra from the locality of Sarsuna ?
(a) 1,11,600
(b) 1,08,000
(c) 1,03,200
(d) 1,00,800
Ans: (a)
Sol:
The final figures of all the subscriptions collected by the four volunteers from the four localities are : with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being :
with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being : The amount collected as subscription by Mr Abhik Mishra from the locality of Sarsuna is denoted by n.
The amount collected as subscription by Mr Abhik Mishra from the locality of Sarsuna is denoted by n.
Of all the values given in the options, only Rs 1,00,800 is not an amount collected as subscription by Mr Abhik Mishra from the locality of Sarsuna
Q4: Which of the following could be the summation of the subscriptions collected (in Rs) by Mr Abhik Mishra from the localities of Bakultala and Sarsuna ?
(a) 2,19,600
(b) 2,38,800
(c) 2,56,400
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a)
Sol:
The final figures of all the subscriptions collected by the four volunteers from the four localities are : with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being :
with the eight different combination of values of m, n, o and p being : The summation of the subscriptions collected by Mr Abhik Mishra from the localities of Bakultala and Sarsuna would be denoted by m + n.
The summation of the subscriptions collected by Mr Abhik Mishra from the localities of Bakultala and Sarsuna would be denoted by m + n.
As calculated previously, m + n = Rs 2,19,600
Hence, the summation of the subscriptions collected (in Rs) by Mr Abhik Mishra from the localities of Bakultala and Sarsuna is Rs 2,19,600.
Direction for questions (5-8):
In a birthday party for kids, six different desserts were available. Each kid had to select 3 out of these 6 deserts under following conditions:
a) The kid who selects Ice-cream has to select Pastry and vice-versa.
b) The kid who selects Candy or Tiramisu, cannot select Ambrosia.
c) The kid who selects Ice-cream cannot select Cookie.
Following are the number of each type of deserts distributed in the party:
Ice-cream: 93 Pastry: 93 Candy: 107 Tiramisu: 112 Cookie: 84 Ambrosia: 42
Q5: How many kids selected combination of Ice-cream, Pastry and Candy?
Ans: 23
Sol:
From given data, we know that,
the kid who selected Ice-Cream and Pastry or none of the two
the kid who selected Candy or Tiramisu didn’t select Ambrosia
the kid who selected Ice-cream and Pastry didn’t select Cookie.
Thus the possible ways of selecting three deserts are:
1) Ice-cream, Pastry and Candy
2) Ice-cream, Pastry and Tiramisu
3) Ice-cream, Pastry and Ambrosia
4) Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie
Let’s start by the desert which least number of kids selected, i.e. Ambrosia – 42
We see that those who selected Ambrosia also selected Ice-cream and Pastry.
So, 42 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Ambrosia.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry:
Ice-cream = 93 – 42 = 51
Pastry = 93 – 42 = 51
Now, let’s consider the desert which was selected by second least number of kids, i.e. Cookie – 84
We see that those who selected Cookie also selected Candy and Tiramisu.
So, 84 kids selected Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Candy, Tiramisu:
Candy = 107 – 84 = 23
Tiramisu = 112 – 84 = 28
Now, let’s consider the remaining desert which was selected by least number of kids, i.e. Candy – 23
These 23 kids must also select Ice-cream and Pastry.
So, 23 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Candy.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry:
Ice-cream = 51 – 23 = 28
Pastry = 51 – 23 = 28
Thus, remaining 28 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry would’ve also selected Tiramisu.
Thus, we get our final table as shows the combination and the number of kids who opted for it: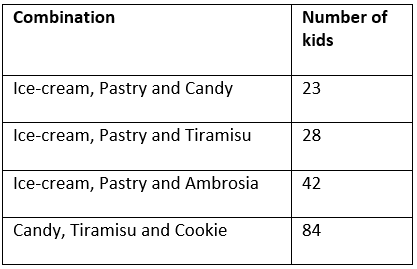 Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
23 is the right answer.
Q6: How many kids were present for the birthday party? (Enter ‘0’ if the answer is ‘cannot be determined’)
Ans: 177
Sol:
From given data, we know that,
the kid who selected Ice-Cream and Pastry or none of the two
the kid who selected Candy or Tiramisu didn’t select Ambrosia
the kid who selected Ice-cream and Pastry didn’t select Cookie.
Thus the possible ways of selecting three deserts are:
1) Ice-cream, Pastry and Candy
2) Ice-cream, Pastry and Tiramisu
3) Ice-cream, Pastry and Ambrosia
4) Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie
Let’s start by the desert which least number of kids selected, i.e. Ambrosia – 42
We see that those who selected Ambrosia also selected Ice-cream and Pastry.
So, 42 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Ambrosia.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry:
Ice-cream = 93 – 42 = 51
Pastry = 93 – 42 = 51
Now, let’s consider the desert which was selected by second least number of kids, i.e. Cookie – 84
We see that those who selected Cookie also selected Candy and Tiramisu.
So, 84 kids selected Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Candy, Tiramisu:
Candy = 107 – 84 = 23
Tiramisu = 112 – 84 = 28
Now, let’s consider the remaining desert which was selected by least number of kids, i.e. Candy – 23
These 23 kids must also select Ice-cream and Pastry.
So, 23 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Candy.
Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry:
Ice-cream = 51 – 23 = 28
Pastry = 51 – 23 = 28
Thus, remaining 28 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry would’ve also selected Tiramisu.
Thus, we get our final table as shows the combination and the number of kids who opted for it: Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Or
Number of kids present in the part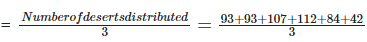
= 531/3 = 177
Q7: How many kids selected Candy and Tiramisu both?
Ans: 84
Sol:
From given data, we know that, the kid who selected Ice-Cream and Pastry or none of the two the kid who selected Candy or Tiramisu didn’t select Ambrosia the kid who selected Ice-cream and Pastry didn’t select Cookie.
Thus the possible ways of selecting three deserts are:
1) Ice-cream, Pastry and Candy
2) Ice-cream, Pastry and Tiramisu
3) Ice-cream, Pastry and Ambrosia
4) Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie
Let’s start by the desert which least number of kids selected, i.e. Ambrosia – 42 We see that those who selected Ambrosia also selected Ice-cream and Pastry. So, 42 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Ambrosia. Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry: Ice-cream = 93 – 42 = 51 Pastry = 93 – 42 = 51
Now, let’s consider the desert which was selected by second least number of kids, i.e. Cookie – 84 We see that those who selected Cookie also selected Candy and Tiramisu. So, 84 kids selected Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie. Thus, remaining kids who selected Candy, Tiramisu: Candy = 107 – 84 = 23 Tiramisu = 112 – 84 = 28
Now, let’s consider the remaining desert which was selected by least number of kids, i.e. Candy – 23 These 23 kids must also select Ice-cream and Pastry. So, 23 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Candy. Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry: Ice-cream = 51 – 23 = 28 Pastry = 51 – 23 = 28
Thus, remaining 28 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry would’ve also selected Tiramisu. Thus, we get our final table as shows the combination and the number of kids who opted for it: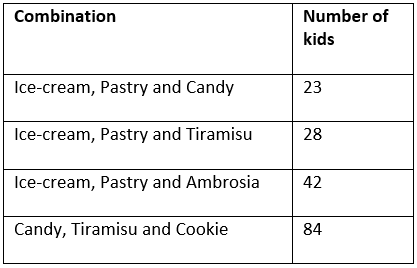 Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Thus, 84 kids selected Candy and Tiramisu.
Q8: In how many ways can a kid select the combination of deserts?
Ans: 4
Sol:
From given data, we know that, the kid who selected Ice-Cream and Pastry or none of the two the kid who selected Candy or Tiramisu didn’t select Ambrosia the kid who selected Ice-cream and Pastry didn’t select Cookie.
Thus the possible ways of selecting three deserts are:
1) Ice-cream, Pastry and Candy
2) Ice-cream, Pastry and Tiramisu
3) Ice-cream, Pastry and Ambrosia
4) Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie
Let’s start by the desert which least number of kids selected, i.e. Ambrosia – 42 We see that those who selected Ambrosia also selected Ice-cream and Pastry. So, 42 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Ambrosia. Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry: Ice-cream = 93 – 42 = 51 Pastry = 93 – 42 = 51
Now, let’s consider the desert which was selected by second least number of kids, i.e. Cookie – 84 We see that those who selected Cookie also selected Candy and Tiramisu. So, 84 kids selected Candy, Tiramisu and Cookie. Thus, remaining kids who selected Candy, Tiramisu: Candy = 107 – 84 = 23 Tiramisu = 112 – 84 = 28
Now, let’s consider the remaining desert which was selected by least number of kids, i.e. Candy – 23 These 23 kids must also select Ice-cream and Pastry. So, 23 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry also selected Candy. Thus, remaining kids who selected Ice cream and Pastry: Ice-cream = 51 – 23 = 28 Pastry = 51 – 23 = 28
Thus, remaining 28 kids who selected Ice-cream and Pastry would’ve also selected Tiramisu. Thus, we get our final table as shows the combination and the number of kids who opted for it: Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
Thus, total number of kids = 23 + 28 + 42 + 84 = 177
A kid can choose the combination of deserts in 4 ways.
Q9: 4 friends Praveen, Varun, Sanjay, and Gautam decided to find out their weight. No 2 persons are of the same weight.They went to a centre that had a machine which does not display the weight. Rather, it takes the weight of the first person standing on it as the base and displays a ‘+’ sign if the weight of the second person is greater than that of the first person and ‘-‘ sign if the weight of the second person is less than that of the first person. Rahul is the owner of the centre and he offers to stand first on the machine to provide a base for comparison. Rahul stands on the machine first and his weight is taken as the base. Praveen, Varun, Sanjay, and Gautam stand on the machine in that order and the results displayed were +, -, + , +. Which of the following statements will help to rank the friends according to their weights?
(a) Rahul is not the lightest person among the five.
(b) Gautam is not the heaviest person among the five.
(c) Praveen is heavier than Sanjay.
(d) Praveen is not the heaviest person among the five.
Ans: (b)
Sol:
Let the weight of Rahul be R.
We know that the machine displayed +, -, + , + in that order.
=> Praveen’s weight > R
Varun’s weight is less than Praveen’s weight. However, we cannot determine whether Varun’s weight is less than Rahul’s weight.
Sanjay is heavier than Varun. Gautam is heavier than Sanjay.
Let us represent the weights of the persons using the first letters of their name.
The relationships that can be established are
R < P > V < S < G
Let us evaluate the options.
Option A:
Rahul is not the lightest person among the five.
=> Varun is the lightest.
No relationship can be established between P and S.
Option C:
Praveen is heavier than Sanjay.
We cannot determine whether Gautam is heavier than Praveen or not.
Option D:
Praveen is not the heaviest person among the five.
=> Gautam is the heaviest among the five.
However, we cannot determine whether Praveen is heavier than Sanjay.
Option B:
Gautam is not the heaviest person among the five.
=>Praveen is the heaviest.
=> V < S < G < P
We can rank the 4 friends using option B and hence, option B is the right answer.
Q10: On her walk along the beach, Alex collected 50 coloured shells, all either calcium or magnesium. She sorted them by category when she got home, and found the following: The number of white magnesium shells with grooves is even and positive.The number of white magnesium shells without any groove equals the number of white calcium shells without grooves.All non-white magnesium shells have grooves, and there are five times as many of them as there are white grooved magnesium shells.There are no grooved calcium shells that are not white.There are exactly 6 white grooved calcium shells.There are exactly 22 calcium shells that are neither grooved nor white. How many magnesium shells did she collect?
(a) 22
(b) 17
(c) 25
(d) 18
Ans: (b)
Sol:
Let x and y be as shown in the table. Therefore, 28+6x+2y=50 => 6x+2y=22. Since x is positive and even, if x=2, y=5 from the eqn. If x=4 => y=-1. Hence, x has to be less than 4. Therefore x=2. No. of mag shells = y+6x = 5+12= 17.
|
93 videos|123 docs|94 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions: Data Caselets - 2 - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What is the CAT exam and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How do I apply for the CAT exam? |  |
| 3. What is the exam pattern for the CAT exam? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare for the CAT exam effectively? |  |
| 5. What are some of the top management institutes in India that accept CAT scores? |  |