Practice Questions: The Other Side of Zero | Mathematics for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1: Identify the smallest number from the list: -7, 0, -9, 5, -1.
Sol: -9 is the smallest as it is farthest to the left on the number line.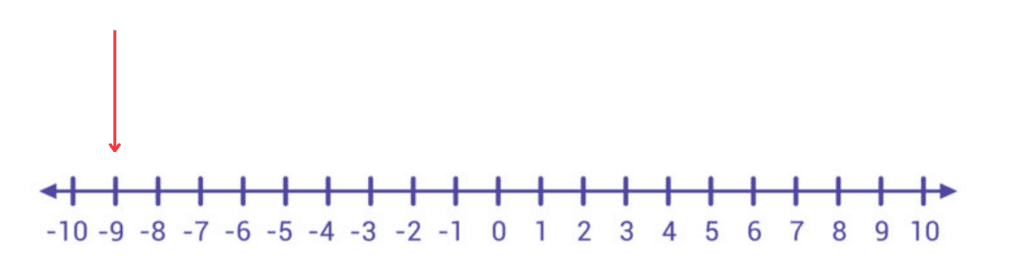
Q2: What is the result of: (-8) + (+12)?
Sol: -8 + 12 = 4. We move 12 steps right from -8.
Q3: Simplify: (+14) - (-3).
Sol: 14 - (-3) = 14 + 3 = 17.
Q4: Find the integer which when added to -10 gives 0.
Sol: -10 + 10 = 0. So, the required integer is +10.
Q5: Compare: Which is greater, -3 or -8?
Sol: -3 is greater because it is closer to 0 on the number line.
Q6: Fill in the blanks: -5, -3, -1, ___, ___, 5.
Sol: The pattern increases by 2: Next terms are 1, 3.
Q7: On a number line, what is 5 units to the left of 0?
Sol: 5 units left of 0 is -5.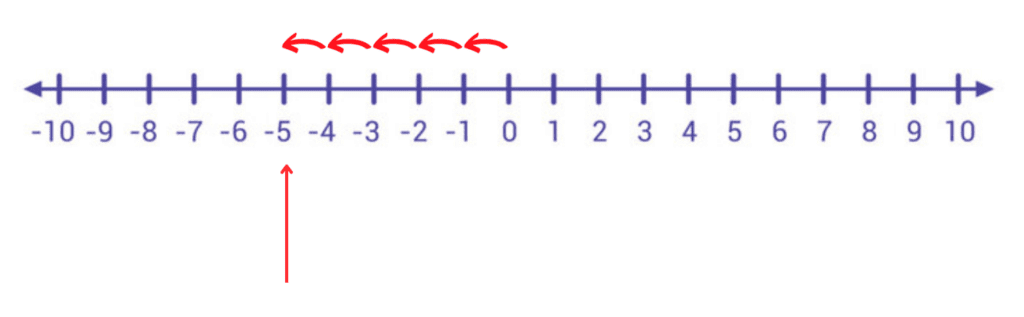
Q8: Which number lies exactly between -10 and 0?
Sol: -5 lies exactly halfway between.
Q9: If Ramesh climbs 4 floors up from floor -2, where does he reach?
Sol: (-2) + 4 = 2. He reaches floor +2.
Q10: What should be added to -6 to get -2?
Sol: -6 + 4 = -2. So, the number is 4.
Q11: Arrange in ascending order: 3, -2, -7, 0, -1
Sol: -7, -2, -1, 0, 3
Q12: From floor +4, a lift goes down 9 floors. Where does it reach?
Sol: 4 + (-9) = -5. It reaches floor -5.
Q13: Fill in the missing number: (-12) + ___ = -5
Sol: The missing number is 7, since -12 + 7 = -5.
Q14: A diver is at -20 m. He rises 12 m. What is his new position?
Sol: -20 + 12 = -8. New position is -8 m.
Q15: Using Brahmagupta's rule: What is (-4) + (+7)?
Sol: Brahmagupta's rule (For adding integers with different signs, subtract the smaller absolute value from the larger and take the sign of the larger number).
7 - 4 = 3
⇒ Answer = +3.
Q16: Using zero pairs, simplify: (+6) + (-4)
Sol: A zero pair is a combination of +1 and –1, which cancel each other out because:
(+1) + (–1) = 0
Represent the numbers:
+6 means 6 positive counters: ➕➕➕➕➕➕
–4 means 4 negative counters: ➖➖➖➖
Make zero pairs:
Match each ➕ with a ➖:
(➕➖) (➕➖) (➕➖) (➕➖) → 4 zero pairs = 0
What’s left?
After cancelling 4 pairs, 2 positive counters remain: ➕➕
Answer: +2
Q17: Convert subtraction to addition: (-5) - (+2)
Sol: -5 + (-2) = -7.
Q18: Compare: Which is smaller, -11 or -8?
Sol: -11 is smaller (farther left on the number line).
Q19: Solve: (-15) + (+5) + (-10)
Sol: Step 1: -15 + 5 = -10. Step 2: -10 + (-10) = -20.
Q20: A deposit of ₹200 is made, then ₹350 withdrawn. What is the balance?
Sol: The person deposits ₹200 into the account.
So, the starting balance is: ₹200
Then, ₹350 is withdrawn:
This means ₹350 is taken out of the account.
Subtract to find the balance:
₹200 – ₹350 = –₹150
What does the negative sign mean?
A negative balance (–₹150) means the person has overdrawn the account and now owes ₹150.
Answer: –₹150 (The account is overdrawn by ₹150)
Q21: Temperature is -3°C in morning, falls by 7°C. Find new temp.
Sol: -3 + (-7) = -10°C
Q22: Fill in the sequence: -15, -10, ___, 0, ___, 10
Sol: Pattern: +5 each step. Missing: -5 and 5.
Q23: What is the opposite of +7?
Sol: The opposite of +7 is -7.
Q24: Which integer is neither positive nor negative?
Sol: The integer neither positive nor negative is 0.
Q25: If you start at -5 and move 8 steps right, what is your final position?
Sol:
-5 + 8 = +3.
|
52 videos|374 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Practice Questions: The Other Side of Zero - Mathematics for Class 6
| 1. What is the main theme of "The Other Side of Zero"? |  |
| 2. How does the article describe the importance of zero in mathematics? |  |
| 3. Can you explain how "The Other Side of Zero" relates to real-life situations? |  |
| 4. What examples does the article provide to illustrate the concept of zero? |  |
| 5. How can understanding the concept of zero benefit students in their studies? |  |
















