Present Tense | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Present Tense? |

|
| Types of Present Tense |

|
| Solved Questions |

|
Introduction
The present tense is essential for effective communication in both spoken and written English. It is crucial for competitive exams, as a strong grasp of grammar and vocabulary can significantly improve your performance. Understanding the different types of present tense is key to mastering this area of grammar.

What is Present Tense?
In English, verbs are classified into three main tenses: past, present, and future. The present tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or regularly, or events that are generally true. Here’s how the three tenses compare:
- Present Tense: Describes current actions or general truths.
- Past Tense: Describes actions that have already occurred.
- Future Tense: Describes actions that will happen later.
For example:
- Rohit prepares a pudding. (Present Tense)
- Rohit prepared a pudding. (Past Tense)
- Rohit will prepare a pudding. (Future Tense)
Present tense helps convey actions that occur in the present, the state of being, or something associated with the current moment.
Types of Present Tense
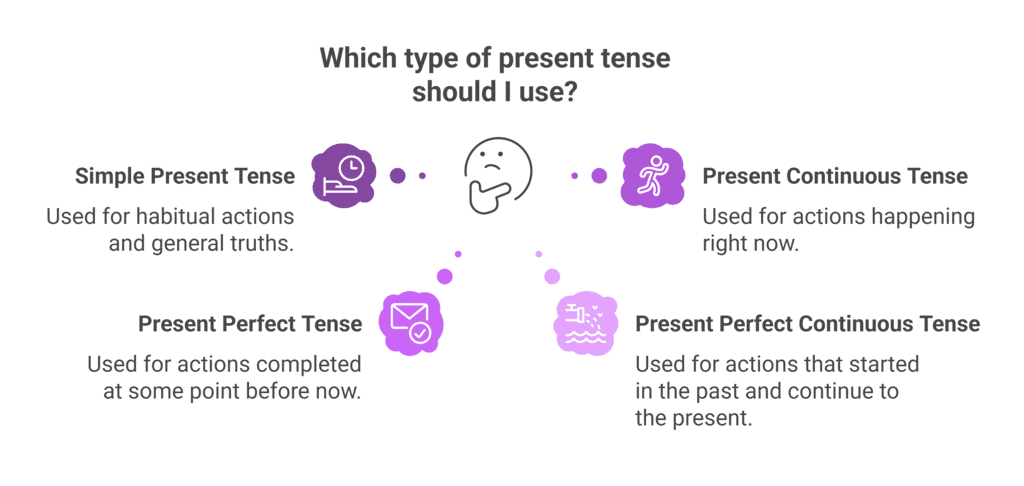
There are four primary types of present tense in English grammar:
- Simple Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Let’s explore each of these in detail:
1. Simple Present Tense
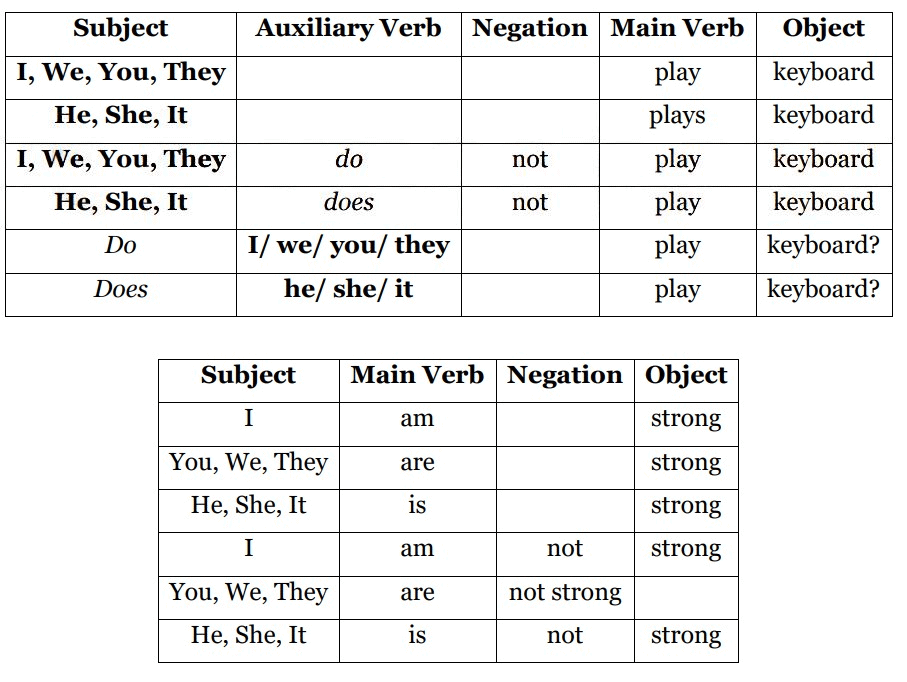
The simple present tense is used to describe universal truths, habitual actions, and regular activities. It’s formed by adding s or es to the verb when the subject is he, she, or it.
Structure: Subject + Base Verb (+ s/es) + Object
Examples:
- The Earth revolves around the Sun. (Universal truth)
- I usually meet my friends on Sundays. (Habitual action)
- She does not like to play. (Negative sentence)
- Do you want to watch a movie tonight? (Interrogative sentence)
Consider the following tables:
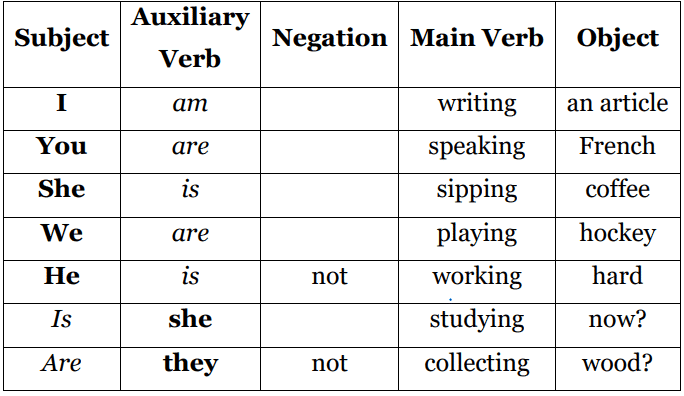
2. Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used to express actions that are currently happening or ongoing at the time of speaking. It can also describe temporary or planned actions in the future.
Structure: Subject + am/is/are + Verb (ing) + Object
Examples:
- I am eating an apple. (Ongoing action)
- The children are getting ready for the party.
- I am working with an NGO. (Long-term action)
- I am going to Tokyo next week. (Planned future action)
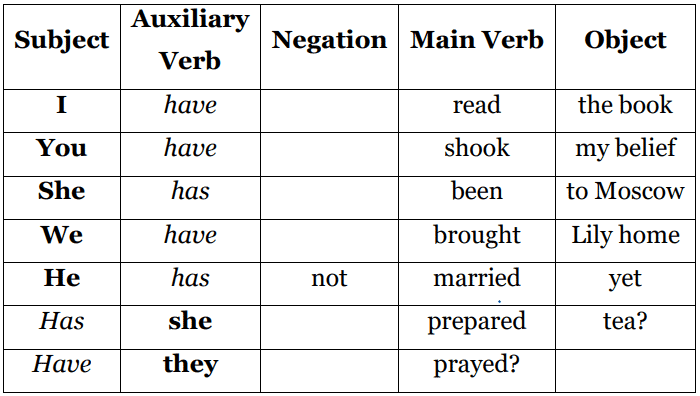
3. Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense connects past actions with the present. It is used for actions that started in the past and have just finished or still have relevance in the present.
Structure: Subject + has/have + Past Participle (V3) + Object
Examples:
- She has written a note.
- We have broken the protocol.
- I have seen the movie. (Referring to a past experience)
- She has worked as a freelance writer for 2 years. (Action started in the past and continues to the present)
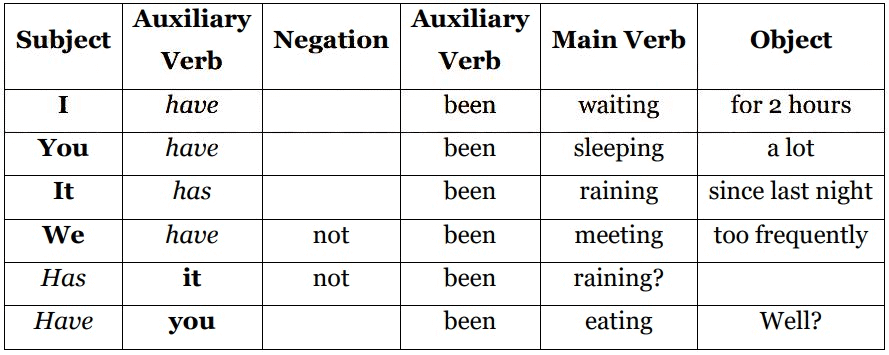
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous tense focuses on the duration of an action that began in the past and continues in the present. Time indicators like since or for are commonly used to specify the duration.
Structure: Subject + has/have + been + Verb (ing) + Object
Examples:
- Prem has been working as a business analyst for 10 years. (Action started in the past and continues)
- I have been going to the gym since last Saturday.
- I have been waiting for 2 hours. (Duration of the action)
Solved Questions
Question 1:
Which of the following sentences is an example of the Simple Present Tense?
A) I am playing football.
B) He plays football every Saturday.
C) I have played football.
D) She will play football tomorrow.
Answer:
B) He plays football every Saturday.Explanation:
The Simple Present Tense is used to describe habitual actions or general truths. The sentence "He plays football every Saturday" is a regular activity, making it an example of the Simple Present Tense.
Question 2:
What is the structure of the Present Continuous Tense?
A) Subject + has/have + past participle + Object
B) Subject + am/is/are + Verb (ing) + Object
C) Subject + Base verb + Object
D) Subject + will + base verb + Object
Answer:
B) Subject + am/is/are + Verb (ing) + ObjectExplanation:
The Present Continuous Tense is formed by combining the subject with "am," "is," or "are," followed by the verb in the -ing form and then the object.
Question 3:
Identify the correct use of the Present Perfect Tense:
A) She has writing a letter.
B) She has written a letter.
C) She wrote a letter.
D) She writes a letter.
Answer:
B) She has written a letter.Explanation:
The Present Perfect Tense is used to describe actions that started in the past and have relevance to the present. The correct form is "has/have + past participle," so "She has written a letter" is the correct sentence.
Question 4:
Which sentence uses the Present Perfect Continuous Tense?
A) I am working on a new project.
B) She has been working on this project since 9 AM.
C) He works in the office.
D) We have worked on this project.
Answer:
B) She has been working on this project since 9 AM.Explanation:
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used to emphasize the duration of an action that started in the past and continues into the present. The sentence "She has been working on this project since 9 AM" describes the ongoing action with the time duration.
Question 5:
Which sentence is an example of the Present Continuous Tense used to describe a planned future action?
A) I am going to Tokyo next week.
B) He goes to Tokyo every year.
C) They are studying for the exam now.
D) She has been traveling for two weeks.
Answer:
A) I am going to Tokyo next week.Explanation:
The Present Continuous Tense can also be used to describe planned future actions. The sentence "I am going to Tokyo next week" indicates a planned future event.
The present tense is vital for expressing current actions, habits, and general truths. It has four main types: Simple Present, Present Continuous, Present Perfect, and Present Perfect Continuous. Understanding the correct usage of these tenses will help you communicate effectively and improve your performance in competetive exams.
|
178 videos|787 docs|126 tests
|
FAQs on Present Tense - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What is the Present Tense in English grammar? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of Present Tense? |  |
| 3. How do I form the Simple Present Tense? |  |
| 4. When should I use the Present Continuous Tense? |  |
| 5. Can you provide an example of the Present Perfect Tense? |  |




















