Pressure | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Meaning of Force |

|
| What causes the force to arise? |

|
| Types of Forces |

|
| Types of Non-Contact Force |

|
| Units of force |

|
| Pressure |

|
| Atmospheric Pressure |

|
Meaning of Force

- Force is defined as a push or pull exerted on an object, which can be applied by both living and non-living entities.
- It results from the interaction between objects, changing the speed, direction, or shape of the object.
- Examples include picking, kicking, shutting, squeezing, pushing, and lifting.
- To move an object from one place to another, a net force must be exerted on it.
- Heavier objects require more force to move than lighter ones.
What causes the force to arise?
The force comes from the interaction between two objects.
- Force consists of gravity, friction, and the push or pull on an object to make it move. It can change the speed or direction of motion.
- An object is either moving or still due to forces. If it's still and stays still, the forces on it are in balance. To make it move, we need to add more force.
- When force is used, there are two objects involved: one giving the force and one receiving it.
- For instance, a soccer ball sitting on the ground is not moving. To set it in motion, you need to apply force to it. To move the ball, a player can kick it.
Force arises due to interaction
- A force occurs when objects interact. When you push or pull something, there is a connection between the object and what is causing the push or pull.
- For instance, when we kick a ball, we apply a force that makes it move. This force comes from the contact between the player's foot and the ball.
Effects of force
- A force can alter an object's size and shape. For instance, when we play with clay, we can modify its shape by exerting pressure with our hands. Similarly, a rubber band's shape changes when it is stretched.
- A force has the ability to affect the speed of a moving object. It can decelerate or completely halt the movement of an object. This is achieved by applying a force in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
- A force can set an object in motion even if it is stationary. For instance, a stationary trolley can be set in motion by applying force to it. Therefore, the movement of an object can be stopped by applying an appropriate force.
- A force can alter the direction of motion of a moving object. For example, kicking a football in a different direction can change its trajectory.
Note: Changing the mass of an object is not a consequence of force.
Types of Forces
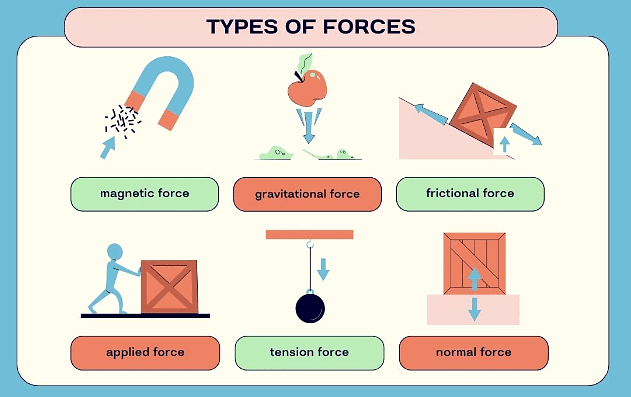
There are two types of forces:
Contact forces:
These forces occur when two objects are physically touching.
Muscular force:
- This force is generated by muscles.
- For instance, lifting objects or carrying heavy items requires muscular force.
- Animals also use muscular force.
Frictional force:
- This force slows down or stops objects and acts opposite to their motion.
- For example, a ball stops rolling due to friction between the ball and the ground.
Non-contact forces:
- These forces occur between objects not in physical contact.
Types of Non-Contact Force
Magnetic force
- Magnetic force is the pull a magnet has on another magnet or on iron.
- Since magnets have invisible magnetic fields, they can attract from a distance.
- For instance, separating iron from garbage using a magnet because of the attractive force between them.
Electrostatic force
- Electrostatic force is the push or pull that charged objects exert on each other.
- For example, lightning is caused by electric charges, which can attract or repel.
- It's why bits of paper are drawn to a comb that's been charged by rubbing it through hair.
Gravitational force
- Gravitational force is what pulls objects toward Earth, a force of attraction between bits of matter.
- For instance, an apple falling from a tree is due to gravitational force.
Magnitude Of Forces
- By term magnitude of forces, we refer to the total amount of all the forces acting on an object. It is the total of all the forces working on an object.
- When two forces push or pull in the same direction, the force's strength increases. It equals the combined strength of both forces.
- When two forces push or pull in opposite directions, the force's strength decreases. It is the difference between the magnitudes of the two forces.
How can we express the force?
- A force is described by its size and the way it points.
- The size of the force is a number.
- When we push something, the force goes away from us. When we pull something, the force moves towards us.
Units of force
- The SI unit of force is called Newton.
- The unit of force is named after the famous scientist Sir Isaac Newton.
- The unit of force can be described as the force required to make a 1kg object accelerate by 1 meter per second.
- The formula for force is F = m × a.
Pressure
- Pressure is a term that describes the force acting on a specific area of a surface. This quantity helps us understand the impact of force.
- Pressure can be illustrated as being directly related to force and inversely related to the area on which it acts.
- Essentially, when the area decreases, the pressure increases, and conversely, when the area increases, the pressure decreases.
Unit of pressure
- The SI unit of pressure is Pascal.
Applications of pressure in our daily life
Broad Straps of shoulder bags:
- The straps on shoulder bags are wider, which increases the surface area in contact and reduces pressure on the shoulders. When the area is broader, the pressure decreases, making it simpler to carry a shoulder bag with a wide strap.
- Elephants have broader feet, which expands the contact area with the ground, leading to reduced pressure and enabling elephants to walk more easily.
- It's easier to drive a sharp iron nail compared to a blunt one because the sharp nail has a smaller area, making it easier to drive it into a wall.
- Using skis helps in walking on snow by increasing the contact area between our feet and the snow, thereby reducing pressure on the snow.
- Peeling vegetables with a dull knife is difficult. Using a sharp knife with sharp edges makes peeling much easier as the smaller surface area of the sharp edge requires less force to cut or peel vegetables.
Pressure Exerted by liquids and Gases
- It is the force exerted by liquids or gases per unit area.
- Liquids and gases apply pressure in all directions.
- The pressure within them increases with depth.
Pressure Exerted By Liquids
- Liquids create pressure because of their weight.
- The pressure from liquids pushes downwards.
- The pressure at the bottom from liquids changes based on how tall the liquid is. The pressure increases as you go deeper.
- For instance, submarines have thick, strong bodies because water pressure is high in the deep sea. The thickness helps the submarine survive this pressure.
- Liquids also apply pressure in all directions on a container's walls.
- For example, if a container is pierced and then filled with water, the water will spurt out in every direction once the obstruction is removed.
- This demonstrates that liquids exert pressure uniformly.
Pressure Exerted by Gases
- Gases exert pressure on container walls like liquids do. Air pressure occurs because tiny gas molecules in the air constantly collide with the container walls.
- For instance, when air is pumped into a bicycle tube using a pump, the bicycle becomes inflated due to the air pressure caused by the collisions of gas molecules in the air with the inner walls of the rubber tube. This is why bicycle tires feel firm.
Atmospheric Pressure
- Atmosphere - The layer of air enveloping our planet is called the atmosphere.
- All fluids, including air, exert pressure known as atmospheric pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure is caused by the weight of the air above us, making air molecules more tightly packed closer to the Earth's surface.
- At sea level, the atmospheric pressure is at its highest.
- Atmospheric pressure acts in all directions and can be measured using a barometer.
- There are two main types of barometers: Mercury barometer and Aneroid barometer.
- The mercury barometer is preferred for measuring atmospheric pressure as it provides a standard unit.
- In a mercury barometer, the height of the mercury column in a glass tube changes with variations in atmospheric pressure.
|
528 videos|2108 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on Pressure - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the meaning of force in physics? |  |
| 2. What causes the force to arise in physics? |  |
| 3. What are the types of forces in physics? |  |
| 4. What are the types of non-contact forces in physics? |  |
| 5. What are the units of force in physics? |  |




















