Class 10 Civics Chapter 1 Previous Year Questions - Power Sharing
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Belgium solved its problem of majoritarianism by strengthening which of the following types of government? (1 Mark)
(a) Unitary
(b) Presidential
(c) Federal
(d) Parliamentary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Federal
Belgium solved its problem of majoritarianism by dividing powers between the central and state governments, creating a federal form of government. This arrangement prevented the domination of one linguistic group over another and maintained unity in the country.
Q2: "Power sharing is the very spirit of democracy." Support the statement by giving suitable arguments. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power sharing is the very spirit of democracy because:
- Involvement of People: In a democracy, people are the source of all political power. They have a right to be consulted on how they are to be governed.
- Legitimacy of Government: A legitimate government is one where citizens participate and acquire a stake in the system through power sharing.
- Respect for Diverse Views: It ensures that due respect is given to different groups and opinions in society, making governance more democratic.
Thus, power sharing upholds the essence of democracy by ensuring participation, consultation, and inclusiveness in decision-making.
Or
Why is power sharing essential for the success of democracy? Explain. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power sharing is essential for the success of democracy because it ensures fairness, equality, and stability in society.
- Prevents Concentration of Power: By dividing powers among different organs and levels of government, it avoids misuse of authority.
- Protects Interests of All Groups: Power sharing gives minorities and weaker sections a voice in governance, making them feel included.
- Maintains Unity and Harmony: When all groups share power, trust grows, conflicts reduce, and democracy becomes stronger.
Thus, power sharing makes democracy more inclusive, stable, and effective.
Q3: "Political power cannot be divided." Analyse suitable arguments against the statement. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The statement “Political power cannot be divided” is incorrect because in a democracy, power sharing is essential. Arguments against the statement are:
- Prevents Concentration of Power: Division of power among organs of government ensures that no single organ can exercise unlimited power.
- Promotes Checks and Balances: Power shared horizontally among legislature, executive, and judiciary maintains balance and accountability.
- Ensures Participation and Stability: Sharing power among different levels of government, social groups, and political parties promotes inclusion and prevents conflict.
Hence, division of power strengthens democracy and ensures the stability of the political system.
Q4: Which one of the following organisations has its headquarter in Brussels? (1 Marks)
(a) United Nations Organisation
(b) European Union
(c) Non-Alignment Movement
(d) South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) European Union
- Brussels, the capital of Belgium, was chosen as the headquarters of the European Union because Belgium’s model of power sharing successfully maintained unity and harmony among diverse communities.
Q5: Which of the following countries is an example of sharing of power between the national and state governments to account for internal diversity? (1 Mark)
(a) United States of America
(b) Australia
(c) Belgium
(d) Switzerland
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Belgium
Belgium shares power between the central government and state governments of the two major regions to accommodate linguistic and cultural diversity. This federal division of power helped prevent conflicts between Dutch-speaking and French-speaking communities.
Q6: "The government measures gradually increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils." Explain the statement. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Sri Lankan government took several steps that made the Tamil people feel left out and unfairly treated.
- In 1956, Sinhala was made the only official language, and Tamil was ignored.
- The government gave more jobs and educational opportunities to Sinhala-speaking people.
- The Constitution protected Buddhism, while Tamil culture and religion were not given equal importance.
Because of these actions, the Tamil people felt neglected and discriminated against, which increased their anger and separation from the government.
Q7: Which of the following group is in majority in Sri Lanka? (1 Mark)
(a) Tamil-speakers
(b) Sinhala-speakers
(c) Telugu-speakers
(d) English-speakers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Sinhala-speakers
In Sri Lanka, 74% of the population speaks Sinhala, making them the majority group, while 18% are Tamil-speakers.
Q8: Explain the effectiveness of vertical distribution of 'power sharing' in the context of India. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, vertical distribution of power means sharing power among different levels of government — the Central Government, State Governments, and local bodies like panchayats and municipalities.
This system is effective because:
- It allows governments at each level to make decisions for their own area, ensuring efficient administration.
- It gives people more participation in decision-making and helps address local needs better.
Thus, vertical power sharing in India makes democracy strong, balanced, and more responsive to the people.
Q9: "Sharing of power between the Union Government and the State Governments is basic to the structure of the Indian Constitution." Analyse the statement with suitable arguments. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, power is shared between the Union Government and the State Governments, and this is a very important part of our Constitution.
- The Constitution clearly divides powers between both levels of government. Some subjects like defence and foreign affairs are handled by the Union Government, while others like police and health are handled by State Governments.
- This system helps both governments to work independently and smoothly in their own areas without interfering with each other.
- It also allows people to take part in decision-making at different levels — national, state, and local — which makes democracy stronger.
Therefore, sharing of power between the Union and the States is basic to the Indian Constitution, as it ensures balance, cooperation, and better governance.
Q10: Explain the effectiveness of horizontal distribution of power in the context of India. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In India, horizontal distribution of power means sharing power among the three organs of government — the Legislature, Executive, and Judiciary.
This system is effective because:
- Each organ checks the other: It prevents any one organ from becoming too powerful. For example, the judiciary can review laws made by the legislature.
- Maintains balance and accountability: It ensures that power is used responsibly and within limits.
Thus, horizontal power sharing in India helps maintain a balance of power, protects democracy, and ensures fair governance.
Q11: How does the Indian Constitution ensure the division of powers between the Union and State Governments? Explain. (3 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Indian Constitution clearly divides powers between the Union Government and the State Governments to ensure smooth functioning and avoid conflicts.
- Three Lists: The Constitution provides a Union List, State List, and Concurrent List.
- The Union List includes subjects like defence and foreign affairs.
- The State List includes subjects like police and public health.
- The Concurrent List includes subjects like education and forests, where both can make laws.
- Clarity of Powers: This clear division helps both levels of government work independently and efficiently in their respective areas.
- Federal Structure: It maintains a federal balance and ensures that power is not concentrated at one level.
Thus, through these constitutional arrangements, India ensures a fair and effective division of power between the Union and the States.
Q12: How is the distribution of power among different social groups beneficial for democracy? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Distribution of power among different social groups helps democracy by making it more inclusive and fair.
- It ensures that minorities and weaker sections get a share in decision-making, so they don’t feel neglected.
- It helps in reducing social conflict and promotes harmony among different religious and linguistic groups.
Thus, sharing power among social groups makes democracy stronger, more equal, and more peaceful.
Q13: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (a): The French-speaking community was rich in comparison to the Dutch-speaking community in Belgium.
Reason (R): Dutch-speaking community got the benefit of economic development and education much later. (1Mark)
(a) Both (a) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (a).
(b) Both (a) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (a).
(c) (a) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
(d) (a) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both (a) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (a).
In Belgium, the French-speaking community was richer and more powerful, while the Dutch-speaking community received the benefits of economic development and education much later, which caused tensions between the two groups.
Q14: Which of the following is an example of horizontal power sharing in Indian democracy? (1 Mark)
(a) Division of power between Central and State Governments.
(b) Division of power between Rural and Urban Governments.
(c) Division of power among Administration, Judiciary, and Army.
(d) Division of power among Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Division of power among Legislative, Executive, and Judiciary.
Horizontal power sharing in India refers to the separation of powers among the three organs of government — the Legislature, Executive, and Judiciary — ensuring that each organ checks the others and prevents misuse of power.
Q15: Choose the correct option to fill the blank. (1 Mark)
The Belgian leaders took a different path than Sri Lanka. They recognised the existence of regional differences and ____________
(a) Religious diversities
(b) Historical diversities
(c) Cultural diversities
(d) Administrative diversities
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) Cultural diversities
- The Belgian leaders recognised regional and cultural diversities and amended their Constitution to ensure fair power sharing among Dutch, French, and German-speaking communities.
Q16: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (a): There was civil war in Sri Lanka.
Reason (R): An Act was passed in 1956 to secure dominance of Sinhala community on the government. (1 Mark)
(a) Both (a) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (a).
(b) Both (a) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (a).
(c) (a) is correct, but (R) is incorrect.
(d) (a) is incorrect, but (R) is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both (a) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (a).
In Sri Lanka, the Sinhala community passed an Act in 1956 making Sinhala the only official language, which led to discrimination against Tamils. This caused anger, distrust, and ultimately resulted in a civil war in the country.
Q17: Belgium took some measures to solve its problem. Read the following measures and choose the correct option:
I. Formation of community government.
II. Following majoritarian policy.
III. By providing equal representation of language groups.
IV. By providing additional powers to local governments. (1 Mark)
(a) Only I, II, and III are correct.
(b) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
(c) Only I, II, and IV are correct.
(d) Only II, III, and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
Belgium solved its problems by:
- forming a community government,
- giving equal representation to Dutch and French-speaking groups, and
- providing more powers to state and local governments.
It did not follow a majoritarian policy like Sri Lanka.
Q18: "The law enacted in 1956 and other Constitutional Provisions led to major conflict between the two communities in Sri Lanka." Support the statement. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
After gaining independence in 1948, Sri Lanka adopted several majoritarian measures that favoured the Sinhala-speaking majority and ignored the Tamil-speaking minority. These steps created deep conflict between the two communities.
Sinhala as the Only Official Language (1956):
The government passed an Act making Sinhala the only official language, completely ignoring Tamil. This made it difficult for Tamil people to get government jobs and access public services.Preferential Policies for Sinhalas:
The government gave preference to Sinhala applicants in universities and government employment, reducing opportunities for Tamils.Protection of Buddhism:
The Constitution gave Buddhism a special status, ignoring the equal rights of Tamils, who were mostly Hindus and Muslims.Denial of Political and Cultural Rights:
Tamil leaders demanded equal political rights, regional autonomy, and recognition of Tamil language, but these demands were repeatedly rejected.Rise of Conflict and Civil War:
As a result, Tamil groups started demanding an independent Tamil state (Tamil Eelam). The distrust and anger grew, leading to a civil war that caused great loss of life, property, and peace in Sri Lanka.
Thus, the 1956 law and other discriminatory policies created a sense of alienation and injustice among Tamils, resulting in a long-lasting ethnic conflict in Sri Lanka.
Q19: "Power sharing increases trust between different groups." Support the statement. (5 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power sharing is an important feature of democracy because it helps to build trust and cooperation among different social and cultural groups. It ensures that no group feels ignored or dominated by another.
Representation of All Groups:
Power sharing gives all social, linguistic, and religious groups a role in governance. When everyone participates in decision-making, it reduces feelings of neglect or inequality.Reduces Social Conflicts:
When power is shared fairly, it prevents anger and violence between communities. For example, Belgium avoided conflict between Dutch and French-speaking people by sharing power equally.Promotes Unity and Stability:
Power sharing helps maintain the unity of the country. People are more likely to support the government when they see their interests being respected.Encourages Cooperation:
It allows different groups to work together, promoting mutual respect and understanding among them.Strengthens Democracy:
When power is distributed and everyone has a voice, democracy becomes stronger and more stable. It prevents domination and builds trust and confidence among citizens.
Thus, power sharing increases trust between different groups by ensuring fairness, equality, and participation in governance, which helps maintain peace and unity in a democratic country.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Identify the primary objective of power-sharing arrangements in Belgium from the following options.(a) Establishing a unitary form of government.
(b) Centralized political control of government.
(c) Establishing cultural and educational matters of Dutch.
(d) Accommodating linguistic and regional interest. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The primary objective of power-sharing arrangements in Belgium was to accommodate the diverse linguistic and regional interests of the country's population, which includes Dutch-speaking, French-speaking, and a small German-speaking community. Belgium implemented a complex system of power sharing that allowed each linguistic group representation in the government to ensure peace and equality among communities, thus promoting social harmony and political stability.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Accommodating linguistic and regional interest.

Q2: Why is power sharing desirable? Explain. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power sharing is desirable because it helps in maintaining peace, stability, and fairness within a society. Here’s why:
- Prevents Conflict: Power sharing ensures that no single group dominates over others. This helps in reducing conflicts and tensions between different communities or groups, which might otherwise arise if one group holds too much power.
- Promotes Democracy: Power sharing is a key feature of a democratic system. It ensures that people from different backgrounds (such as ethnic, religious, or social groups) have a say in decision-making, making the system more inclusive.
- Encourages Cooperation: When power is shared, different groups are encouraged to cooperate and work together for the common good. This leads to more balanced and fair policies.
- Protects Minority Rights: Power sharing helps protect the rights of minority groups by ensuring that they have representation in government and decision-making processes, preventing their interests from being ignored.
- Ensures Political Stability: When different groups feel included in the governance process, it leads to greater political stability and reduces the chances of unrest or rebellion.
In summary, power sharing is desirable because it promotes fairness, reduces conflicts, supports democracy, and ensures that all groups have a voice in the political system.
Q3: Which of the following was the primary objective of Belgium to form the separate government in Brussels? (CBSE 2024)
(a) Promoting cultural events.
(b) Managing international relations.
(c) Enforcing local laws.
(d) Ensuring linguistic accommodation.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Ensuring Linguistic accommodation.
Belgium created a separate government in Brussels primarily to ensure linguistic accommodation between its two main communities: the Dutch-speaking Flemish and the French-speaking Walloons. Brussels, being a bilingual city, required a system that could manage the linguistic diversity in the region and ensure that both linguistic groups were fairly represented and their cultural needs met. This system of accommodation helped in reducing tensions between the Flemish and Walloon communities.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q4: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:Assertion (A): Sri Lanka adopted 'Tamil' as the official language of the State.
Reason (R): The Government of Sri Lanka adopted a series of majoritarian measures. (2023)
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Assertion (A): This is false. Sri Lanka adopted Sinhala, not Tamil, as the sole official language of the state in 1956, through the Sinhala Only Act. This led to discontent among the Tamil-speaking minority.
Reason (R): This is true. The Government of Sri Lanka did adopt a series of majoritarian measures, such as making Sinhala the official language and prioritizing Sinhala speakers in state employment and education, which marginalized the Tamil community.
Q5: Consider the following statements on Power Sharing and choose the correct option.
I. It deepens democracy.
II. It helps to reduce conflicts among social groups.
III. It is a way to ensure political stability.
IV. It brings socio-economic struggles. (2023)
(a) I, II and III
(b) III, Ill and IV
(c) I, III and IV
(d) I, II and IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
I. It deepens democracy: Power sharing allows various groups to participate in governance, making the political system more inclusive and democratic.
II. It helps to reduce conflicts among social groups: By giving different social groups a stake in political power, it reduces the chances of conflict, as everyone feels represented.
III. It is a way to ensure political stability: When power is shared among various groups, it promotes stability because it prevents any one group from dominating and causing unrest.
IV. This statement is incorrect: Power sharing aims to address socio-economic struggles rather than create them.
Q6: Consider the following statements on Power Sharing and choose the correct option :
(I) Majoritarianism is the real spirit of democracy.
(II) It creates balance and harmony in different groups.
(III) It reduces the possibility of conflict among social groups.
(IV) Power sharing is the essence of democracy. (2023)
(a) I, II and III
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, III and IV
(d) I, II and IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
II. It creates balance and harmony in different groups: Power sharing helps ensure that different social groups can coexist peacefully by allowing them to have a voice in governance.
III. It reduces the possibility of conflict among social groups: By sharing power, it addresses the concerns of various groups, which helps prevent tensions and conflicts from escalating.
IV. Power sharing is the essence of democracy: In a democracy, it is crucial for different groups to have representation and influence in decision-making processes.
I is incorrect because majoritarianism, which favors the majority, can undermine the rights and voices of minority groups, thus not reflecting the true spirit of democracy.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q7: Which one of the following elements is NOT included in the Belgium model? (Term-1,2021-22)(a) Dutch and French speaking ministers shall be equal in the government.
(b) Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments.
(c) Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation.
(d) There is a community government which has special powers of administration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
There is a community government in Belgium, but it does not have "special powers of administration" in the way implied. Instead, it is responsible for cultural, educational, and language-related matters, ensuring that the needs of each linguistic community are respected. Hence, this option is not accurate in describing the Belgium model.
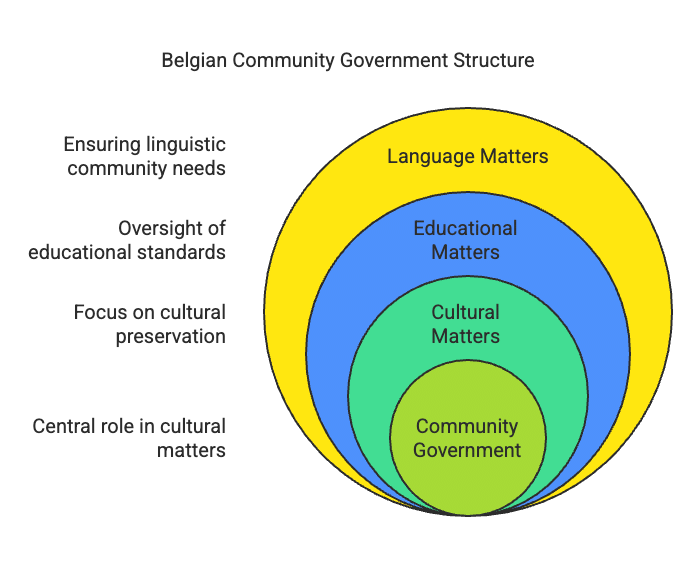
Q8: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the most appropriate option.
Assertion (A): Majority community is dominant in a few democratic states.
Reason (R): Dominance can undermine the unity of the country. (Term-1, 2021-22)
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation of the A.
(b) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of the A.
(c) A is correct, but R is incorrect.
(d) A is incorrect, but R is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Assertion (A): This is true. In some democratic states, the majority community can dominate decision-making, which may marginalise minority groups.
Reason (R): This is true. When the majority excludes or sidelines minorities, it can lead to dissatisfaction and conflict, threatening the country's unity and stability.
Q9: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the most appropriate option.
Assertion (A): The distrust between Sinhalese and Tamil communities turned into widespread conflict in Sri Lanka
Reason (R): 1956 Act recognised Sinhala as the only official language. (Term-1, 2021-22)
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation of the A.
(b) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of the A.
(c) A is correct, but R is incorrect.
(d) A is incorrect, but R is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Assertion (A): This is true. The distrust between the Sinhalese and Tamil communities in Sri Lanka escalated into widespread conflict, culminating in a brutal civil war.
Reason (R): This is true. The 1956 Act, which made Sinhala the sole official language, was one of the key majoritarian measures taken by the Sinhalese-dominated government. This decision marginalized the Tamil community and fueled their resentment, leading to tensions and eventually violent conflict.
Q10: Two statements are given below as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the most appropriate option.
Assertion (A): Power-sharing is good.
Reason (R): It helps to reduce the possibility of conflicts between social groups. (Term-1, 2021-22)
(a) Both A and R are correct, and R is the correct explanation of the A.
(b) Both A and R are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of the A.
(c) A is correct, but R is incorrect.
(d) A is incorrect, but R is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Assertion (A): This is true. Power-sharing is considered beneficial as it promotes inclusivity and ensures that all groups in society have a voice in governance.
Reason (R): This is true. Power-sharing reduces the likelihood of conflict by addressing the grievances of different social groups, thereby fostering harmony and stability.
Q11: What is NOT an integral part of the government? (Term-1, 2021-22)
(a) Office of the Prime Minister
(b) Legislature
(c) Executive
(d) Judiciary
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
While the Office of the Prime Minister is an important position in the government, it is not a separate branch or integral part of the government structure itself. The three main integral parts of the government are the Legislature (which makes laws), the Executive (which enforces laws), and the Judiciary (which interprets laws). The Prime Minister operates within the executive branch but does not represent a distinct part of the government like the others.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q12: 59 percent of the total population of Belgium live in the ______ region. (2021 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 59 percent of the total population of Belgium live in the Flemish region.
Q13: How did the Belgium government accommodate the social differences? (2021 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Belgian government has implemented a unique model to accommodate its social differences:
- Equal representation: Both Dutch and French-speaking populations have equal representation in the central government.
- Federal structure: Belgium is a Federal state, granting significant powers to state governments.
- Independent state governments: State governments operate independently and are not subordinate to the central government.
- Community government: There is a separate government for each language community, handling cultural and educational matters.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q14: Which one of the following is a major religious group of Sri Lanka? (2020)(a) Christian and Tamil
(b) Buddhist and Hindu
(c) Sinhali and Tamil
(d) Sinhali and Christian
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In Sri Lanka, the major religious groups are primarily linked to the two main religions: Buddhism and Hinduism. The question asks for a major religious group in Sri Lanka. While "Sinhali and Tamil" represent the two primary ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, they are not religious groups. "Christian and Tamil" is also incorrect as Tamil is an ethnic group, not a religion. Buddhism and Hinduism are the major religions practiced in Sri Lanka. The Sinhala people, who mostly practice Buddhism, form a significant part of the population, while the Tamil community, which includes many Hindus, is also a major group. Thus, Buddhism and Hinduism represent the prominent cultural and religious identities among the different caste groups in the country.
 Q15: Under which of the following is power shared in the 'Community Government’ of Belgium? (2020)
Q15: Under which of the following is power shared in the 'Community Government’ of Belgium? (2020)
(a) Different social groups
(b) Different organs of government
(c) Central and State government
(d) State government and Community government
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In Belgium, the Community Government is designed to represent and share power among different social groups, such as linguistic communities (like the Flemish and French speakers). This system ensures that the diverse interests and identities within the country are recognized and that each group has a say in governance, promoting unity and reducing conflict among them.
Q16: State any one step taken in Belgium to rule out the problem of regional differences and cultural diversities. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Equal representation in the central government is a key step taken in Belgium to address regional differences and cultural diversities.
The following measures have been implemented:
- The constitution mandates that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers in the central government is equal.
- Special laws require support from a majority of members from each linguistic group for certain decisions.
- State governments have been granted significant powers, operating independently of the central government.
- Brussels has a separate government that ensures equal representation for both communities.
Q17: The Belgium model of ‘Community government’ worked well because_______ (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Belgium model of 'Community government' worked well because it recognized the belonging of individuals to one language community.
This approach has several advantages:
- It promotes cultural identity by acknowledging the distinct languages spoken.
- It allows for tailored governance that addresses the unique needs of each community.
- It helps to maintain social harmony and prevent conflicts between different linguistic groups.
Overall, this model has contributed to a stable and inclusive political environment in Belgium.
Q18: Describe the horizontal power-sharing arrangements. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Horizontal power-sharing involves the distribution of power among various branches of government.
The key features are:
- Power is shared among different organs of government, including the legislature, executive, and judiciary.
- Each organ exercises distinct powers, ensuring that no single organ can dominate.
Q19: Why is there a need to give space to diverse social groups in the administration of a democratic country? Give any one reason. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It is necessary to give space to diverse social groups in the administration of a country to avoid majoritarianism, accumulation of power in the hands of a particular social group which would lead to social conflicts.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q20: Why was there an acute problem in Brussels during 1950s and 1960s between the two communities? (2019 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: During the 1950s and 1960s, tensions arose in Brussels between the two main communities in Belgium due to several factors:
- The French-speaking community was a minority but was relatively wealthy and influential.
- The Dutch-speaking community felt resentment as they had access to economic development and education much later.
- Brussels posed a unique challenge: While the Dutch-speaking people were the majority in the country, they were a minority in the capital.
Q21: Explain the major repercussions of passing Sinhala as the only official language in Sri Lanka in 1956. (2019 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The major repercussion of passing Sinhala as the only official language in Sri Lanka in 1956 was the increase in the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils. This led to the launch of parties and struggles for the recognition of Tamil as an official language.
Q22: Explain any one benefit of 'Power-Sharing'. (AI2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power-sharing helps to reduce the possibility of conflicts between different social groups. A social conflict often leads to violence and political instability. Power sharing helps to ensure the stability of political order.
Q23: How did the idea of power-sharing emerge? Explain different forms that have common arrangements of power-sharing. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The idea of power-sharing has emerged contrary to the notions of undivided political power. Earlier, it was believed that all powers of a government must reside in one person or group located in one place. It was felt that if the power to decide was dispersed, it would not be possible to make quick decisions and enforce them. However, these notions have changed with the emergence of democracy.
Different forms that have common arrangements of Power Sharing:
- Horizontal power-sharing: This involves distributing power among different branches of government, such as the legislature, executive, and judiciary. Each branch checks the others, preventing any one branch from having unlimited power and ensuring a balance among institutions.
- Vertical power-sharing: This refers to the division of power between different levels of government, such as the central government and state governments. In India, the constitution defines the powers of each level, ensuring clarity in governance.
- Empowering social groups: Power can also be shared among various social groups, including religious and linguistic minorities. An example of this is the system of reserved constituencies in assemblies and Parliament, which aims to give minority communities a fair representation.
- Political parties and pressure groups: Power-sharing is evident in how political parties, pressure groups, and social movements influence those in power. This competition helps prevent power from being concentrated in a single entity, allowing for diverse representation of ideologies and social interests.
Q24: Explain with examples the accommodative experience of Belgium for peace and harmony. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The accommodative experience of Belgium for peace and harmony:
(1) Dutch and French speaking ministers got equal say and powers in the central government.
(2) Many Powers of the central government have been transferred to state government.
(3) The State government is no longer subordinate to the Central government. This helped in delegation of duties.
(4) Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation.
(5) There is a third kind of government called community government elected by the people belonging to Dutch, French and German communities no matter where they live.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q25: Explain the three measures taken by Sri Lanka, as per the Act passed in 1956. (2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The three measures taken by Sri Lanka under the Act passed in 1956 are:
- The government declared Sinhala as the only official language, ignoring Tamil.
- Preferential policies were implemented, favouring Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
- A new Constitution mandated that the state would protect and promote Buddhism.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q26: How and when was Sinhala recognized as the official language of Sri Lanka? (2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Sinhala was officially recognised as the only language of Sri Lanka through an Act passed in 1956.
- This decision established Sinhala as the sole official language.
- It disregarded the Tamil language, leading to significant political and social implications.
- Subsequent government policies favoured Sinhala speakers in education and employment.
Q27: What is the prudential reason behind power-sharing? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The prudential reason for power-sharing is to avoid the concentration of power in one individual or group.
This is important because:
- It helps prevent authoritarianism, where one party has unchecked control.
- It reduces the risk of oppression of minority groups.
- Power-sharing promotes political stability and peace.
Q28: What does 'the system of checks and balances' ensure in power-sharing? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The system of checks and balances ensures that:
- No single individual or institution can hold unlimited power.
- It prevents the abuse of power by distributing authority.
- It protects the rights and interests of various groups within society.
Q29: Mention any one characteristic of power-sharing. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: One characteristic of power-sharing is the sharing of power between different levels of government or between different communities or groups within a society.
Q30: How is the ethnic composition of Belgium very complex? Explain. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The ethnic composition of Belgium is complex for several reasons:
- Approximately 59% of the population resides in the Flemish region and speaks Dutch.
- About 40% live in the Wallonia region and communicate in French.
- Only 1% of Belgians speak German.
- In Brussels, 80% of the population speaks French, while 20% speak Dutch.
Q31: How did Sri Lanka and the Belgium government try to solve the ethnic problem? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Sri Lanka and the Belgium government tried to solve the ethnic problem in different ways:
(i) The Belgium government respected the feelings and interests of different communities and regions, establishing a federal structure and power-sharing between the Union Government and its constituent units.
(ii) Sri Lanka adopted majoritarianism, passing an Act in 1956 to recognize Sinhala as the only official language, favoring Sinhala applicants for positions, and protecting and fostering Buddhism through the Constitution.
Q32: "Attempts at forced integration often sow the seeds of disintegration". Support the statement with suitable arguments. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Forced integration can lead to disintegration due to the following reasons:
- Integration through force can create feelings of resentment and conflict among different regions or communities.
- Sharing power and resources often raises fears of domination by one group over another.
- People prefer to maintain their autonomy rather than being overshadowed by others.
- Historical examples, such as the breakup of the USSR, illustrate the negative effects of forced integration.
Q33: "Sharing of powers makes a country more powerful and united." Do you agree with this statement and why? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Yes, I agree with the statement that the sharing of powers makes a country more powerful and united. This is because:
(i) Power-sharing ensures that no single community or group dominates the decision-making process, promoting inclusivity and fairness.
(ii) It allows for the representation of diverse interests and perspectives, leading to better policies and governance.
(iii) Power-sharing can prevent the marginalization of certain communities or regions, reducing conflicts and promoting social cohesion.
(iv) By distributing power, it strengthens the democratic principles of participation, accountability, and checks and balances.
Q34: Why is power-sharing necessary in democracy? Explain. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power-sharing is necessary in democracy for several reasons:
- Conflict Reduction: It helps to minimise conflicts between different social groups.
- Political Stability: Power-sharing promotes a stable political environment, reducing the risk of violence and instability.
- Unity Preservation: Imposing the will of the majority can seem appealing but ultimately harms national unity.
- Majority Tyranny: The oppression of minorities can lead to negative consequences for the majority as well.
- Democratic Spirit: True democracy involves sharing power with those affected by its exercise, ensuring that citizens have a say in governance.
- Legitimacy: A legitimate government is one where citizens participate and have a stake in the system.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q35: Which factor is responsible for increasing the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamil? (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The majoritarianism policy in Sri Lanka has significantly increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils.
Key points include:
- The policy favoured the Sinhalese community, leading to feelings of exclusion.
- It resulted in discrimination in political rights and job opportunities for Tamils.
- Government actions ignored the interests of the Tamil population.
Q36: Which type of powers does the community government of Belgium enjoy? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The community government of Belgium enjoys cultural and educational powers, as well as issues related to language.
Q37: State any two measures adopted by Sri Lanka in 1956 as part of their majoritarian policy. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two measures adopted by Sri Lanka in 1956 as part of their majoritarian policy were:
(i) They declared Sinhala as an official language.
(ii) They tried to promote their religion, Buddhism.
Q38: What system of power-sharing is called "Checks and Balances"? (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The system of power-sharing called "Checks and Balances" refers to the distribution of powers among different institutions of government, where each institution has the ability to check the actions of the others to ensure a balance of power.
Q39: Give reasons why power-sharing is desirable. (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Power-sharing is desirable for several reasons:
- Prevents domination: It stops one community from overpowering others, promoting equality.
- Encourages inclusivity: It accommodates diverse interests and identities, fostering social harmony.
- Reduces conflict: It lowers the chances of tensions and disputes between communities.
- Strengthens democracy: It ensures participation, accountability, and checks in decision-making.
- Improves governance: It allows better representation and responsiveness to citizens' needs.
Q40: What is a Homogenous Society? (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: It is a society which shares a common language, ethnicity and culture. For example, Japan and South Korea.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q41: Who formed the majority in terms of population in Sri Lanka? (2014) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The majority of the population in Sri Lanka is formed by the Sinhala community.
Q42: What is the state religion of Sri Lanka? (2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The state religion of Sri Lanka is Buddhism.
Q43: In which city is the headquarters of the European Union located? (2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The headquarters of the European Union is located in Brussels.
|
88 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Civics Chapter 1 Previous Year Questions - Power Sharing
| 1. What is power-sharing and why is it important in a democracy? |  |
| 2. What are the different forms of power-sharing in a democratic setup? |  |
| 3. How does power-sharing contribute to the stability of a nation? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of countries where power-sharing has been implemented? |  |
| 5. What challenges can arise from power-sharing arrangements? |  |

















