Q11: The flux linkage (λ) and current (i) relation for an electromagnetic system is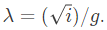 When i = 2A and g (air-gap length) = 10cm, the magnitude of mechanical force on the moving part, in N, is ________. (SET-2 (2016))
When i = 2A and g (air-gap length) = 10cm, the magnitude of mechanical force on the moving part, in N, is ________. (SET-2 (2016))
(a) 128.52
(b) 165.65
(c) 188.56
(d) 214.25
Ans: (c)
Sol: Energy in magnetic system,
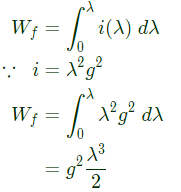 Now, mechanical force,
Now, mechanical force,
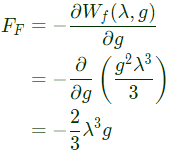
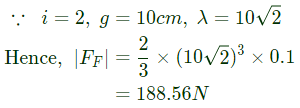
Q12: The direction of rotation of a single-phase capacitor run induction motor is reversed by (SET-2 (2016))
(a) interchanging the terminals of the AC supply
(b) interchanging the terminals of the capacitor
(c) interchanging the terminals of the auxiliary winding
(d) interchanging the terminals of both the windings
Ans: (c)
Sol: Inter changing the terminals of the auxiliary winding.
Q13: A 220 V, 3-phase, 4-pole, 50 Hz inductor motor of wound rotor type is supplied at rated voltage and frequency. The stator resistance, magnetizing reactance, and core loss are negligible. The maximum torque produced by the rotor is 225 % of full load torque and it occurs at 15% slip. The actual rotor resistance is 0.03 Ω/phase. The value of external resistance (in Ohm) which must be inserted in a rotor phase if the maximum torque is to occur at start is ______. (SET-2 (2015))
(a) 0
(b) 0.18
(c) 0.24
(d) 0.28
Ans: (b)
Q14: A 200 V, 50 Hz, single-phase induction motor has the following connection diagram and winding orientations as shown. MM' is the axis of the main stator winding(M1M2) and AA' is that of the auxiliary winding(A1A2). Directions of the winding axis indicate direction of flux when currents in the windings are in the directions shown. Parameters of each winding are indicated. When switch S is closed, the motor (2009)
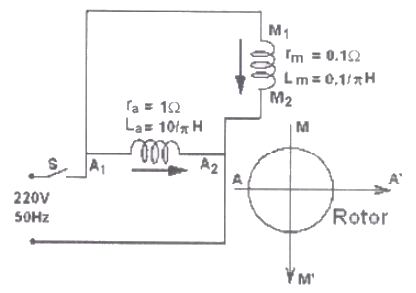 (a) rotates clockwise
(a) rotates clockwise
(b) rotates anti-clockwise
(c) does not rotate
(d) rotates momentarily and comes to a halt
Ans: (b)
Sol: f = 50Hz
Impedance of main winding
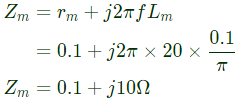 Impedance of auxiliary winding,
Impedance of auxiliary winding,
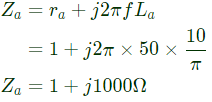 Current through main winding,
Current through main winding,
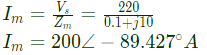 Current through auxiliary winding
Current through auxiliary winding
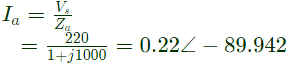 Thaing Vs as the reference
Thaing Vs as the reference
 Im leads Ia the field crreated by the two current also have same difference thereby constituting an unbalanced field system, The result is the production of the starting torque.
Im leads Ia the field crreated by the two current also have same difference thereby constituting an unbalanced field system, The result is the production of the starting torque.
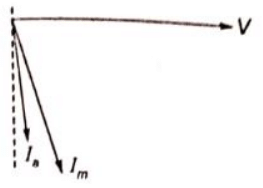
Space orientation of the field
 The motor rotates in the direction of leading phase to lagging phase.In this case, the motor rotates anti-clockwise.
The motor rotates in the direction of leading phase to lagging phase.In this case, the motor rotates anti-clockwise.
Q15: A 230 V, 50 Hz, 4-pole, single-phase induction motor is rotating in the clockwise (forward) direction at a speed of 1425 rpm. If the rotor resistance at standstill is 7.8 Ω, then the effective rotor resistance in the backward branch of the equivalent circuit will be (2008)
(a) 2Ω
(b) 4Ω
(c) 78Ω
(d) 156Ω
Ans: (a)
Sol: Rotor resistance at stand still, R = 7.8Ω
Synchronous speed,
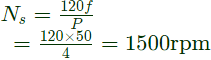 The slip(s) of rotor with respect to forward field
The slip(s) of rotor with respect to forward field
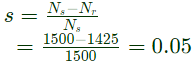 The slip of rotor with respect to backward field
The slip of rotor with respect to backward field
= 2 − s = 2 − 0.05 = 1.95
Effective rotor resistance
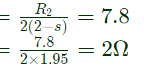
Q16: In a stepper motor, the detent torque means (2008)
(a) minimum of the static torque with the phase winding excited
(b) maximum of the static torque with the phase winding excited
(c) minimum of the static torque with the phase winding unexcited
(d) maximum of the static torque with the phase winding unexcited
Ans: (d)
Sol: Detent torque: It is amount of torque that the motor produces when it is not energized. No current is flowing through the windings.
Q17: A three-phase, three-stack, variable reluctance step motor has 20 poles on each rotor and stator stack. The step angle of this step motor is (2007)
(a) 3°
(b) 6°
(c) 9°
(d) 18°
Ans: (b)
Sol: No. of teeth = No. of poles = 20
Step angle,
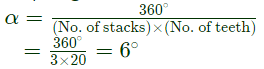
Q18: For a single phase capacitor start induction motor, which of the following statements is valid ? (2006)
(a) The capacitor is used for power factor improvement
(b) The direction of rotation can be changed by reversing the main winding terminals
(c) The direction of rotation cannot be changed
(d) The direction of rotation can be changed by interchanging the supply terminals
Ans: (b)
Sol: 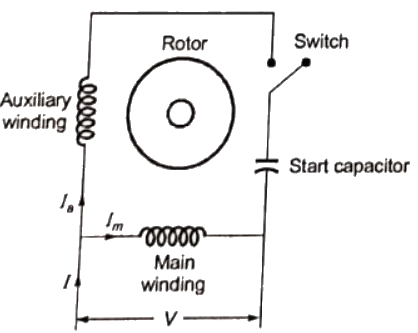 Start capacitor is used to provide 90° phase difference between Im and Ia.
Start capacitor is used to provide 90° phase difference between Im and Ia.
If supply terminals are interchanged, Ia and Im will flow in the opposite direction. So, toque will act in the smae direction. Therefore, the direction of rotation will remainsame.
Q19: In a single phase induction motor driving a fan load, the reason for having a high resistance rotor is to achieve (2005)
(a) low starting torque
(b) quick acceleration
(c) high efficiency
(d) reduced size
Ans: (b)
Sol: In 1 − ϕ induction motor, total torque developed is given by
Ttotal = Tf − Tb
where,
Tf = Torque developed due ot forward field.
Tb = Torque developed due to backward field
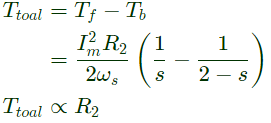 Higher is the rotor resistance (R2), more is the total torque developed (Ttotal) which results in quick acceleration.
Higher is the rotor resistance (R2), more is the total torque developed (Ttotal) which results in quick acceleration.
Q20: For a 1.8°, 2-phase bipolar stepper motor, the stepping rate is 100 steps/second. The rotational speed of the motor in rpm is (2004)
(a) 15
(b) 30
(c) 60
(d) 90
Ans: (b)
Sol: Stepping rate is 100 steps/sec.
Step required for one revolution = 360°/1.8 = 200 steps.
Therefore, time required for one revolution = 2 seconds
rev/sec = 0.5 rps
rev/minute = 30rpm
Q21: A single-phase, 230 V, 50 Hz, 4-pole, capacitor-start induction motor had the following stand-still impedances.
Main winding Zm = 6.0 + j4.0Ω
Auxiliary winding Za = 8.0 + j6.0Ω
The value of the starting capacitor required to produce 90° phase difference between the currents in the main and auxiliary windings will be (2004)
(a) 176.84 μF
(b) 187.24 μF
(c) 256.26 μF
(d) 280.86 μF
Ans: (a)
Sol: 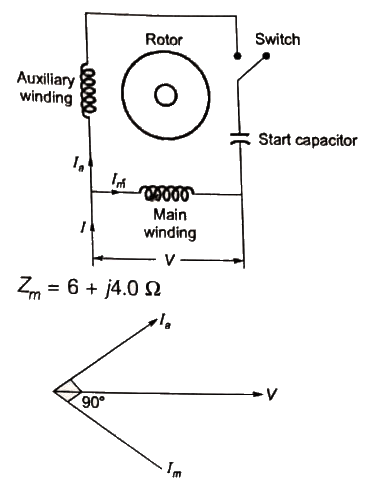 Supply voltage V is taken as reference.
Supply voltage V is taken as reference.
Current in main winding
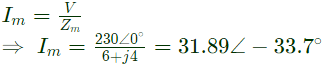 Staring capacitor (C) wil be connected in series with the auxilary winding, so modified auxiliary winding impedance.
Staring capacitor (C) wil be connected in series with the auxilary winding, so modified auxiliary winding impedance.
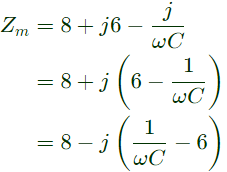 Current in auxiliary winding,
Current in auxiliary winding,
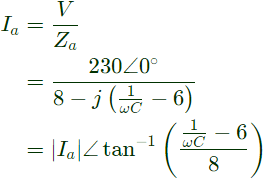 Capacitor is provided to make angle between Ia and Im90°.
Capacitor is provided to make angle between Ia and Im90°.
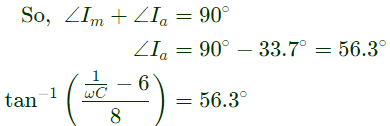
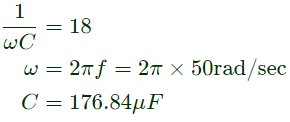
Q22: A rotating electrical machine having its self-inductances of both the stator and the rotor windings, independent of the rotor position will be definitely not develop (2004)
(a) starting torque
(b) synchronizing torque
(c) hysteresis torque
(d) reluctance torque
Ans: (d)
Sol: 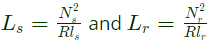 where,
where,
Ls and Lr are self inductances of stator and rotor. Ns and Nr are no. of turns energized in stator and rotor.
Rls = Reluctance seen by the stator flux.
Rlr = Reluctance seen by the rotor flux.
As Ls and Lr are independent of the rotor position, the reluctances Rls and Rlr does not vary with the rotor movement. Therefore, reluctance torque terms.
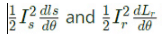 become zero.
become zero.
Q23: For a linear electromagnetic circuit, the following statement is true (2004)
(a) Field energy is equal to the co-energy
(b) Field energy is greater than the co-energy
(c) Field energy is lesser than the co-energy
(d) Co-energy is zero
Ans: (a)
Sol: 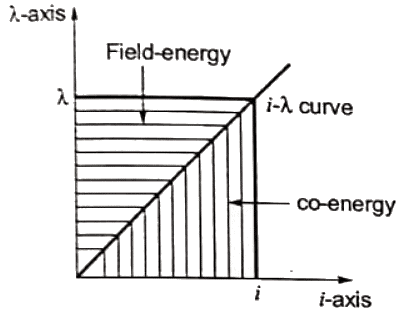 Where, λ = Nϕ = Flux linkage
Where, λ = Nϕ = Flux linkage
Field energy is the energy absorbed by the magnetic system to establish flux ϕ.
For a linear electromagnetic circuit
Field energy = Co-energy = (1/2) λi
Q24: The type of single-phase induction motor having the highest power factor at full load is (2004)
(a) shaded pole type
(b) split-phase type
(c) capacitor-start type
(d) capacitor-run type
Ans: (d)
Sol: Capacitor start type motor has high staring torque and therefore is used for hard starting loads such as compressor, conveyors, pumps etc.
Capacitor-run type motor has better running power factor and efficiency and a quiter and smoother operation. It is used for both easy and hard to start loads. Moder applications of such motors are ceiling fans, blower etc.
Q25: The following motor definitely has a permanent magnet rotor (2004)
(a) DC commutator motor
(b) Brushless dc motor
(c) Stepper motor
(d) Reluctance motor
Ans: (b)
Sol: Brushless dc motor definitely has a permanent magnet.
Q26: For a given stepper motor, the following torque has the highest numerical value (2004)
(a) Detent torque
(b) Pull-in torque
(c) Pull-out torque
(d) Holding torque
Ans: (c)
Sol: Detent torque: It is amount of torque that the motor produces when it is not energized. No current is slowing through the winding.
Holding Torque: It is amount of torque that the motor produces when it has rated current flowing through the winding but motor is at rest..
Pull-in Torque: Shows the maximum value of torque at given speeds that the motor can start, stop, or reverse in synchronism with the input pulses.
Pull-out Torque: Shows the maximum value of torque at given speeds that the motor can generate while running in synchronism. If the motor is run outside of this curve, it will stall.
Q27: A single-phase induction motor with only the main winding excited would exhibit the following response at synchronous speed (2003)
(a) Rotor current is zero
(b) Rotor current is non-zero and is at slip frequency
(c) Forward and backward rotaling fields are equal
(d) Forward rotating field is more than the backward rotating field
Ans: (d)
Sol: A 1−ϕ induction motor with only the main winding excited would have forward rotating field is more than the backward rotating field at synchronous speed.
Q28: Group-I lists different applications and Group-II lists the motors for these applications. Match the application with the most suitable motor and choose the right combination among the choices given thereafter (2003)
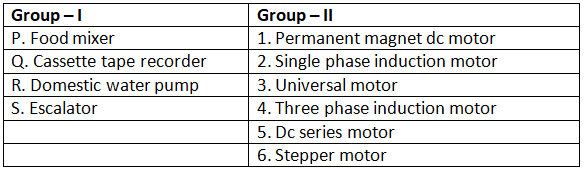
(a) P-3 Q-6 R-4 S-5
(b) P-1 Q-3 R-2 S-4
(c) P-3 Q-1 R-2 S-4
(d) P-3 Q-2 R-1 S-4
Ans: (c)
Sol: Universal motors are used where light weight is important., as in vacuum cleaners and portable tools e.g. food mixer which usually operate at high speed (1500-15000 rpm). Domestic water pump are usually of low rating. So single phase induction motor can be used for such application. Three phase induction motor is suitable for escalator as it has high starting torque.
Q29: The hysteresis loop of a magnetic material has an area of 5 cm2 with the scales given as 1 cm = 2 AT and 1 cm = 50 mWb. At 50 Hz, the total hysteresis loss is (2001)
(a) 15 W
(b) 20 W
(c) 25 W
(d) 50 W
Ans: (c)
Sol: The area under the hysteresis wave is ameans to measure the hysteresis loss per cycle.
Area under the curve
= 5 cm2
= 5 x (2AT x 50mWb)
= 500 mW
For a cycle of 50 Hz,
Loss = 500mW × 50Hz = 25W
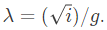 When i = 2A and g (air-gap length) = 10cm, the magnitude of mechanical force on the moving part, in N, is ________. (SET-2 (2016))
When i = 2A and g (air-gap length) = 10cm, the magnitude of mechanical force on the moving part, in N, is ________. (SET-2 (2016))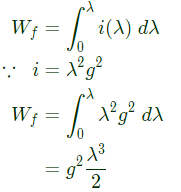 Now, mechanical force,
Now, mechanical force,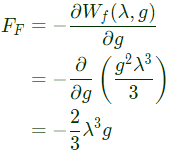
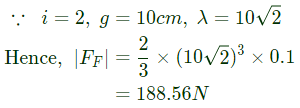
 (a) rotates clockwise
(a) rotates clockwise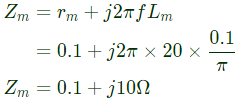 Impedance of auxiliary winding,
Impedance of auxiliary winding,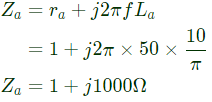 Current through main winding,
Current through main winding,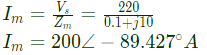 Current through auxiliary winding
Current through auxiliary winding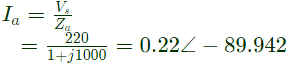 Thaing Vs as the reference
Thaing Vs as the reference Im leads Ia the field crreated by the two current also have same difference thereby constituting an unbalanced field system, The result is the production of the starting torque.
Im leads Ia the field crreated by the two current also have same difference thereby constituting an unbalanced field system, The result is the production of the starting torque. The motor rotates in the direction of leading phase to lagging phase.In this case, the motor rotates anti-clockwise.
The motor rotates in the direction of leading phase to lagging phase.In this case, the motor rotates anti-clockwise.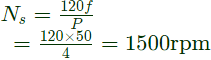 The slip(s) of rotor with respect to forward field
The slip(s) of rotor with respect to forward field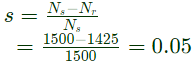 The slip of rotor with respect to backward field
The slip of rotor with respect to backward field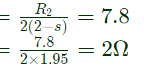
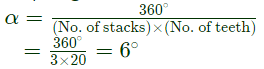
 Start capacitor is used to provide 90° phase difference between Im and Ia.
Start capacitor is used to provide 90° phase difference between Im and Ia.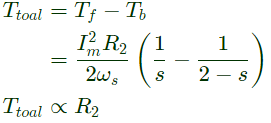 Higher is the rotor resistance (R2), more is the total torque developed (Ttotal) which results in quick acceleration.
Higher is the rotor resistance (R2), more is the total torque developed (Ttotal) which results in quick acceleration. Supply voltage V is taken as reference.
Supply voltage V is taken as reference.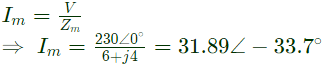 Staring capacitor (C) wil be connected in series with the auxilary winding, so modified auxiliary winding impedance.
Staring capacitor (C) wil be connected in series with the auxilary winding, so modified auxiliary winding impedance.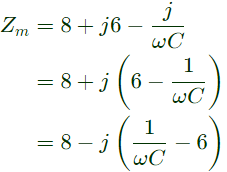 Current in auxiliary winding,
Current in auxiliary winding,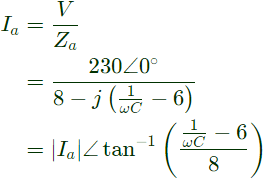 Capacitor is provided to make angle between Ia and Im90°.
Capacitor is provided to make angle between Ia and Im90°.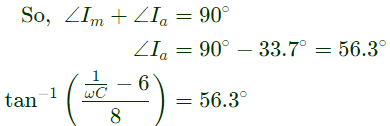
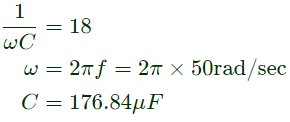
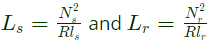 where,
where,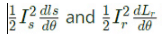 become zero.
become zero. Where, λ = Nϕ = Flux linkage
Where, λ = Nϕ = Flux linkage





















