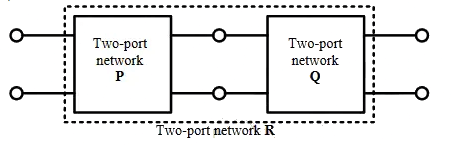
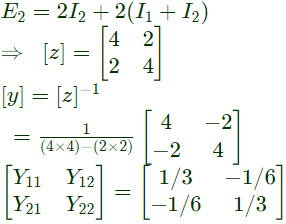Q1: Two passive two-port network P and Q are connected as shown in the figure. The impedance matrix of network P is 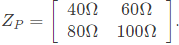 The admittance matrix of network
The admittance matrix of network 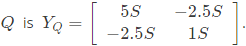 Let the ABCD matrix of the two-port network R in the figure be
Let the ABCD matrix of the two-port network R in the figure be 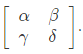 The value of β in Ω is _______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) (2024)
The value of β in Ω is _______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) (2024)
 (a) -25.36
(a) -25.36
(b) -19.8
(c) -22.36
(d) -15.25
Ans: (b)
Sol: 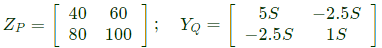 From Zp matrix
From Zp matrix
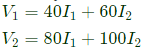 Convert Z-parameters in to ABCD parameters
Convert Z-parameters in to ABCD parameters
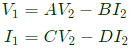 From equation (ii),
From equation (ii),
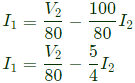 Sub equation (iii) in equation (i),
Sub equation (iii) in equation (i),
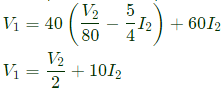 From equation (iii) and (iv),
From equation (iii) and (iv),
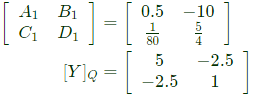
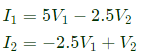 Convert Y-parameters to ABCD parameters From equation (vi),
Convert Y-parameters to ABCD parameters From equation (vi),
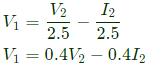 Sub equation (vii) in equation (v),
Sub equation (vii) in equation (v),
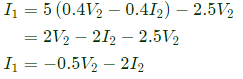 From equation (vii) and equation (viii),
From equation (vii) and equation (viii),
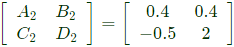
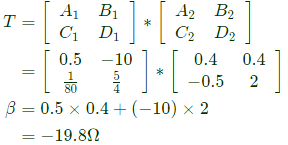
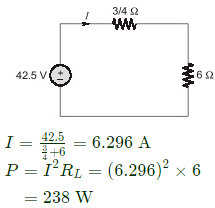
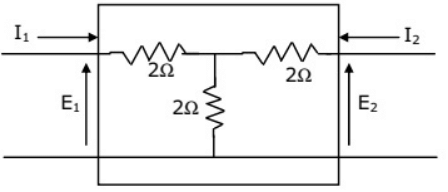
Q2: The admittance parameters of the passive resistive two-port network shown in the figure are
y11 = 5 S, y22 = 1 S, y12 = y21 = −2.5 S
The power delivered to the load resistor RL in Watt is ____ (Round off to 2 decimal places). (2023)
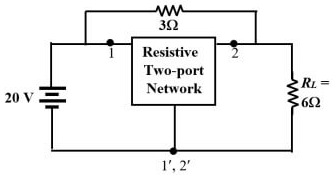 (a) 238
(a) 238
(b) 452.25
(c) 632.12
(d) 145.25
Ans: (a)
Sol: 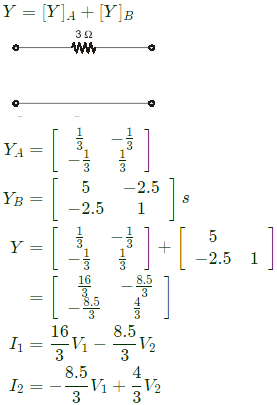

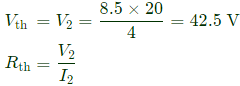
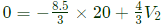
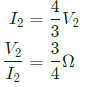 Equivalent circuit
Equivalent circuit
Q3: In the two-port network shown, the h11 parameter (where, h11= V1/I1, when V2 = 0) in ohms is _____________ (up to 2 decimal places). (2018)
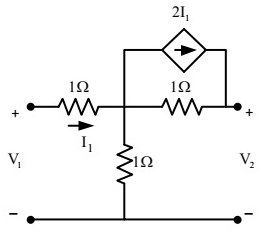 (a) 0.25
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.75
(d) 0.85
Ans: (b)
Sol: 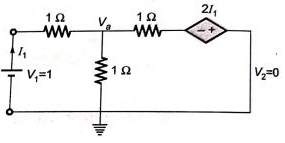 By KCL,
By KCL,
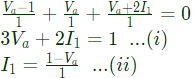 Substitute equation (ii) in equation (i) [/latex]
Substitute equation (ii) in equation (i) [/latex]
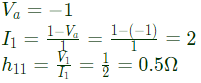
Q4: Two passive two-port networks are connected in cascade as shown in figure. A voltage source is connected at port 1.
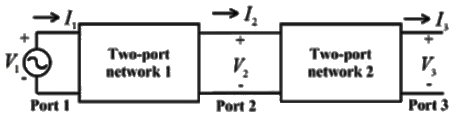
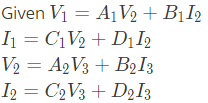 A1, B1, C1, D1, A2, B2, C2 and D2 are the generalized circuit constants. If the Thevenin equivalent circuit at port 3 consists of a voltage source VT and impedance ZT connected in series, then (SET-1 (2017))
A1, B1, C1, D1, A2, B2, C2 and D2 are the generalized circuit constants. If the Thevenin equivalent circuit at port 3 consists of a voltage source VT and impedance ZT connected in series, then (SET-1 (2017))
(a) 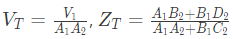
(b) 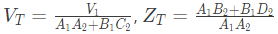
(c) 
(d) 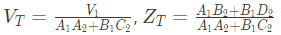
Ans: (d)
Sol: For two port network, we can write,
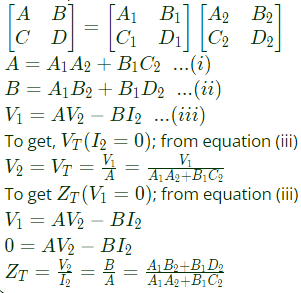
Q5: The z-parameters of the two port network shown in the figure are
z11 = 40Ω, z12 = 60Ω, z21 = 80Ω and z22 = 100Ω.
The average power delivered to RL = 20Ω, in watts, is _______. (SET-2 (2016))
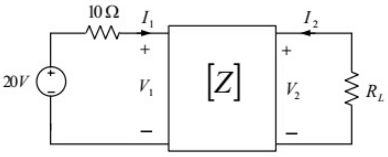 (a) 18.25
(a) 18.25
(b) 24.35
(c) 28.45
(d) 35.55
Ans: (d)
Sol: 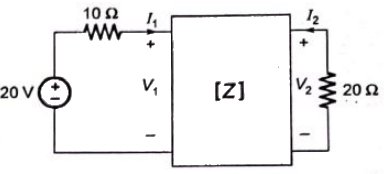
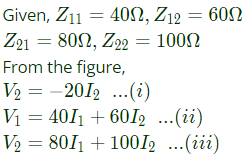 From equation (i) and (iii), we get
From equation (i) and (iii), we get
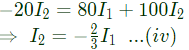 Using equation (ii) and (iv), we get
Using equation (ii) and (iv), we get
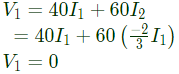 From the figure,
From the figure,
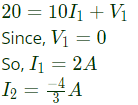 Power dissipated in
Power dissipated in
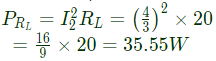
Q6: The driving point input impedance seen from the source Vs of the circuit shown below, in Ω, is ______. (SET-2 (2016))
 (a) 10
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 40
Ans: (b)
Sol: To find impedance seen by Vs
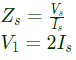
 Applying KCL at node A,
Applying KCL at node A,
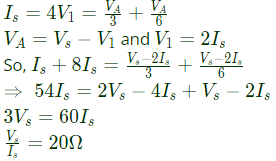
Q7: The driving point impedance Z(s) for the circuit shown below is (SET-3 (2014))
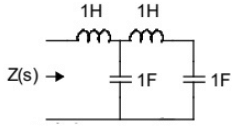 (a)
(a) 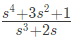
(b) 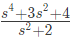
(c) 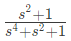
(d) 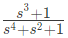
Ans: (a)
Sol: 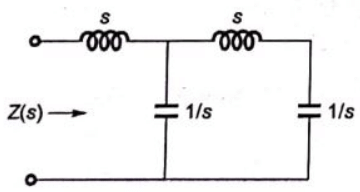 Driving point impedance, Z(s) is ,
Driving point impedance, Z(s) is ,
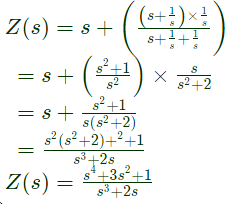
Q8: With 10 V dc connected at port A in the linear nonreciprocal two-port network shown below, the following were observed:
(i) 1 Ω connected at port B draws a current of 3 A
(ii) 2.5 Ω connected at port B draws a current of 2 A
 For the same network, with 6 V dc connected at port A, 1 Ω connected at port B draws 7/3 A. If 8 V dc is connected to port A, the open circuit voltage at port B is (2012)
For the same network, with 6 V dc connected at port A, 1 Ω connected at port B draws 7/3 A. If 8 V dc is connected to port A, the open circuit voltage at port B is (2012)
(a) 6 V
(b) 7 V
(c) 8 V
(d) 9 V
Ans: (b)
Sol: (i)
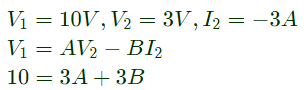
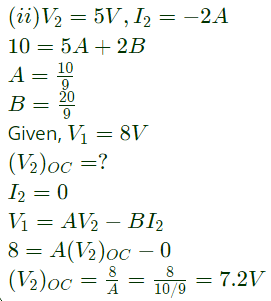
Q9: With 10 V dc connected at port A in the linear nonreciprocal two-port network shown below, the following were observed:
(i) 1 Ω connected at port B draws a current of 3 A
(ii) 2.5 Ω connected at port B draws a current of 2 A
 With 10 V dc connected at port A, the current drawn by 7 Ω connected at port B is (2012)
With 10 V dc connected at port A, the current drawn by 7 Ω connected at port B is (2012)
(a) 3/7A
(b) 5/7A
(c) 1A
(d) 9/7A
Ans: (c)
Sol: 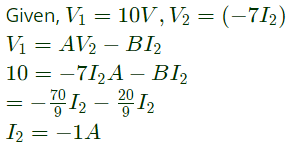 -ve sign is signifies that current is drawn.
-ve sign is signifies that current is drawn.
Q10: The two-port network P shown in the figure has ports 1 and 2, denoted by terminals (a, b) and (c, d) respectively. It has an impedance matrix Z with parameters denoted by Zij. A 1 Ω resistor is connected in series with the network at port 1 as shown in the figure. The impedance matrix of the modified two-port network (shown as a dashed box ) is (2010)
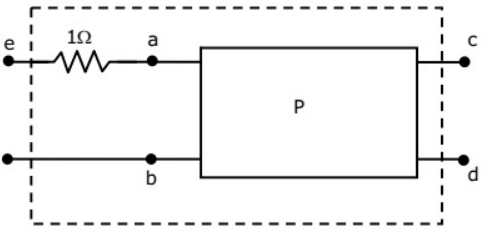 (a)
(a) 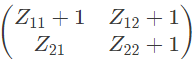
(b) 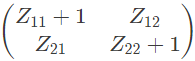
(c) 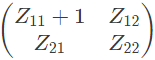
(d) 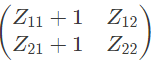
Ans: (c)
Sol: 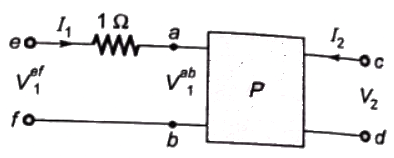
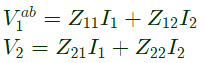 As, 1Ω resistor is connected in series with the network as port-1.
As, 1Ω resistor is connected in series with the network as port-1.
V2 does not get affected,
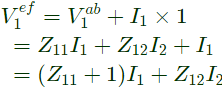 Modified Z-parameter
Modified Z-parameter 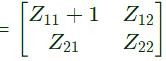
Q11: The parameter type and the matrix representation of the relevant two port parameters that describe the circuit shown are (2006)
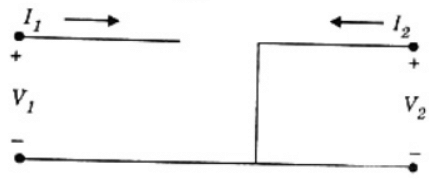 (a) z parameters,
(a) z parameters, 
(b) h parameters,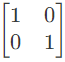
(c) g parameters,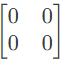
(d) z parameters,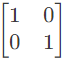
Ans: (c)
Sol: 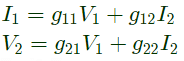
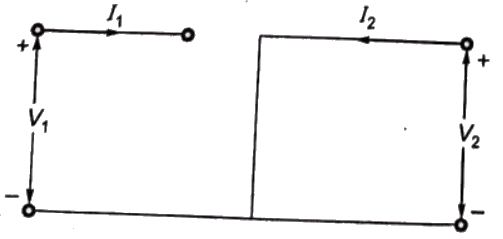 Since port-1 is open circuit, I1 = 0
Since port-1 is open circuit, I1 = 0
Port-2 is short-circuit, V2 = 0
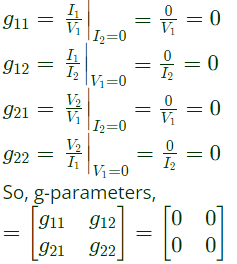
Q12: The parameters of the circuit shown in the figure are
Ri = 1 MΩ, Ro = 10 Ω, A = 106 V/V.
If vi = 1μV, then output voltage, input impedance and output impedance respectively are (2006)
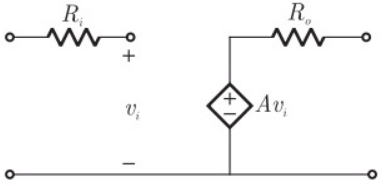 (a) 1V, ∞, 10Ω
(a) 1V, ∞, 10Ω
(b) 1 V, 0, 10Ω
(c) 1 V, 0, ∞
(d) 10 V, ∞, 10 Ω
Ans: (a)
Sol: Output voltage V0 = AVi
V0 = 106 × 1 × 10−6 = 1V
To calculate input impedance, Vdc source is connected at input port
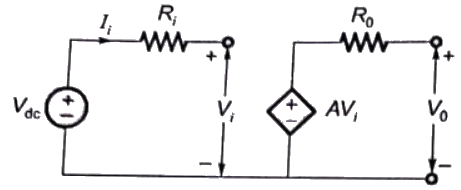 Input impedance
Input impedance
 as loop is not closed, Ii = 0
as loop is not closed, Ii = 0
So, 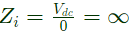
To calculate output impedance, Vdc source is connected at output port.
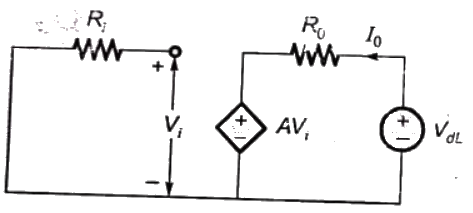 Output impedance,
Output impedance,
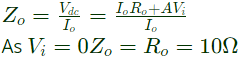
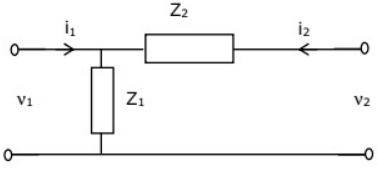
Q13: Two networks are connected in cascade as shown in the figure. With usual notations the equivalent A, B, C and D constants are obtained. Given that, C = 0.025∠45°, the value of Z2 is (2005)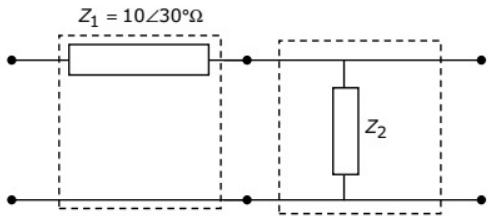 (a) 10∠30°Ω
(a) 10∠30°Ω
(b) 40∠−45°Ω
(c) 1 Ω
(d) 0 Ω
Ans: (b)
Sol: 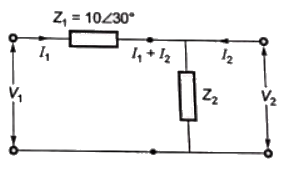
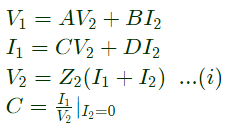 Putting I2 = 0 in equation (i)
Putting I2 = 0 in equation (i)
Q14: For the two port network shown in the figure, the Z-matrix is given by (2005)
 (a)
(a) 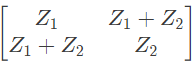
(b) 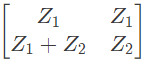
(c) 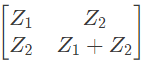
(d) 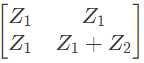
Ans: (d)
Sol: 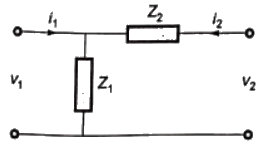
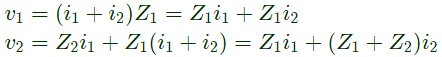 From above, we can write,
From above, we can write,
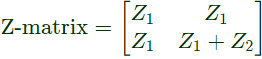
Q15: The Z-matrix of a 2-port network as given by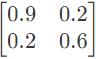
The element Y22 of the corresponding Y-matrix of the same network is given by (2004)
(a) 1.2
(b) 0.4
(c) -0.4
(d) 1.8
Ans: (d)
Sol: 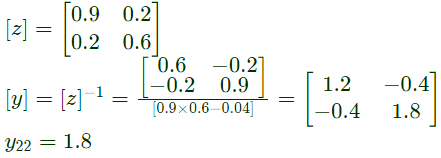
Q16: The h-parameters for a two-port network are defined by 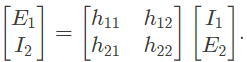 For the two-port network shown in figure, the value of h12 is given by (2003)
For the two-port network shown in figure, the value of h12 is given by (2003)
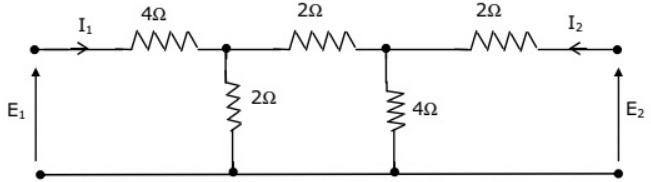 (a) 0.125
(a) 0.125
(b) 0.167
(c) 0.625
(d) 0.25
Ans: (d)
Sol: 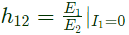 h12 is ratio of E1 to E2 for the input open-circuited condition.
h12 is ratio of E1 to E2 for the input open-circuited condition.
Assuming I1 = 0
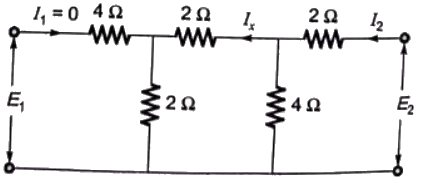
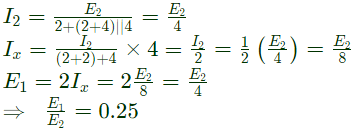
Q17: A two port network, shown in figure is described by the following equations
 The admittance parameters Y11, Y12, Y21, Y22 for the network shown are (2002)
The admittance parameters Y11, Y12, Y21, Y22 for the network shown are (2002)
(a) 0.5 mho, 1 mho, 2 mho and 1 mho respectively
(b) 1/3 mho, -1/6 mho, -1/6 mho and 1/3 mho respectively
(c) 0.5 mho, 0.5 mho, 1.5 mho and 2 mho respectively
(d) -2/5 mho, -3/7 mho, 3/7 mho and 2/5 mho respectively
Ans: (b)
Sol: Using KVL,
E1 = 2I1 + 2(I1+I2)
Again using KVL,
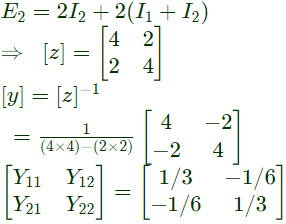
Q18: A passive 2-port network is in a steady-state. Compared to its input, the steady state output can never offer (2001)
(a) higher voltage
(b) lower impedance
(c) greater power
(d) better regulation
Ans: (c)
Sol: For a passive two port network, output powe can never be grater than input power.
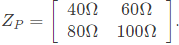 The admittance matrix of network
The admittance matrix of network 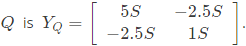 Let the ABCD matrix of the two-port network R in the figure be
Let the ABCD matrix of the two-port network R in the figure be 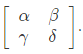 The value of β in Ω is _______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) (2024)
The value of β in Ω is _______ (rounded off to 2 decimal places) (2024) (a) -25.36
(a) -25.36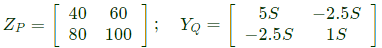 From Zp matrix
From Zp matrix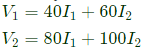 Convert Z-parameters in to ABCD parameters
Convert Z-parameters in to ABCD parameters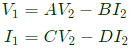 From equation (ii),
From equation (ii),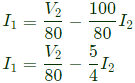 Sub equation (iii) in equation (i),
Sub equation (iii) in equation (i),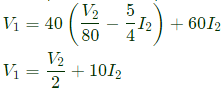 From equation (iii) and (iv),
From equation (iii) and (iv),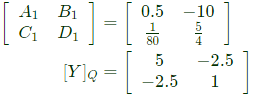
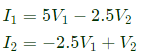 Convert Y-parameters to ABCD parameters From equation (vi),
Convert Y-parameters to ABCD parameters From equation (vi), 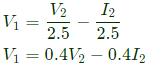 Sub equation (vii) in equation (v),
Sub equation (vii) in equation (v),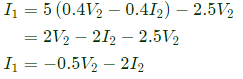 From equation (vii) and equation (viii),
From equation (vii) and equation (viii),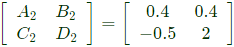
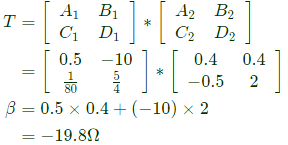
 (a) 238
(a) 238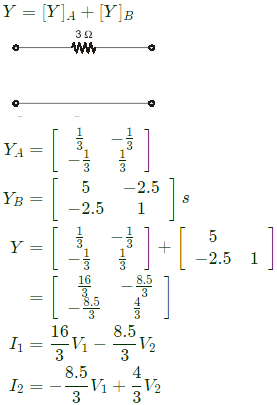

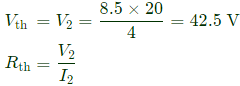
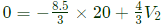
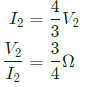 Equivalent circuit
Equivalent circuit
 (a) 0.25
(a) 0.25 By KCL,
By KCL,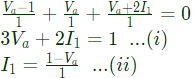 Substitute equation (ii) in equation (i) [/latex]
Substitute equation (ii) in equation (i) [/latex]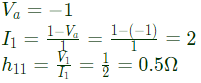

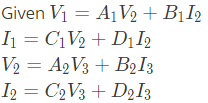 A1, B1, C1, D1, A2, B2, C2 and D2 are the generalized circuit constants. If the Thevenin equivalent circuit at port 3 consists of a voltage source VT and impedance ZT connected in series, then (SET-1 (2017))
A1, B1, C1, D1, A2, B2, C2 and D2 are the generalized circuit constants. If the Thevenin equivalent circuit at port 3 consists of a voltage source VT and impedance ZT connected in series, then (SET-1 (2017))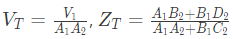
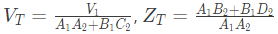

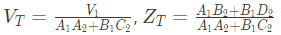
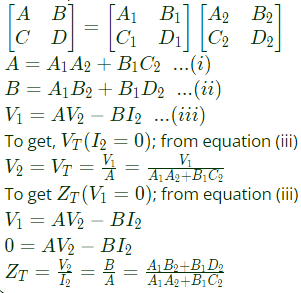
 (a) 18.25
(a) 18.25
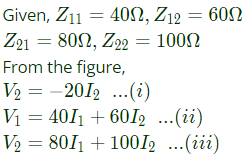 From equation (i) and (iii), we get
From equation (i) and (iii), we get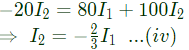 Using equation (ii) and (iv), we get
Using equation (ii) and (iv), we get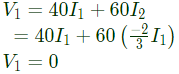 From the figure,
From the figure,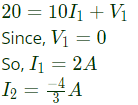 Power dissipated in
Power dissipated in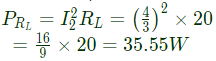
 (a) 10
(a) 10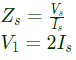
 Applying KCL at node A,
Applying KCL at node A,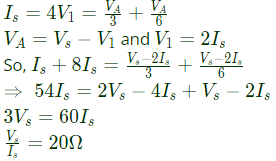
 (a)
(a) 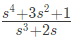
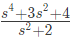
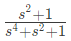
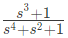
 Driving point impedance, Z(s) is ,
Driving point impedance, Z(s) is ,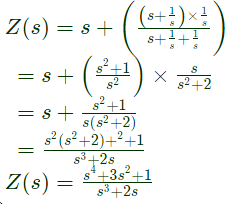
 For the same network, with 6 V dc connected at port A, 1 Ω connected at port B draws 7/3 A. If 8 V dc is connected to port A, the open circuit voltage at port B is (2012)
For the same network, with 6 V dc connected at port A, 1 Ω connected at port B draws 7/3 A. If 8 V dc is connected to port A, the open circuit voltage at port B is (2012)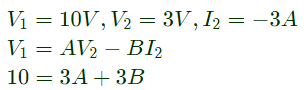
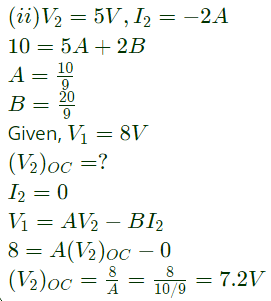
 With 10 V dc connected at port A, the current drawn by 7 Ω connected at port B is (2012)
With 10 V dc connected at port A, the current drawn by 7 Ω connected at port B is (2012)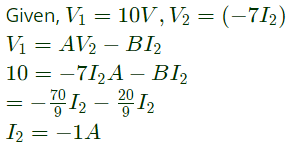 -ve sign is signifies that current is drawn.
-ve sign is signifies that current is drawn. (a)
(a) 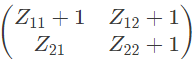
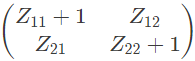
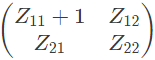
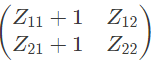

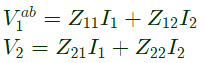 As, 1Ω resistor is connected in series with the network as port-1.
As, 1Ω resistor is connected in series with the network as port-1.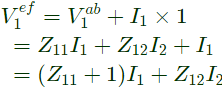 Modified Z-parameter
Modified Z-parameter 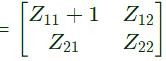
 (a) z parameters,
(a) z parameters, 
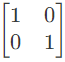
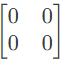
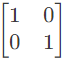
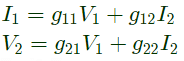
 Since port-1 is open circuit, I1 = 0
Since port-1 is open circuit, I1 = 0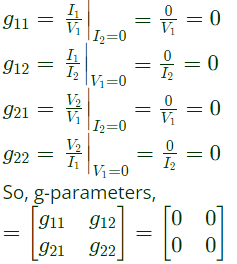
 (a) 1V, ∞, 10Ω
(a) 1V, ∞, 10Ω Input impedance
Input impedance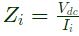 as loop is not closed, Ii = 0
as loop is not closed, Ii = 0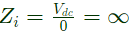
 Output impedance,
Output impedance,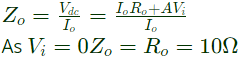
 (a) 10∠30°Ω
(a) 10∠30°Ω
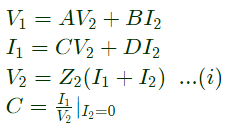 Putting I2 = 0 in equation (i)
Putting I2 = 0 in equation (i)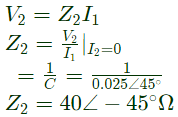
 (a)
(a) 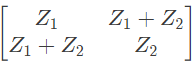
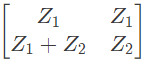
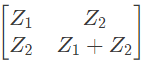
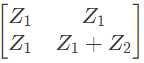

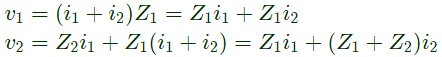 From above, we can write,
From above, we can write,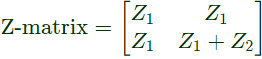
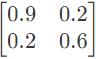
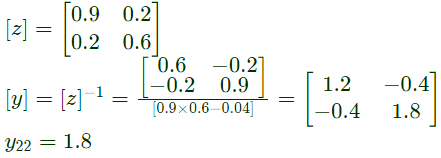
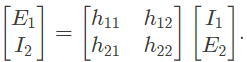 For the two-port network shown in figure, the value of h12 is given by (2003)
For the two-port network shown in figure, the value of h12 is given by (2003) (a) 0.125
(a) 0.125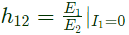 h12 is ratio of E1 to E2 for the input open-circuited condition.
h12 is ratio of E1 to E2 for the input open-circuited condition.
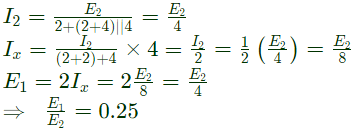
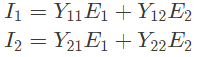
 The admittance parameters Y11, Y12, Y21, Y22 for the network shown are (2002)
The admittance parameters Y11, Y12, Y21, Y22 for the network shown are (2002)