JEE Main Previous Year Questions (2016- 2024): Electrochemistry | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. Given that the standard potentials (E°) and Cu2+/Cu and Cu+/Cu are 0.34 V and 0.522 V respectively, the E° of Cu2+/Cu+ is (2020)
(1) 0.182 V
(2) +0.158 V
(3) −0.182 V
(4) −0.158 V
Ans. (2)
Given,
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu; E° 0.34 V (1)
Cu+ + e- → Cu; E° = 0.522 V (2)
For Cu2+ + e- → Cu+ ; E°Cu2+/Cu+ x V
On reversing Eq. (2), we get
Cu → Cu+ + e- ; E° = - 0.522 V (3)
From Eq. (1) and Eq. (3), we get
ΔG°3 = ΔG°1 + ΔG°2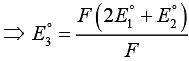
⇒ E°3 = 2 x 0.34 + (- 0.522)
⇒ E°3 = 0.68 - 0.522 = 0.158 V
Q.2. The equation that is incorrect is: (2020)
(1)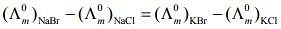
(2)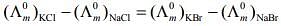
(3)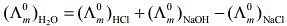
(4)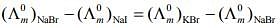
Ans. (4)
According to Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions, the incorrect equation is: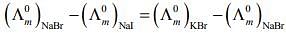
From L.H.S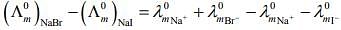
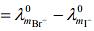
From R.H.S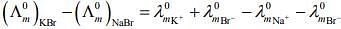

Hence, L.H.S is not equal to R.H.S.
Q.3. What would be the electrode potential for the given half-cell reaction at pH = 5?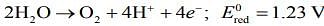
(R = 8.314 J and mol−1 K−1; T = 298 K; oxygen under standard atm pressure of 1 bar) (2020)
Ans. (1.525)
For the half-cell reaction,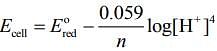 (1)
(1)
Substituting the values in Eq. (1), we get
⇒ 
⇒ Ecell = + 1.23 + 0.059 x 5 [Given: pH = 5]
⇒ Ecell = 1.525 V
Q.4. For an electrochemical cell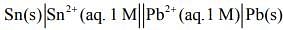 the ratio
the ratio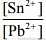 when this cell attains equilibrium is _______.
when this cell attains equilibrium is _______.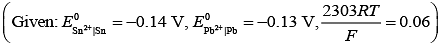 (2020)
(2020)
Ans. (2.15)
For the given electrochemical cell
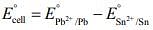
= 0.13 - (-0.14) = 0.01 V
From the Nernst equation for given electrochemical cell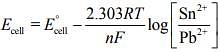 (1)
(1)
Substituting the given values in Eq. (1), we get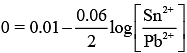 [At Equilibrium, Ecell = 0]
[At Equilibrium, Ecell = 0]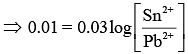
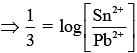 (2)
(2)
Taking antilog of Eq. (2), we get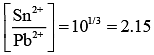
Q.5. 108 g of silver (molar mass 108 g mol-1) is deposited at cathode from AgNO3(aq) solution by a certain quantity of electricity. The volume (in L) of oxygen gas produced at 273 K and 1 bar pressure from water by the same quantity of electricity is ________ . (2020)
Ans. (5.67)
The moles of AgNO3 deposited at cathode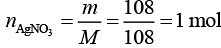
At anode: 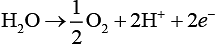
At cathode: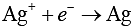
Thus, 1 F required to deposit 1 mol of Ag and 2 F required to produce 0.5 mol of oxygen gas.
⇒ 1 F will produce 0.25 mol of oxygen gas.
Thus, the volume of oxygen gas produced at 273 K and 1 bar pressure can be calculated using ideal gas equation.
⇒ pV = nRT
Q.6. Amongst the following, the form of water with the lowest ionic conductance at 298 K is (2020)
(1) distilled water
(2) saline water used for intravenous injection
(3) water from a well
(4) sea water
Ans. (1)
Due to the absence of the mineral in the distilled water, the ionic conductance is minimum among the all liquid forms of water.
Q.7. The anodic half-cell of lead-acid battery is recharged using electricity of 0.05 Faraday. The amount of PbSO4 electrolyzed (in gm) during the process is: (Molar mass of PbSO4 = 303 g mol-1) (2019)
(1) 22.8
(2) 15.2
(3) 7.6
(4) 11.4
Ans. (3)
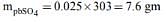
Q.8. If the standard electrode potential for a cell is 2 V at 300 K, the equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) ⇌ Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s)
at 300 K is approximately
(R= 8JK-1 mol-1, F= 96000 C mol-1) (2019)
(1) e-80
(2) e-160
(3) e320
(4) e160
Ans. (4)
We know that, 
After putting the given values, we get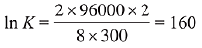
∴ K = e160
Q.9. In the cell
Pt(s)|H2(g, lbar) / HCl(aq)||AgCl(s)/Ag(s)|Pt(s), the cell potential is 0.92 V when a 10-6 molal HCl solution is used. The standard electrode potential of (AgCl/Ag, Cl-) electrode is: (2019)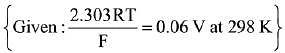
(1) 0.94 V
(2) 0.76 V
(3) 0.40 V
(4) 0.20 V
Ans. (4)
Given that:
Pt(s)|H2(g, lbar) / HCl(aq)||AgCl(s)/Ag(s)|Pt(s)
Ecell = 0.92 V
Net cell reaction: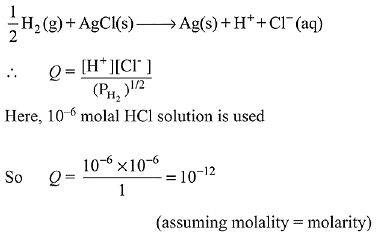
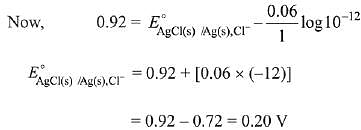
Q.10. For the cell Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Mx+ (aq) | M(s), different half cells and their standard electrode potentials are given below: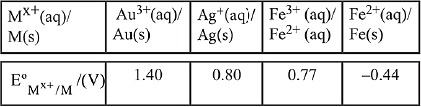
If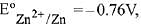 , which cathode will give a maximum value of E°cell per electron transferred? (2019)
, which cathode will give a maximum value of E°cell per electron transferred? (2019)
(1) Ag+/Ag
(2) Fe3+/Fe2+
(3) Au3+/Au
(4) Fe2+/Fe
Ans. (1)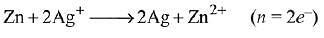
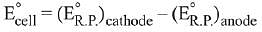

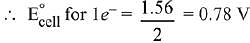
Q.11. Given the equilibrium constant:
KC of the reaction:
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) is
10 x 1015. Calculate the E°cell of this reaction at 298 K. (2019)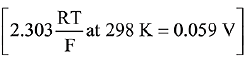
(1) 0.04736 mV
(2) 0.4736 mV
(3) 0.4736 V
(4) 0.04736 V
Ans. (3)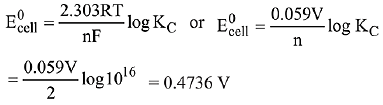
Q.12. The standard electrode potential E° and its temperature coefficient 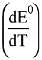 for a cell are 2 V and -5 x 10-4 VK-1 at 300 K respectively. The cell reaction is:
for a cell are 2 V and -5 x 10-4 VK-1 at 300 K respectively. The cell reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu
The standard reaction enthalpy (ΔrH°) at 300 K in kJ mol-1 is,
[Use R= 8 JK-1 mol-1 and F = 96,000 C mol-1] (2019)
(1) -412.8
(2) -384.0
(3) 192.0
(4) 206.4
Ans. (1)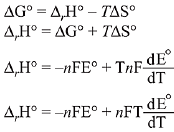
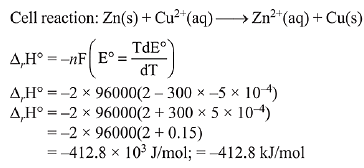
Q.13. Λ0m for NaCl, HCl and NaA are 126.4, 425.9 and 100.5 cm2 mol-1, respectively. If the conductivity of 0.001 M HA is 5 x 10-5 Scm-1, degree of dissociation of HA is: (2019)
(1) 0.50
(2) 0.25
(3) 0.125
(4) 0.75
Ans. (3)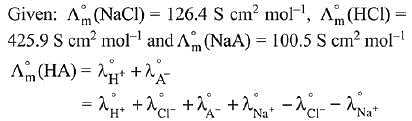
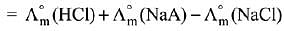
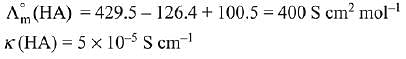
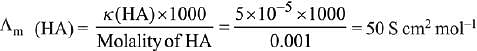

Q.14. Given that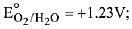

The strongest oxidising agent is: (2019)
(1) Au3+
(2) O2
(3) S2O82-
(4) Br2
Ans. (3)
More positive is the reduction potential stronger is the oxidising agent. Reduction potential is maximum for S2O82-. Therefore, it is the strongest oxidising agent amongst the given species.
Q.15. Calculate the standard cell potential (in V) of the cell in which following reaction takes place:
Fe2+ (aq) + Ag+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Ag(s)
Given that (2019)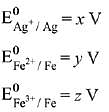
(1) x - z
(2) x - y
(3) x + 2y - 3z
(4) x + y - z
Ans. (3)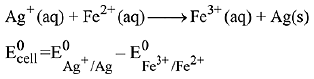
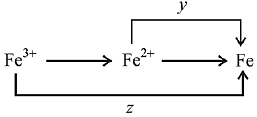
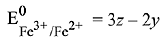
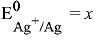 (given)
(given)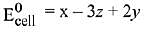
Q.16. The standard Gibbs energy for the given cell reaction in kJ mol-1 at 298 K is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + Cu(s),
E° = 2 V at 298 K
(Faraday's constant, F = 96000 C mol-1) (2019)
(1) - 384
(2) 384
(3) 192
(4) - 192
Ans. (1)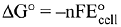
= -2 (96000) 2 V = - 384000 J/mol
= -384 kJ/mol
Q.17. A solution of Ni (NO3)2 is electrolysed between platinum electrodes using 0.1 Faraday electricity. How many moles of Ni will be deposited at the cathode? (2019)
(1) 0.05
(2) 0.20
(3) 0.15
(4) 0.10
Ans. (1)
According to the Faraday’s law of electrolysis, nF of current is required for the deposition of 1 mol According to the reaction,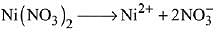
2 F of current deposits = 1 mol
∴ 0.1 F of current deposits = 0.1/2 = 0.05 mol
Q.18. Consider the statements S1 and S2 :
S1 : Conductivity always increases with decrease in the concentration of electrolyte.
S2 : Molar conductivity always increases with decrease in the concentration of electrolyte.
The correct option among the following is: (2019)
(1) Both S1 and S2 are wrong
(2) S1 is wrong and S2 is correct
(3) Both S1 and S2 are correct
(4) S1 is correct and S2 is wrong
Ans. (2)
Conductivity of an electrolyte is the conductance of 1 cm3 of the given electrolyte. It increases with the increase in concentration of electrolyte due to increase in the number of ions per unit volume. Molar conductivity (λm) is the conductance of a solution containing 1 mole of the electrolyte. It increases with the decrease of concentration due to increase in the total volume having one mole of electrolyte. Thus, interionic attraction increases and degree of ionisation decreases. Therefore, (S1) is wrong and (S2) is correct.
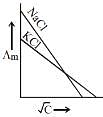
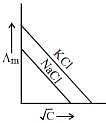
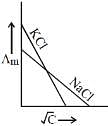
Q.19. Which one of the following graphs between molar conductivity (Λm) versus √C is correct? (2019)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 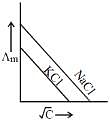
Ans. (2)
Both NaCl and KCl are strong electrolytes and as Na+(aq⋅) has less conductance than K+(aq⋅) due to more hydration. Therefore, the graph of option (2) is correct.
Q.20. Given :
Co3+ + e- → Co2+; E° = + 1.81 V
Pb4+ + 2e- → Pb2+; E° = + 1.67 V
Ce4+ + e- → Ce3+; E° = + 1.61 V
Bi3+ + 3e- → Bi; E° = + 0.20 V
oxidizing power of the species will increase in the order: (2019)
(1) Ce4+ < Pb4+ < Bi3+ < Co3+
(2) Bi3+ < Ce4+ < Pb4+ < Co3+
(3) Co3+ < Ce4+ < Bi3+ < Pb4+
(4) Co3+ < Pb4+ < Ce4+ < Bi3+
Ans. (2)
Higher the reduction potential, higher will be oxidising power. So, Bi3+ < Ce4+ < Pb4+ < Co3+
Q.21. How long (approximate) should water be electrolysed by passing through 100 amperes current so that the oxygen released can completely burn 27.66 g of diborane? (2018)
(Atomic weight of B = 10.8 u)
(1) 6.4 hours
(2) 0.8 hours
(3) 3.2 hours
(4) 1.6 hours
Ans. (3)
B2H6 + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
According to balanced equation:
27.66 g B2H6 i.e. 1 mole B2H6 requires 3 mole of O2. Now this oxygen is produced by electrolysis of water.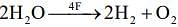
1 mole O2 is produced by 4 F charge
∴ 3 mole O2 will be produced by 12 F charge
∴ Now applying
Q = It
12 x 96500 C = 100 x t(s)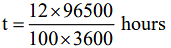
t = 3.2 hours
Q.22. When an electric current is passed through acidified water, 112 mL of hydrogen gas at N.T.P. was collected at the cathode in 965 seconds. The current passed, in ampere, is: (2018)
(1) 0.1
(2) 0.5
(3) 1.0
(4) 2.0
Ans. (3)
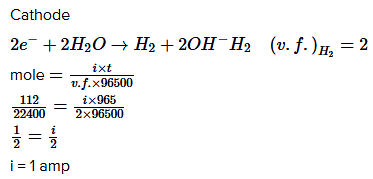
Q.23. When 9.65 ampere current was passed for 1.0 hour into nitrobenzene in acidic medium, the amount of p-aminophenol produced is: (2018)
(1) 109.0 g
(2) 98.1 g
(3) 9.81 g
(4) 10.9 g
Ans. (3)
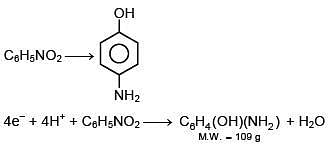
(v.f.) = 4 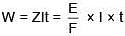
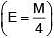
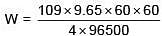
W = 9.81 g
Q.24. Given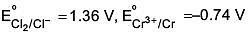
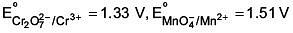
Among the following, the strongest reducing agent is (2017)
(1) Cr
(2) Mn2+
(3) Cr3+
(4) Cl-
Ans. (1)
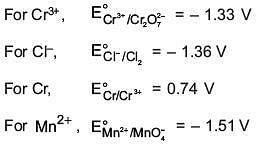
Positive E° is for Cr, hence it is strongest reducing agent.
Q.25. Consider the following standard electrode potentials (E° in volts) in aqueous solution: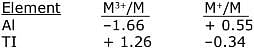
Based on these data, which of the following statements is correct? (2017)
(1) Tl3+ is more stable than Al3+
(2) Al+ is more stable than Al3+
(3) Tl3+ is more stable than Al+
(4) Tl+ is more stable than Al+
Ans. (4)
ΔG is -ve
Q.26. What is the standard reduction potential (E°) for Fe3+ → Fe?
Given that: (2017)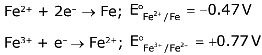
(1) –0.057 V
(2) + 0.30 V
(3) – 0.30 V
(4) + 0.057 V
Ans. (1)
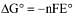
(i) Fe2+ + 2e- → Fe; E° = -0.47V;
(ii) Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+; E° = +0.77V;
(iii) Fe3+ + 3e- → Fe
ΔG° = -nFE° = -2(-0.47)F = 0.94F
ΔG° = -nFE° = -1(-0.77)F = 0.77F
On adding : ΔG° = +0.17F
ΔG° = -nFE°
E° for (Fe3+ → Fe)
= 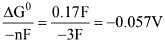
Q.27. To find the standard potential of M3+/M electrode, the following cell is constituted: Pt/M/M3+ (0.001 mol L-1)/Ag+ (0.01 mol L-1)/Ag
The emf of the cell is found to be 0.421 volt at 298 K. The standard potential of half reaction M3+ + 3e- → M at 298 K will be: (Given EΘAg+/ Ag at 298 K = 0.80 volt) (2017)
(1) 0.38 volt
(2) 1.28 volt
(3) 0.32 volt
(4) 0.66 volt
Ans. (3)
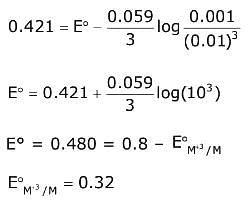
Q.28. Galvanization is applying a coating of: (2016)
(1) Pb
(2) Cr
(3) Cu
(4) Zn
Ans. (4)
Galvanization is applying a coating of zinc.
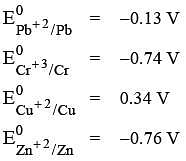
Q.29. What will occur if a block of copper metal is dropped into a beaker containing a solution of 1M ZnSO4? (2016)
(1) The copper metal will dissolve and zinc metal will be deposited.
(2) The copper metal will dissolve with evolution of oxygen gas.
(3) The copper metal will dissolve with evolution of hydrogen gas.
(4) No reaction will occur.
Ans. (4)
If a block of copper metal is dropped into a beaker containing solution of 1 M ZnSO4, no reaction will occur because
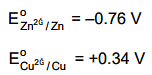
Hence Cu can't displace Zn from ZnSO4 solution.
Q.30. Identify the correct statement: (2016)
(1) Corrosion of iron can be minimized by forming an impermeable barrier at its surface.
(2) Iron corrodes in oxygen-free water.
(3) Iron corrodes more rapidly in salt water because its electrochemical potential is higher.
(4) Corrosion of iron can be minimized by forming a contact with another metal with a higher reduction potential.
Ans. (1)
Fact
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















