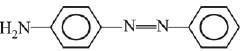
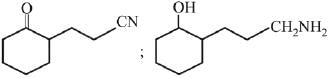
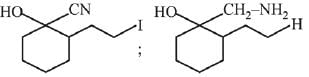
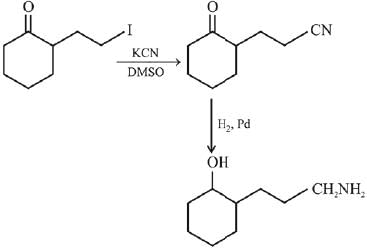
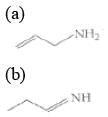
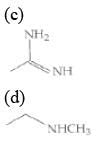
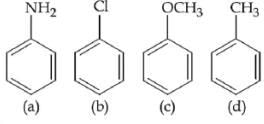
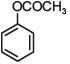
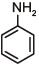
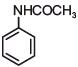
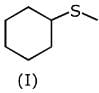
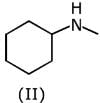
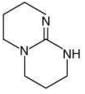
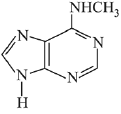
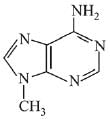
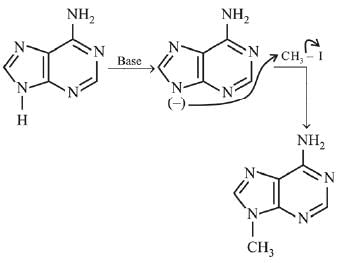
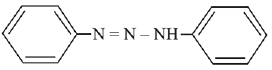Q.1. The increasing order of pKb for the following compounds will be (2020)
(I) NH2 - CH = NH
(II) 
(III) CH3 - NH - CH3
(1) (II) < (III) < (I)
(2) (I) < (II) < (III)
(3) (III) < (I) < (II)
(4) (II) < (I) < (III)
Ans. (4)
Since, compound (B) is the derivative of guanidine, thus, it has lowest pKb value. In compound (A), the amine is sp2 hybridized, which is more basic than sp3 hybridized amine. Hence, the correct increasing order of pKb value is: (II) < (I) < (III).
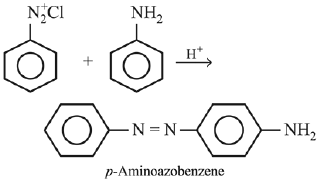
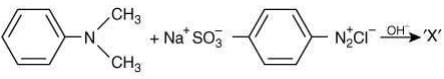
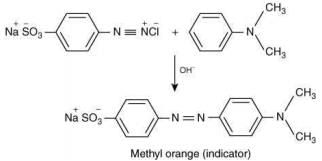
Q.2. Consider the following reaction:

The product ‘X' is used (2020)
(1) In protein estimation as an alternative to ninhydrin
(2) In acid base titration as an indicator
(3) As food grade colorant
(4) In laboratory test for phenols
Ans. (2)
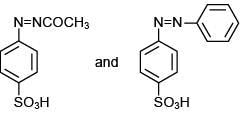
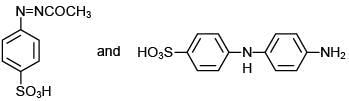
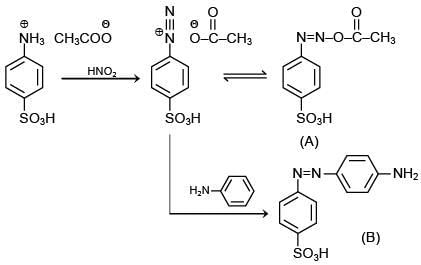
The reaction involved is

Thus, the product formed is methyl orange, which is used as an indicator in acid-base titration.
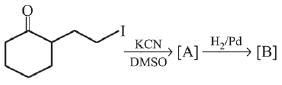
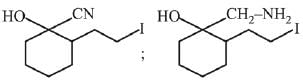
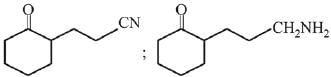
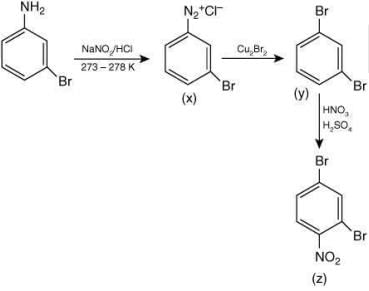
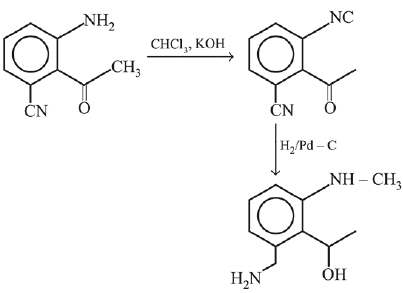
Q.3. In the following reaction sequence,

the major product B is (2020)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (1)
The reaction involved is

Q.4. The major product Z obtained in the following reaction scheme is (2020)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (2)
The reaction involved is

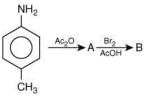
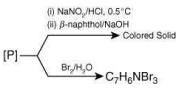
Q.5. Consider the following reactions,

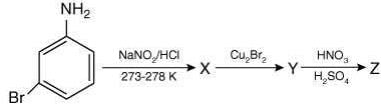
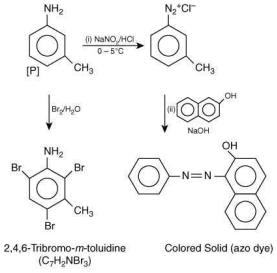
The compound [P] is (2020)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)
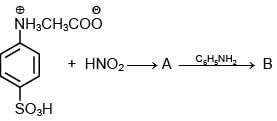
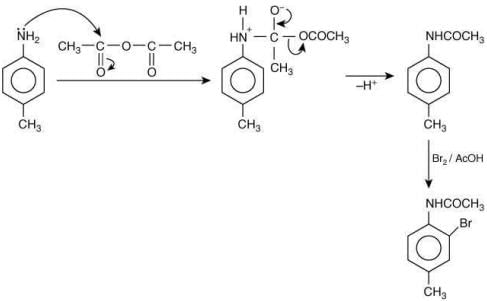
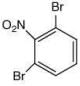
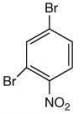
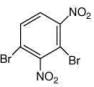
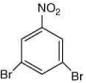
Since, compound, P give color solid on diazotization followed by α-naphthol, so the compound P is -o/-m/-p-toluidine. From the second reaction, a tribromo product is obtained on reaction with bromine water, hence, the compound P must be m-toluidine. The reaction involved is

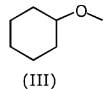
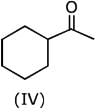
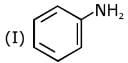
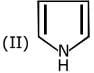
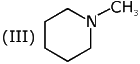
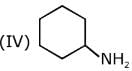
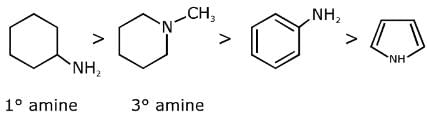
Q.6. The decreasing order of basicity of the following amines is (2020)
(I) 
(II) 
(III) 
(IV) 
(1) (I) > (III) > (IV) > (II)
(2) (III) > (I) > (II) > (IV)
(3) (II) > (III) > (IV) > (I)
(4) (III) > (II) > (I) > (IV)
Ans. (4)
The basicity of the amines depends upon the availability of the lone pairs of electrons of nitrogen atom in the amines.
(I) The lone pairs of electrons of nitrogen in aniline is delocalized in the benzene ring, thus, they are very less available for protonation.
(II) In pyridine, the nitrogen atom is sp2 hybridized, thus, it is more basic than aniline.
(III) In cyclohexylamine, the lone pairs of electrons as very much available for protonation, thus, it is most basic among the given amines.
(IV) In pyrrole, the lone pair of electrons involved in ring to increasing the stability of pyrrole by making it aromatic, thus the lone pairs of electrons of nitrogen are not available for protonation.
Hence, the correct decreasing order of basicity the following amines is: (III) > (II) > (I) > (IV).
Q.7. Arrange the following amines in the decreasing order of basicity: (2019)

(1) I > II > III
(2) III > I > II
(3) III > II > I
(4) I > III > II
Ans. (2)
Compound,  is most basic as the lone pair of nitrogen is easily available for the donation.
is most basic as the lone pair of nitrogen is easily available for the donation.
In case of compound  lone pair is not in-volved in resonance but nitrogen atom is sp2 hybrid-sed whereas in compound II the lone pair of nitrogen is involved in aromaticity which makes it least basic.
lone pair is not in-volved in resonance but nitrogen atom is sp2 hybrid-sed whereas in compound II the lone pair of nitrogen is involved in aromaticity which makes it least basic.
Q.8. The major product of the following reaction is: (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)
Reaction involved for the given reaction:

Q.9. The increasing basicity order of the following compounds is: (2019)
(A) CH3CH2NH2
(B) 
(C) 
(D) 
(1) (D) < (C) < (B) < (A)
(2) (D) < (C) < (A) < (B)
(3) (A) < (B) < (C) < (D)
(4) (A) < (B) < (D) < (C)
Ans. (2)

So, order of basic strength is:


(B) > (A) > (C) > (D)
Q.10. The major product formed in the reaction given below will be: (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (Bonus)

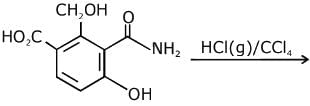
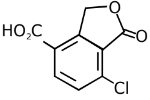
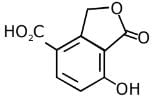
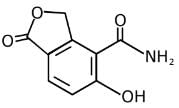
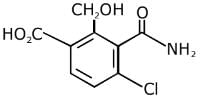
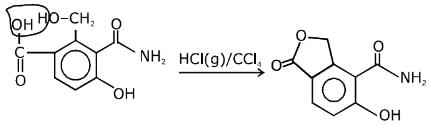
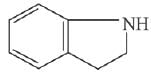
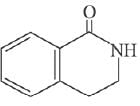
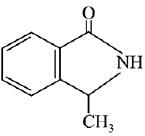
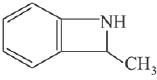
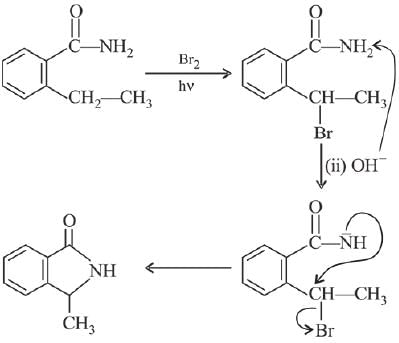
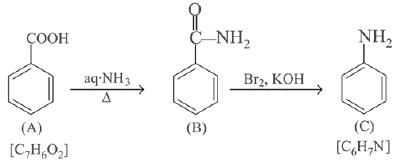
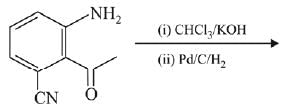
Q.11. An aromatic compound ‘A’ having molecular formula C7H6O2 on treating with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B'. The compound ‘B’ on reaction with molecular bromine and potassium hydroxide provides compound ‘C’ having molecular formula C6H7N. The structure of ‘A’ is: (2019)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (1)
Reaction involved:

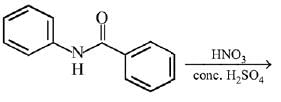
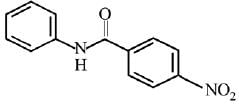
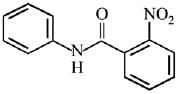
Q.12. What will be the major product in the following mononitration reaction? (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (4)
In the given nitration reaction, major product will be formed as per the activating group, -NH part of  is activating while,
is activating while,  part is deactivating group.
part is deactivating group.

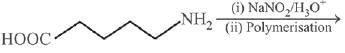
Q.13. The polymer obtained from the following reactions is (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
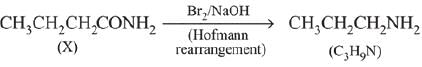
Ans. (3)


Q.14. A compound ‘X’ on treatment with Br2/NaOH, provided C3H9N, which gives positive carbylamine test. Compound ‘X’ is: (2019)
(1) CH3COCH2NACH3
(2) CH3CH2COCH2CH2
(3) CH3CH2CH2CONH2
(4) CH3CON(CH3)2
Ans. (3)


Q.15. The major product of the following reaction is: (2019)


(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (1)


Q.16. In the following compounds, the decreasing order of basic strength will be: (2019)
(1) C2H5NH2 > NH3 > (C2H5)2NH
(2) (C2H5)2NH > NH3 > C2H5NH2
(3) (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3
(4) NH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH
Ans. (3)

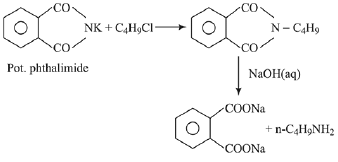
Q.17. Which of the following amines can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide reaction? (2019)
(1) n-butylamine
(2) triethylamine
(3) t-butylamine
(4) neo-pentylamine
Ans. (1)
Primary amines are prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis

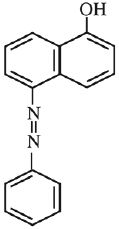
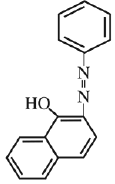
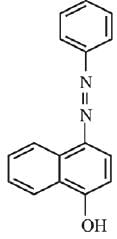
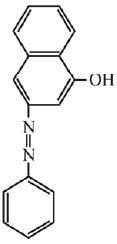
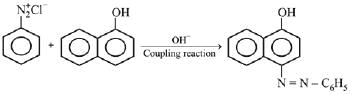
Q.18. Coupling of benzene diazonium chloride with 1 -naphthol in alkaline medium will give: (2019)
(1)

(2)

(3)

(4)

Ans. (3)

Q.19. The major product in the following reaction is: (2019)

(1) 
(2)
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (4)

Q.20. The major product obtained in the following reaction is: (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (4)

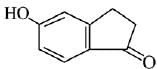
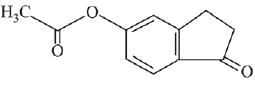
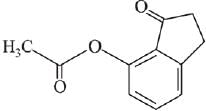
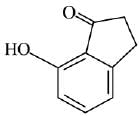
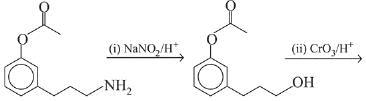
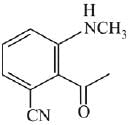
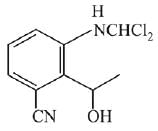
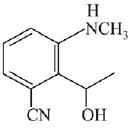
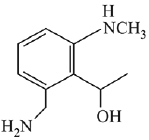
Q.21. Aniline dissolved in dilute HCl is reacted with sodium nitrate at 0°C. This solution was added drop wise to a solution containing equimolar mixture of aniline and phenol in dil. HCl. The structure of the major product is: (2019)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)
In acidic medium aniline is more reactive than phenol that’s why electrophilic aromatic substitution of  takes place with aniline.
takes place with aniline.

Q.22. Hinsberg’s reagent is: (2019)
(1) C6H5COCI
(2) SOCl2
(3) C6H5SO2Cl
(4) (COCl)2
Ans. (3)
Hinsberg’s reagent is benzenesulphonyl chloride. It is used for detection of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Q.23. The major products A and B for the following reactions are, respectively: (2019)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)

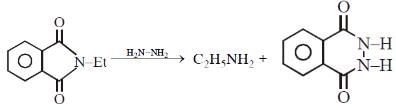
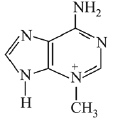
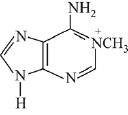
Q.24. Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) can be obtained from N-ethylphthalimide on treatment with: (2019)
(1) NH2NH2
(2) CaH2
(3) NaBH4
(4) H2O
Ans. (1)
reagent is NH2 - NH2 byproduct will be

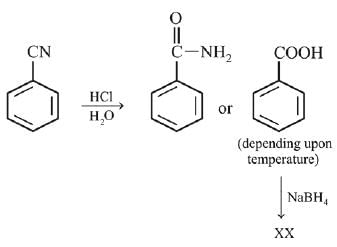
Q.25. Which of the following is NOT a correct method of the preparation of benzylamine from cyanobenzene? (2019)
(1) H2/Ni
(2) (i) LiAlH4
(ii) H3O+
(3) (i) SnCl2 + HCl(gas)
(ii) NaBH4
(4) (i) HCl/H2O
(ii) NaBH4
Ans. (4)

Q.26. Benzene diazonium chloride on reaction with aniline in the presence of dilute hydrochloric acid gives: (2019)
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)

Q.27. The increasing order of basicity of the following compounds is: (2018)


(1) (a) < (b) < (c) < (d)
(2) (b) < (a) < (c) < (d)
(3) (d) < (b) < (a) < (c)
(4) (b) < (a) < (d) < (c)
Ans. (4)
Order of base nature depends on electron donation tendency.
In compound (b) nitrogen is sp2 hybridized so least basic among all given compound
Compound (c) is a very strong nitrogeneous organic base as a lone pair of one nitrogen is delocalized in resonance and make another nitrogen negatively charged and conjugate acid have two equivalent resonating structure.
Thus it is most basic in given compound.
(d) is secondary amine more than (a) which is a primary amine.
Q.28. The increasing order of nitration of the following compounds is: (2018)

(1) (a) < (b) < (d) < (c)
(2) (a) < (b) < (c) < (d)
(3) (b) < (a) < (c) < (d)
(4) (b) < (a) < (d) < (c)
Ans. (3)
Nitration is electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Methoxy and amino groups are strongly activating groups. Methyl group is weakly activating group.
Since among methyl and methoxy group, methoxy group is more reactive than methyl group, (c) is more reactive than (d).
Even-though amino group is strongly activating group, it gets protonated in presence of acid to form anilinium ion which is strongly deactivating. Hence, (a) is less reactive than (c) and (d).
Note:
The activating groups increases the electron density on benzene ring and increases the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The deactivating groups decreases the electron density on benzene ring and decreases the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Q.29. Products A and B formed in the following reactions are respectively: (2018)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (1)

Q.30. Which of the following compounds will form significant amount of meta product during mono-nitration reaction? (2017)
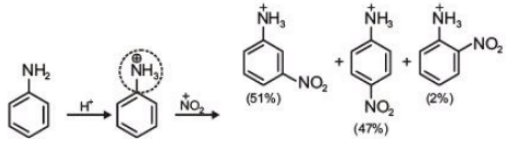
(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)
(a) Nitration reactions take place in presence of concentrated HNO3+ concentrated H2SO4.
(b) Aniline acts as a base. In presence of H2SO4, its protonation takes place and anilinium ion is formed
(c) Anilinium ion is a strongly deactivating group and meta directing in nature so it gives meta nitration product in a significant amount.

Q.31. The major product expected from the following reaction is: (2017)

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 
(4) 
Ans. (3)

Q.32. A mixture containing the following four compounds is extracted with 1 M HCl. The compound that goes to aqueous layer is: (2017)




(1) IV
(2) II
(3) I
(4) III
Ans. (2)
A mixture containing four compounds is extracted with 1M HCl. The compound that goes to aqueous layer is compound (II) It is an amine. Pure amine is water insoluble. On reaction with HCl, it forms hydrochloride salt which is water soluble.
Hence, the option (2) is correct answer.
Q.33. Among the following compounds, the increasing order of their basic strength is: (2017)




(1) (II) < (I) < (III) < (IV)
(2) (II) < (I) < (IV) < (III)
(3) (I) < (II) < (IV) < (III)
(4) (I) < (II) < (III) < (IV)
Ans. (1)
Order of basicity

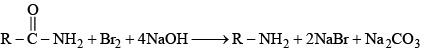
Q.34. In the Hofmann bromamide degradation reaction, the number of moles of NaOH and Br2 used per mole of amine produced are: (2016)
(1) One mole of NaOH and one mole of Br2.
(2) Four moles of NaOH and two moles of Br2.
(3) Two moles of NaOH and two moles of Br2.
(4) Four moles of NaOH and one mole of Br2.
Ans. (4)

Q.35. The test to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amine is: (2017)
(1) Mustard oil test
(2) C6H5SO2Cl
(3) Sandmeyer's reaction
(4) Carbylamine reaction
Ans. (2)
Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) is used to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
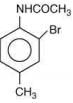
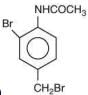
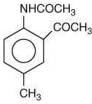
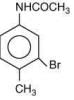
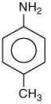
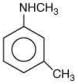
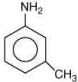
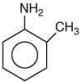
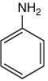
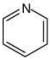
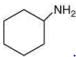
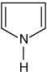
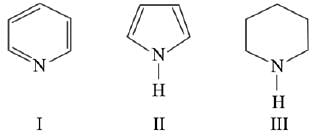
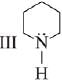 is most basic as the lone pair of nitrogen is easily available for the donation.
is most basic as the lone pair of nitrogen is easily available for the donation.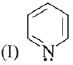 lone pair is not in-volved in resonance but nitrogen atom is sp2 hybrid-sed whereas in compound II the lone pair of nitrogen is involved in aromaticity which makes it least basic.
lone pair is not in-volved in resonance but nitrogen atom is sp2 hybrid-sed whereas in compound II the lone pair of nitrogen is involved in aromaticity which makes it least basic.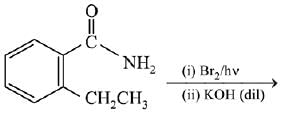
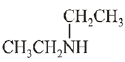
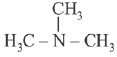
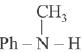


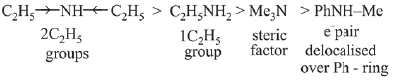
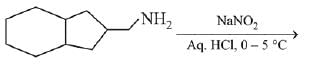
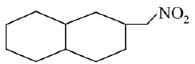
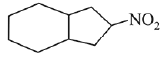
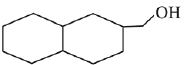
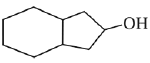
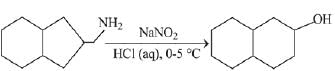
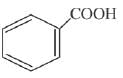
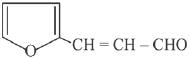
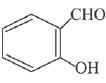
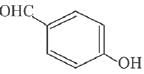
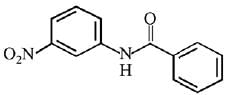
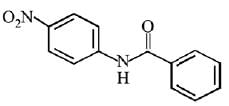
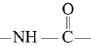 is activating while,
is activating while, 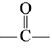 part is deactivating group.
part is deactivating group.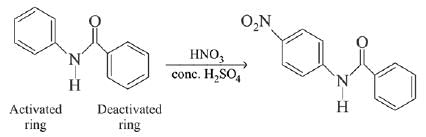
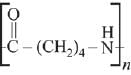
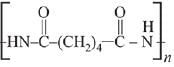
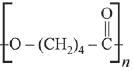
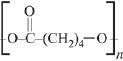
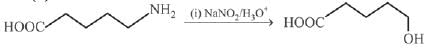
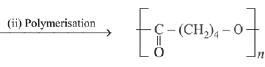
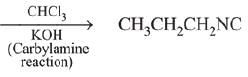
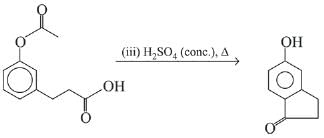
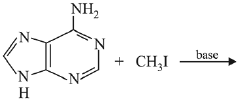
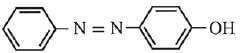
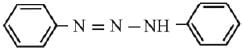
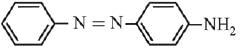
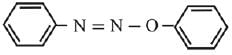
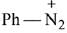 takes place with aniline.
takes place with aniline.