Primary Memory | Computer Architecture & Organisation (CAO) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Primary memory is a segment of computer memory that can be accessed directly by the processor. In a hierarchy of memory, primary memory have access time less than secondary memory and greater than cache memory. Generally, primary memory has a storage capacity lesser than secondary memory and greater than cache memory.
Need of Primary Memory
In order to enhance the efficiency of the system, memory is organized in such a way that access time for the ready process is minimized. The following approach is followed to minimize access time for the ready process.
- All programs, files, and data are stored in secondary storage that is larger and hence has greater access time.
- Secondary memory can not be accessed directly by a CPU or processor.
- In order, to execute any process operating system loads the process in primary memory which is smaller and can be accessed directly by the CPU.
- Since only those processes are loaded in primary memory which is ready to be executed, the CPU can access those processes efficiently and this optimizes the performance of the system.
This organization of memory in a stepwise manner is known as Memory Hierarchy.
Classification of Primary Memory
Primary memory can be broadly classified into two parts:
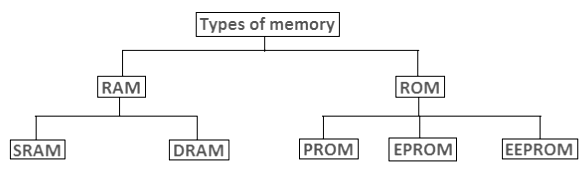
- Read-Only Memory (ROM)
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
Read-Only Memory
Any data which need not be altered are stored in ROM. ROM includes those programs which run on booting of the system (know as a bootstrap program that initializes OS) along with data like algorithm required by OS. Anything stored in ROM cannot be altered or changed.
Types of ROM:
ROM can be broadly classified into 4 types based on their behavior:
- MROM: Masked ROM are hardwired and pre-programmed ROM. Any content that is once written cannot be altered anyhow.
- PROM: Programmable ROM can be modified once by the user. The user buys a blank PROM and writes the desired content but once written content cannot be altered.
- EPROM: Erasable and Programmable ROM Content can be changed by erasing the initial content which can be done by exposing EPROM to UV radiation. This exposure to ultra-violet light dissipates the charge on ROM and content can be rewritten on it.
- EEPROM: Electrically Erasable and Programmable ROM Content can be changed by erasing the initial content which could be easily erased electrically. However, one byte can be erased at a time instead of deleting in one go. Hence, reprogramming of EEPROM is a slow process.
Random Access Memory
Any process in the system which needs to be executed is loaded in RAM which is processed by the CPU as per Instructions in the program. Like if we click on applications like Browser, firstly browser code will be loaded by the Operating system into the RAM after which the CPU will execute and open up the Browser.
Types of RAM:
RAM can be broadly classified into SRAM (Static RAM) and DRAM (Dynamic RAM) based on their behavior:
- DRAM: Dynamic RAM or DRAM needs to periodically refresh in few milliseconds to retain data. DRAM is made up of capacitors and transistors and electric charge leaks from capacitors and DRAM needs to be charged periodically. DRAM is widely used in home PCs and servers as it is cheaper than SRAM.
- SRAM: Static RAM or SRAM keeps the data as long as power is supplied to the system. SRAM uses Sequential circuits like a flip-flop to store a bit and hence need not be periodically refreshed. SRAM is expensive and hence only used where speed is the utmost priority.
Primary Memory is volatile in nature?
Content of primary memory may or may not vanish when power is lost depending on if it is stored in RAM or ROM.
- Content of ROM is non-volatile in nature, they are stored even when power is lost.
- Content of RAM is volatile in nature, it vanishes when power is lost.
When cache memory comes into existence?
Data in primary memory can be accessed faster than secondary memory but still, access times of primary memory are generally in few microseconds, whereas CPU is capable of performing operations in nanoseconds. Due to the time lag between accessing data and acting of data performance of the system decreases as the CPU is not utilized properly, it may remain idle for some time. In order to minimize this time gap new segment of memory is Introduced known as Cache Memory.
|
20 videos|105 docs|48 tests
|
|
20 videos|105 docs|48 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|


















