Primary Sources of Data: Qualitative Methods | Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Interviews: Unstructured or In-Depth |

|
| Evaluation of Unstructured Interviews |

|
| Interviews: Group Interviews |

|
| Observation: Participant |

|
| Observation: Non-Participant |

|
| Case Studies |

|
Interviews: Unstructured or In-Depth
In qualitative research, sociologists employ unstructured or in-depth interviews, which lack a standardized interview schedule, allowing flexibility in the interview process.
In-depth interviews vary from completely unstructured to semi-structured formats. A completely unstructured interview resembles a purposeful conversation, where the interviewer may pose an initial question, enabling the interviewee to freely discuss their experiences. In contrast, a semi-structured interview involves a list of questions, topics, or issues the interviewer aims to address, which can be explored in any order, with the flexibility to pursue topics raised by the interviewee.
Evaluation of Unstructured Interviews
Advantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- They offer flexibility, allowing interviewers to clarify questions and ask probing follow-up questions, unlike standardized methods.
- Respondents can express their views in their own words, raising significant points the researcher may not have considered.
- Rich, detailed data is collected, providing deep insights into interviewees’ experiences.
- Complex issues can be explored, resulting in high-validity data.
- Sociologists can build strong rapport with interviewees, facilitating exploration of sensitive topics.
- Feminist sociologists favor in-depth interviews for fostering an equal relationship between interviewer and interviewee, enabling open expression of experiences and emotions.
Disadvantages of Unstructured Interviews:
- They are time-consuming and costly, requiring trained and salaried interviewers.
- Encouraging interviewees to open up and sustain conversation can be challenging, even with training, potentially reducing data validity if respondents are reserved.
- The absence of a standardized schedule makes replication difficult, leading to low reliability.
- The small sample size limits generalizability compared to survey research.
- The interviewer effect, where unintentional influence or leading questions skew responses, can undermine data validity.
- Interview bias and social desirability bias may lead interviewees to provide answers they believe are expected or socially favorable, reducing data validity.
Interviews: Group Interviews
Group interviews involve a researcher interviewing multiple participants simultaneously on various topics. They are typically associated with qualitative research and may complement other methods. A focus group, a specific type of group interview, centers on one topic, examining how participants interact and respond to each other’s perspectives.
Evaluation of Group Interviews
Advantages of Group Interviews
- They provide access to diverse perspectives and experiences, making them valuable for exploring topics.
- Interviewing multiple people at once saves time and reduces costs.
- The group setting may make participants feel more comfortable discussing experiences due to peer support.
- Group dynamics can inspire new ideas for the researcher to explore.
Disadvantages of Group Interviews
- Participants may influence each other, and dominant voices can overshadow others, limiting equal participation.
- Managing group discussions, especially on sensitive topics, can be challenging for the researcher.
- Transcribing discussions is difficult when participants talk over one another.
- Confidentiality cannot be guaranteed, raising ethical concerns.
Observation: Participant
Sociologists use participant observation (PO) to study people in everyday settings by joining their activities, either overtly or covertly, to record observations over time. PO is common in ethnographic studies to explore social and cultural influences on groups.
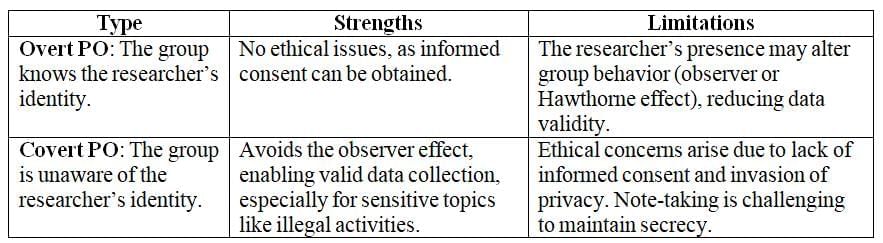
Evaluation of Participant Observations
Advantages of Participant Observations
- Researchers observe groups in their natural environments, unlike standardized methods like surveys.
- Long-term engagement allows rapport-building, yielding valid data.
- Observing from the group’s perspective provides deep, rich data.
- PO may be the only viable method for studying groups resistant to interviews, such as drug users or religious cults.
Disadvantages of Participant Observations
- PO is often more time-consuming and expensive than other methods.
- Researchers may become overly involved, leading to biased findings and reduced data validity.
- The unique nature of PO makes replication impossible, limiting reliability and generalizability.
- Gaining entry and building trust with the group can be challenging.
Observation: Non-Participant
Non-participant observation involves observing a group’s activities in their natural setting without participating. The researcher may be present, use video recordings, or employ an observation schedule to systematically log behaviors at regular intervals (e.g., noting classroom activities every 30 seconds).
Evaluation of Non-Participant Observations
Advantages of Non-Participant Observations:
- Using an observation schedule allows replication to verify reliability, supporting generalizability.
- Non-participant observers remain detached, maintaining objectivity and collecting highly valid data.
Disadvantages of Non-Participant Observations:
- The observer’s external position hinders rapport-building, reducing data validity.
- Non-participation limits understanding of the group’s social world or dynamics, further affecting data validity.
Case Studies
Sociologists conduct case studies, such as Ball’s (1981) study on banding and expectations in a mixed comprehensive school. A case study is a detailed, often longitudinal examination of an institution (e.g., a school or hospital) or a series of related events (e.g., moral panics like mods and rockers). They typically produce qualitative data using methods like in-depth or group interviews, observation, or mixed methods. Researchers may use triangulation, comparing case study data with secondary sources like official statistics or questionnaires.
Evaluation of Case Studies
Advantages of Case Studies:
- They allow exploration of complex issues, yielding high-validity data compared to standardized methods.
- Mixed methods provide rich, detailed insights into real-life situations, enhancing data validity.
Disadvantages of Case Studies:
- Small sample sizes limit representativeness, making generalization difficult.
- Ethical issues, such as lack of informed consent or confidentiality, may arise (e.g., identifying a school’s location despite anonymity).
|
131 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Primary Sources of Data: Qualitative Methods - Sociology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are unstructured interviews and how do they differ from structured interviews? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using in-depth interviews in qualitative research? |  |
| 3. How do group interviews work and what are their benefits? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between participant observation and non-participant observation? |  |
| 5. What are case studies and how are they used in qualitative research? |  |














