Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Notes > Civil Law for Judiciary Exams > Primary and Secondary Evidence
Primary and Secondary Evidence | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Primary Evidence |

|
| Understanding Secondary Evidence |

|
| Difference Between Primary and Secondary Evidence |

|
| Judicial Pronouncements on Primary and Secondary Evidence |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
The legal system relies on evidence to establish facts and ensure just outcomes. Primary and secondary evidence are crucial concepts defined by the Indian Evidence Act.
Primary Evidence
- Primary evidence, or best evidence, are original documents presented in court without prior notice. They hold the highest value and take precedence over secondary evidence. For example, a signed contract is primary evidence in a breach of contract case.
- Primary evidence is irreplaceable and offers the most accurate representation of a fact. If the original document is lost, a certified copy can serve as primary evidence, ensuring the reliability of information.
Understanding Secondary Evidence
- Secondary evidence is information presented when primary evidence is not available.
- It serves as a replacement for the original evidence, such as copies or duplicates.
- In legal contexts, secondary evidence is generally considered less reliable than primary evidence.
- If primary evidence is inaccessible and the reason for its unavailability is explained, secondary evidence may be accepted in court.
Acceptance of Secondary Evidence
- Secondary evidence must be justified by demonstrating the unavailability of primary evidence.
- It can only be introduced when there is a valid reason for the absence of primary evidence.
Example of Secondary Evidence
- If a crucial document is lost due to a fire and cannot be produced in court, a copy of the document may be considered secondary evidence.
- When a witness cannot be present to testify, a recorded statement of their testimony could serve as secondary evidence.
Question for Primary and Secondary EvidenceTry yourself: What is primary evidence?View Solution
Difference Between Primary and Secondary Evidence
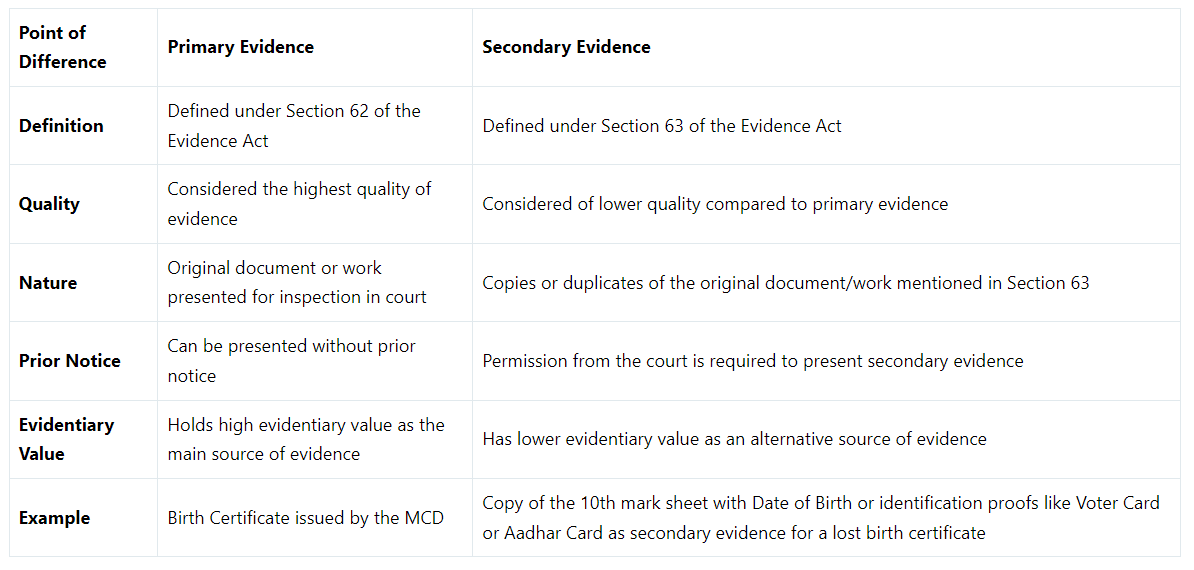
Judicial Pronouncements on Primary and Secondary Evidence
- Importance of Primary and Secondary Evidence:
- Primary evidence holds utmost importance in legal proceedings.
- Secondary evidence is admissible only in the absence of primary evidence.
- J. Yashoda v. Smt. K. Shobha Rani (2007):
- Secondary evidence can be presented only if primary evidence is unavailable.
- Failure to prove the validity of the original document prohibits the introduction of secondary evidence regarding its contents.
- H. Siddiqui (dead) by LRs Vs. A. Ramalingam (2011):
- Court requires a rational reason and factual basis for the non-production of original documents to permit the use of secondary evidence.
- Rakesh Mohindra v. Anita Beri and Ors. (2016):
- Establishing a plausible reason for the non-production of primary evidence is necessary before presenting secondary evidence.
- Acceptance of secondary evidence is contingent upon proving the loss, destruction, or intentional withholding of original documents by the opposing party.
- Chandra v. M. Thangamuthu (2010):
- Secondary evidence must be authenticated with foundational evidence to ensure it is a true replica of the original.
- Exceptions to the primary evidence rule aim to assist parties unable to produce the original document due to uncontrollable circumstances.
Conclusion
- In the legal system, the distinction between primary and secondary evidence holds significant importance when establishing facts and presenting proof. Primary evidence, considered the highest quality of evidence, comprises original documents or works presented directly to the court for inspection. It stands as the main and most reliable source of evidence, carrying substantial evidentiary value.
- On the contrary, secondary evidence serves as a substitute for primary evidence when the latter is unavailable. Despite being of lower quality, secondary evidence can be admitted if the party provides a valid justification for the non-production of primary evidence. However, the court demands a rational explanation and a factual foundation for the introduction of secondary evidence.
- Judicial pronouncements have illuminated the importance of primary evidence and set forth stringent criteria for the admission of secondary evidence. These pronouncements underscore that secondary evidence can only be accepted under circumstances where primary evidence cannot be produced due to factors beyond the control of the party. The authentication and establishment of the genuineness of the secondary evidence are also crucial prerequisites for its admissibility. This framework ensures the reliability and integrity of evidence presented in legal proceedings.
Question for Primary and Secondary EvidenceTry yourself: When can secondary evidence be presented in a legal proceeding?View Solution
The document Primary and Secondary Evidence | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams is a part of the Judiciary Exams Course Civil Law for Judiciary Exams.
All you need of Judiciary Exams at this link: Judiciary Exams
|
363 docs|256 tests
|
FAQs on Primary and Secondary Evidence - Civil Law for Judiciary Exams
| 1. What is primary evidence? |  |
Ans. Primary evidence refers to the original document or material object that is presented as evidence in court. It is considered to be the best evidence available.
| 2. What is secondary evidence? |  |
Ans. Secondary evidence is evidence that is not the original document or object but is used to prove the content of the original document. It is considered less reliable than primary evidence.
| 3. When is secondary evidence accepted in court? |  |
Ans. Secondary evidence is accepted in court when the original primary evidence is not available or cannot be produced. The party seeking to introduce secondary evidence must provide a valid reason for not being able to produce the original.
| 4. Can you provide an example of secondary evidence? |  |
Ans. An example of secondary evidence is a photocopy of a document when the original document is lost or unavailable. The photocopy is considered secondary evidence and can be used in court to prove the content of the original document.
| 5. What is the difference between primary and secondary evidence? |  |
Ans. The main difference between primary and secondary evidence is that primary evidence is the original document or object, while secondary evidence is a copy or substitute for the original. Primary evidence is considered more reliable and is preferred in court.
Related Searches















