Principles of Non-Finite Verbs (Part - 2) | English Class 8 PDF Download
Participle
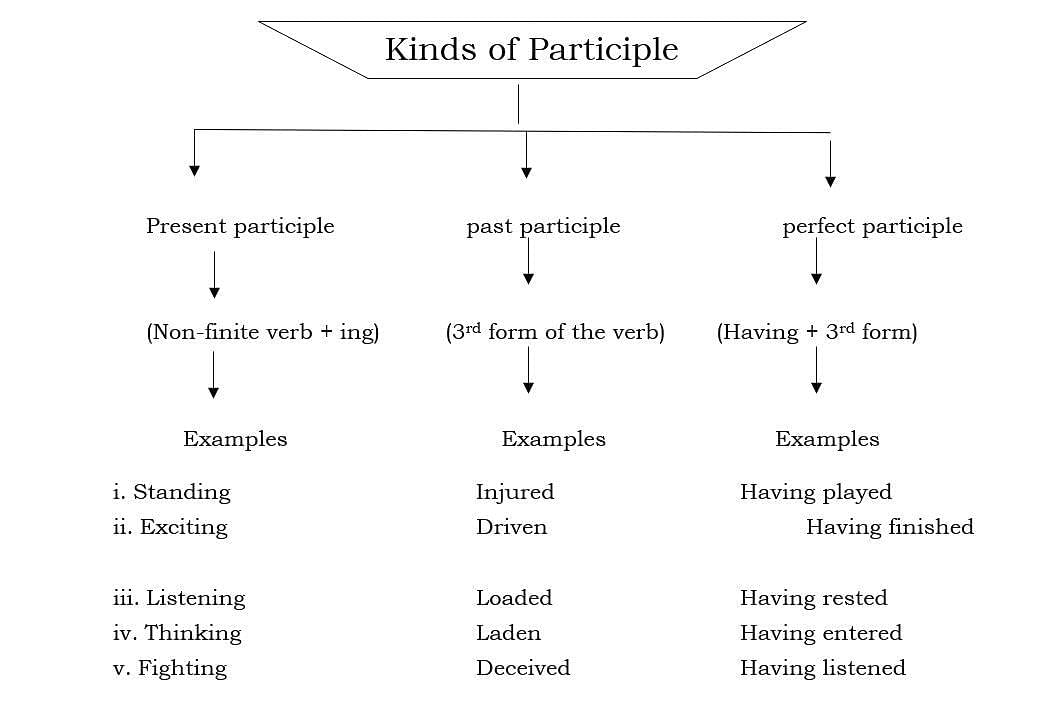
A Participle is the form of verb that has the characteristics of a verb as well as an adjective. Its form is Verb + Adjective = Participle. For example; He told me an amusing incident. Participles are of Three Types:
- Present Participle
- Perfect Participle
- Past Participle
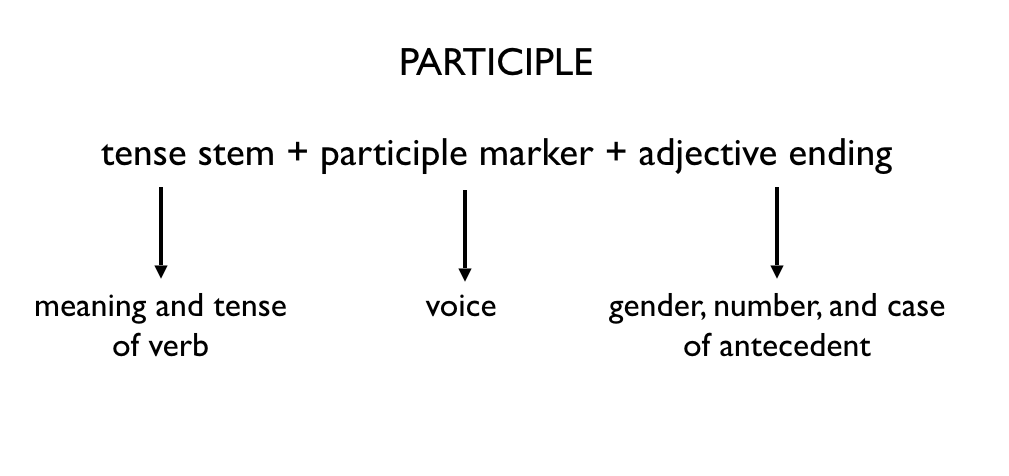
1. Present Participle:
- Form: V1 + ing; as talking, singing, working, etc.
Uses of Present Participle
- As an adjective; e.g.,
(i) It was an interesting story.
(ii) I saw a drowning man.
In the above sentences, the bold words are Present Participles used as adjectives. - As a subject complement; e.g.,
(i) This film is entertaining.
(ii) She entered the room sobbing.
In the above sentences, the bold words are Present Participles used as subject complement. - As an object complement; e.g.,
(i) I saw the man digging the field.
(ii) He left me crying.
In the above sentences, the bold words are Present Participles used as an object complement. - To combine main sentences; e.g.,
(i) The criminal saw the police. He ran away.
Seeing the police, the criminal ran away.
(ii) We entered the room. We were talking.
We entered the room talking.
2. Perfect Participle:
- Form: Having + V3 (past participle)
Uses of Perfect Participle
- In Active voice — having + past participle; as having done.
- In Passive voice — having been + past participle; as having been done.
Present Participles help to combine sentences; e.g.
(i) I have completed the task. I want to play with my friends.
Having completed the task, I want to play with my friends. (Active Voice)
(ii) They collected money. They went to see a movie.
Having collected money, they went to see a movie. (Active Voice)
(iii) The man was caught. He became upset.
Having been caught, the man became upset. (Passive Voice)
(iv) The dance lesson was completed. The girls started chatting.
The dance lesson having been completed, the girls started chatting. (Passive Voice)
3. Past Participle:
- Form: V1 + –d/ –ed/ –en/ –n
Uses of Past Participle
- As an adjective; e.g.,
(i) I picked up fallen leaves.
(ii) The tired man slept soundly.
In the above sentences, the bold words are Past Participles used as an adjective. - As a subject complement; e.g.,
(i) The girl looks worried.
(ii) The shop was burnt.
In the above sentences, the bold words are Past Participles used as a subject complement. - To combine sentences; e.g.,
(i) She entered the room. She was accompanied by her sister.
Accompanied by her sister, she entered the room.
(ii) He was alerted by the sound. He leapt to his feet.
Alerted by the sound, he leapt to his feet.
|
36 videos|330 docs|56 tests
|
FAQs on Principles of Non-Finite Verbs (Part - 2) - English Class 8
| 1. What are participles and how are they used in sentences? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of sentences using present and past participles? |  |
| 3. How do participles function in passive voice constructions? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a participle and a gerund? |  |
| 5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid when using participles? |  |





















