Probability Distribution (Part - 2) | Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Probability Distributions |

|
| Important Terminology |

|
| Types of Probability Distributions |

|
| Discrete Probability Distributions |

|
| Continuous Probability Distribution |

|
Probability Distributions
- A probability distribution is a mapping of all the possible values of a random variable to their corresponding probabilities for a given sample space.
- The probability distribution is denoted as P(X = x) which can be written in short form as P(x)
Important Terminology
Before discussing Probability distributions in detail, we should know the following terminology1. Probability Function
- The probability distribution can also be referred to as a set of ordered pairs of outcomes and their probabilities. This is known as the Probability function f(x).
2. Probability Mass Function (PMF)
- A function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to a specific value.
- Mathematical Representation:
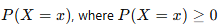 and
and 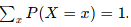
3. Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF)
- The Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) is defined as the probability that a random variable X with a given probability distribution f(x) will be found at a value less than x.
- The cumulative distribution function is a cumulative sum of the probabilities up to a given point.
- The CDF is denoted by F(x) and is mathematically described as:
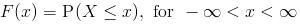
4. Moment Generating Functions (MGF)
- For a random variable X, the moment generating function MX(t) is defined as:
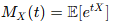 , where t is a real number and
, where t is a real number and 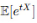 is the expected value of etx
is the expected value of etx
Types of Probability Distributions
Probability Distributions are basically of two types
1. Discrete Probability Distribution
2. Continuous Probability Distribution
Now we will further discuss Discrete and Continuous Probability distributions and their types
Discrete Probability Distributions
- A discrete probability distribution is a statistical function that describes the probability of each possible outcome in a discrete random experiment. In this distribution, the set of possible outcomes is finite or countably infinite, and each outcome has an associated probability. These probabilities must satisfy two conditions:
Non-negativity: For every outcome xi, the probability P(xi) is greater than or equal to 0.
P(xi) ≥ 0, for all i.Normalization: The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes must equal 1.
In mathematical terms:
∑ P(xi) = 1,
where the summation runs over all possible outcomes.
- For example, the probability of obtaining a certain number x when you toss a fair die is given by the probability distribution table below.
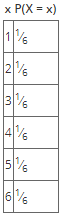
- For a discrete probability distribution, the set of ordered pairs (x,f(x)), where x is each outcome in a given sample space and f(x) is its probability, must follow the following:
P(X = x) = f(x)
f(x) ≥ 0
∑x f(x) = 1 - Discrete Probability distributions are subdivided into the following types
1. Poisson Distribution
- PMF:
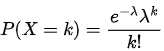
- Expected Value (E(X)): λ
- Variance (Var(X)): λ
- Moment Generating Function (M(t)):
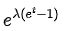
2. Binomial Distribution (X∼B(n,p)
- PMF:
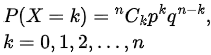
- Expected Value (E(X)): np
- Variance (Var(X)): npq
- Moment Generating Function (M(t)): (q + pet )n
3. Uniform Distribution
- Expected Value (E(X)): (n+1)/2
- Variance (Var(X)): (n2-1)/12
- Moment Generating Function (M(t)):
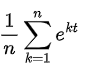
 |
Download the notes
Probability Distribution (Part - 2)
|
Download as PDF |
4. Two-Point Distribution
- PMF:
P(X = a) = p
P(X=b) = 1 = P - Expected Value (E(X)): ap + b(1-p)
- Variance (Var(X)): p(1-p)(a-b)2
- Moment Generating Function (M(t)): peat + (1-p)
Continuous Probability Distribution
- A Continuous Probability Distribution is a probability distribution in which the random variable can take any value within a given range.
- Unlike discrete distributions, where the random variable takes on distinct, separate values, continuous distributions represent outcomes that form a continuum.
- Consequently, the continuous probability distribution is found as
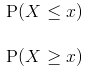
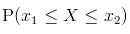
and so on. - While a discrete probability distribution is characterized by its probability function (also known as the probability mass function), continuous probability distributions are characterized by their probability density functions.
- Since we look at regions in which a given outcome is likely to occur, we define the Probability Density Function (PDF) as the a function that describes the probability that a given outcome will occur at a given point.
This can be mathematically represented as: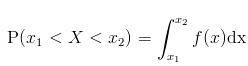
- In other words, the area under the curve, For a continuous probability distribution, the set of ordered pairs (x,f(x)), where x is each outcome in a given sample space and f(x) is its probability, must follow the following:
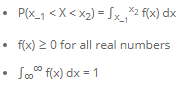
- Cumulative Distribution Function for a Continuous Probability Distribution
- Following are the types of Continuous Probability Distributions,
1. Uniform Distribution:
X is said to have uniform distribution on [a,b] if its PDF is given by 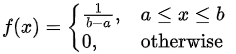
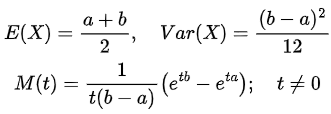
2. Gamma Distribution:
An R.V. X is said to have gamma distribution with parameters a and p if its PDF is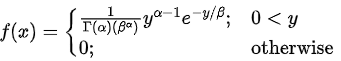 we write X∼G (α,β)
we write X∼G (α,β)
E(X) = αβ
Var (X) = αβ2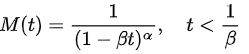
3. Beta Distribution:
An R.V. X is said to have beta distribution with parameters α&β (α > 0, β > 0) if its PDF is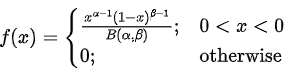 we write X∼B (α,β)
we write X∼B (α,β)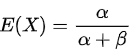
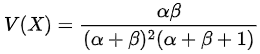
Note: if α = β = 1, we have U(0,1)
4. Cauchy Distribution:
An R.V. is said to have Cauchy distribution with parameters μ and θ if its PDF is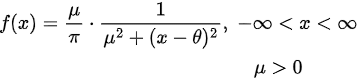
we write X∼C (μ,θ)
|
2 videos|44 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Probability Distribution (Part - 2) - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics
| 1. What is a probability distribution? |  |
| 2. What are the types of probability distributions? |  |
| 3. How is the mean calculated in a probability distribution? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between discrete and continuous probability distributions? |  |
| 5. How are probability distributions used in real-life applications? |  |






















