Production & Use of Fertilisers | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
What are fertilisers?
Fertilisers provide mineral ions needed for healthy growth in plants. As plants grow, they absorb mineral ions from the water in the soil through their root hair cells. Over time, the concentration of these ions decreases, so farmers and gardeners add fertilisers to the soil. Fertilisers are usually sold as solid powders or granules
Fertilisers are usually sold as solid powders or granules
Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
Fertilisers are formulations which may contain nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium compounds to promote plant growth. Fertilisers that supply all three elements are often called NPK fertilisers, after the chemical symbols for these three elements.Fertiliser compounds must be soluble in water so they can be absorbed by the root hair cells:
- ammonium ions, NH4+, and nitrate ions, NO3-, are sources of soluble nitrogen
- phosphate ions, PO43-, are a source of soluble phosphorus
- all common potassium compounds dissolve in water to produce potassium ions, K+
The table shows some examples of fertilisers, their formula and the essential elements they provide: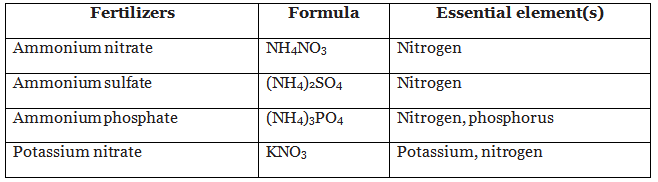
Example: Urea, (NH2)2CO, is used as a fertiliser. Name the essential element it provides.
Nitrogen
The Importance of Ammonia in making Fertilisers
- Ammonia (NH3) is an alkali and when it is involved in neutralisation reactions, it produces the ammonium ion (NH4+) which is present in lots of fertilisers.
- However, ammonia can also be oxidised to make nitric acid (HNO3), which is the source of the nitrate ion (NO3-).
- Ammonia can be neutralised by nitric acid, to make the salt ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). This can be represented by the following equation:
NH3 + HNO3 → NH4NO3 - When this reaction takes place in aqueous solution, the reaction is more correctly represented by the following equation:
Ammonium hydroxide + nitric acid → ammonium nitrate + water
NH4OH + HNO3 → NH4NO3 + H2O
Mining Raw Mmaterials for Fertilisers
- Minerals are extracted from the crust which can be used as fertilisers or as raw materials from which to make fertilisers.
- Potassium chloride and potassium sulfate can be used as fertilisers because they contain potassium ions.
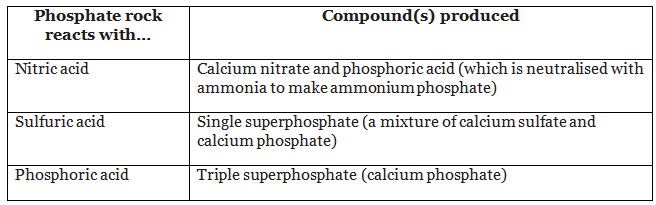
- Phosphate rock cannot be used as a fertiliser because it is insoluble but it can be used to make fertilisers.
- Phosphate rock contains phosphorus compounds. When it reacts with acids, useful soluble compounds are made:
Role of NPK Fertilisers in Plant Growth
- Compounds containing nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus are used as fertilisers to increase crop yields
- NPK fertilisers are formulations containing appropriate ratios of all three elements
- From these three essential elements:
- Nitrogen promotes healthy leaves,
- Potassium promotes growth, healthy fruit and flowers
- Phosphorus promotes healthy roots
- A distinct advantage of artificial fertilisers is that they can be designed for specific needs whereas in natural fertilizers, such seaweed or manure, the proportions of elements cannot be controlled
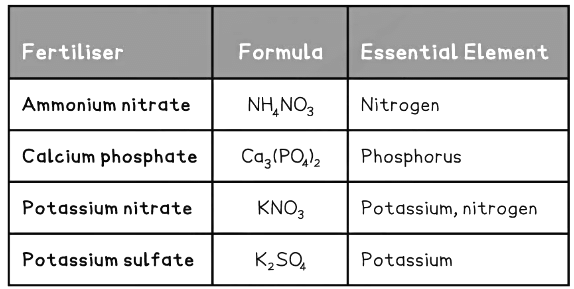
- Fertiliser compounds contain the following water soluble ions:
- Ammonium ions, NH4+ and nitrate ions, NO3–, which are sources of soluble nitrogen
- Phosphate ions, PO43-, which are a source of soluble phosphorus
- Most common potassium compounds dissolve in water to produce potassium ions, K+
Exam Tip
Fertilisers must be water soluble so the nutrients they provide can be effectively absorbed and transported by the plant.
Use of Ammonia in Manufacturing Fertilisers
- Ammonia is an alkaline substance and neutralises acids producing a salt and water
- The salt it produces contains the ammonium ion, NH4+, which is a component of several fertilisers
- Ammonia also undergoes oxidation to produce nitric acid, HNO3
- Nitric acid is used as the source of the nitrate ion, NO3–, which is another important ion found in fertilisers
- Ammonium nitrate, a fertiliser and one of the most important ammonium salts, is made by reacting ammonia with nitric acid:
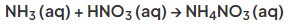
- It is prepared on large scale industrial proportions but can also be prepared in the laboratory using a different method
- In the laboratory it is prepared by titrating ammonia with sulfuric acid:
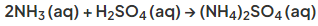
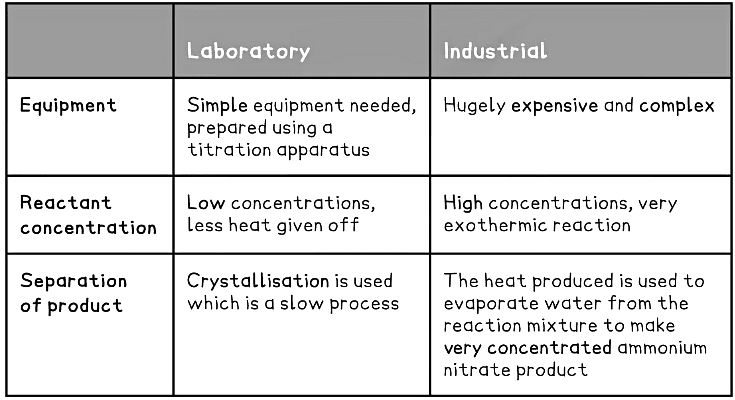
Exam Tip
Notice that when writing ammonia solution as NH3 (aq), water does not appear to be a product of the neutralisation reaction. However, ammonia solution may also be written as, NH4OH (aq), ammonium hydroxide, in which case water is produced:
NH4OH (aq) + HNO3 (aq) → NH4NO3 (aq) + H2O (l)
Either formula may be used to show the reactions.
Use of Phosphate Rock
- The Earth’s crust also contains useful minerals which are useful raw materials for making fertilisers
- Phosphate rocks contain potassium chloride and potassium sulfate as they provide potassium
- The rock itself is insoluble in water to it is usually reacted with acid to produce useful compounds with water soluble compounds:
- With nitric acid, phosphoric acid and calcium nitrate are produced
- The phosphoric acid is neutralised with ammonia forming ammonium phosphate
- With sulfuric acid, a mixture of calcium phosphate and calcium sulfate is produced - this is know as single superphosphate
- With phosphoric acid, calcium phosphate is produced - this is known as triple superphosphate
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|



















