Programming Concept | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Programming Language |

|
| Terms Related to Programming |

|
| Language Translator |

|
| Generations of Programming Languages |

|
| Algorithm |

|
| Flow Chart |

|
| Error |

|
A program can be defined as a sequence of instructions designed to perform a specific computing task. The individual who writes or executes these instructions is known as a programmer. Programmers use specialized languages, known as programming languages, to create programs. Examples of these languages include C and Java. Ada Lovelace is celebrated as the world's first programmer.
Programming Language
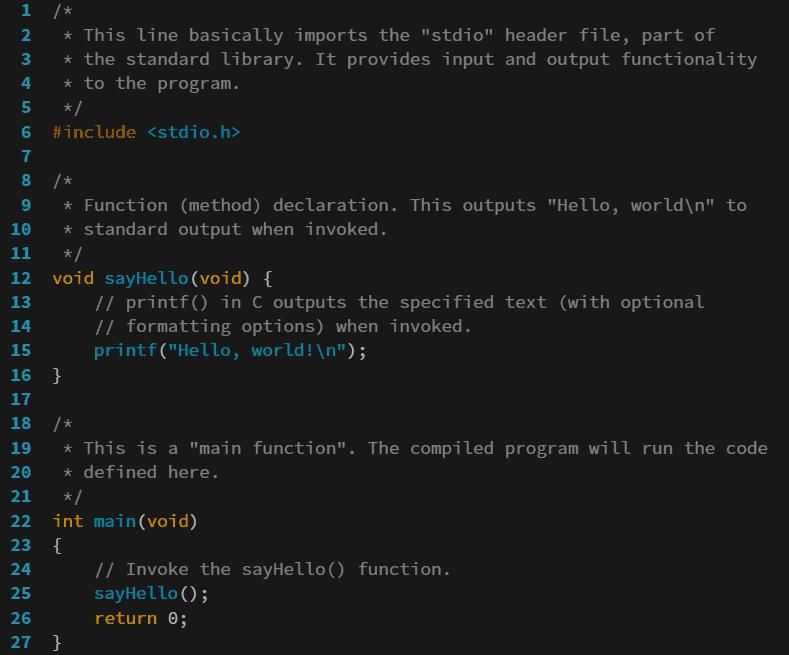
- Programming language: A programming language consists of commands, instructions, and syntax used to develop software.
- Straightforward: It should be straightforward, easy to learn, and consistent in its syntax and semantics.
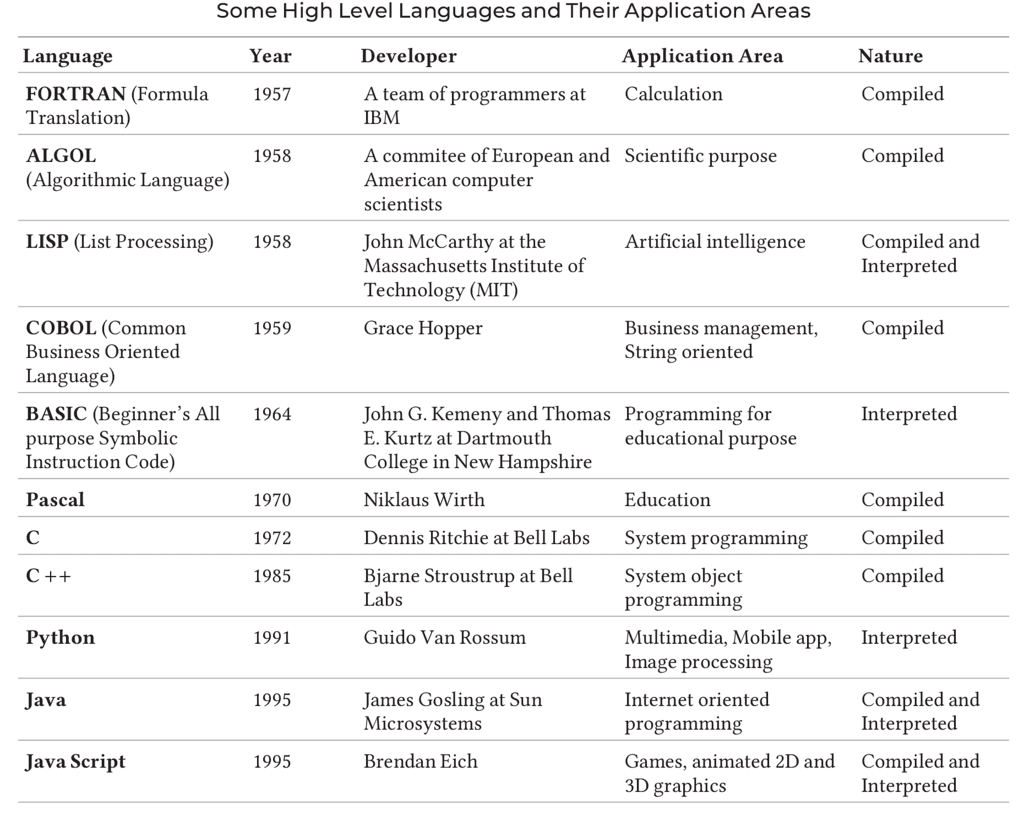
Programming languages are broadly categorized into three types:
Low-Level Languages (LLL)
These are more complex and operate directly with a computer's instruction set, often used for system software development.
- Machine Language: The only language that computers natively understand, often referred to as machine code, object code, or binary language. It consists of binary digits (0s and 1s) that computers read and interpret.
- Assembly Language: A low-level language that provides a more human-readable way to interact with computer hardware through structured commands that replace binary code.
Medium-Level Languages (MLL)
- These languages act as an intermediary between raw hardware and the programming layer of a computer system, designed to enhance the efficiency of translated code before it is processed. An example is C.
High-Level Languages (HLL)
- Advanced programming languages that are not tied to a specific computer system and are designed for specific tasks. They are generally easier to understand and use.
- The main advantages of high level languages over low level languages is that they are easier to read, write and understand. e.g. BASIC, C, FORTRAN, Java, Python, etc.
Terms Related to Programming
- Program Documentation: This refers to detailed documentation that provides a thorough procedural description of a program. It explains how the software is constructed and outlines what the program does, including the requirements for input data and the effects of executing specific programming tasks.
- OOP (Object-Oriented Programming): OOP is a programming paradigm where programs are viewed as collections of objects. Each object is an instance of a class, and the focus is on using these objects to design and implement software.
- Debugging: Debugging is the process of identifying, fixing, or bypassing errors (bugs) in computer program code.
Language Translator
It converts programming language into machine language.
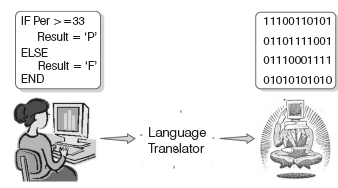
Depending on the programming language used, language translators fall into three categories:
Assembler: Converts a program written in assembly language into machine language. Assembly language uses mnemonic codes that are machine-dependent and can be challenging to learn.
- Interpreter: Converts a high-level language (HLL) program into machine language line-by-line. It halts execution and reports errors immediately if they occur, requiring the user to fix them before continuing. While interpreters are useful for debugging and are suitable for novice programmers, they are generally slower and consume less memory.
- Compiler: Translates an HLL program into machine language that the processor can understand. Each HLL requires a specific compiler. A compiler processes the entire program at once, creating an object program. Once compiled, the source program is no longer needed as the object program can be executed. The compiler reports all errors along with their line numbers.
Generations of Programming Languages
Programming languages are categorized into five generations, reflecting advancements in technology:
First Generation Languages (1GLs):
These are low-level languages such as machine language.Second Generation Languages (2GLs):
Also low-level, these languages include assembly language.Third Generation Languages (3GLs):
High-level languages like Java fall into this category.Fourth Generation Languages (4GLs):
These languages feature statements similar to human language and are commonly used in database and scripting programming.Fifth Generation Languages (5GLs):
These languages use visual tools to aid program development. Visual Basic is a notable example of a 5GL.
Algorithm
An algorithm is a methodical, step-by-step approach to solving a problem, often used in data processing, calculations, and other computer or mathematical tasks.
Flow Chart
- A flow chart visually represents the sequence of steps and decisions required to complete a process.
- Steps are illustrated within diagram shapes and connected by lines and directional arrows.
Error
An error, commonly known as a bug, is an unexpected issue that disrupts the proper functioning of a computer.
Types of Errors:
Errors are classified into four categories:
- Syntax Error: Occurs when the rules of the programming language are not followed. The compiler detects and reports these errors.
- Semantic Error: Happens when the statements in the program are not meaningful to the compiler, leading to issues in the code.
- Logical Error: Results in incorrect or undesired output due to errors in the program's logic.
- Runtime Error: Arises during program execution, typically due to illegal operations performed in the code.
Tit-Bits
- Reserved words are words that a programming language has set aside for its own use.
- Pseudocode is not a programming language, but simply an informal way of describing a program. It does not follow any syntax strictly.
- Looping is a control structure which is used in a program to execute a particular set of statements repeatedly.
- Data Flow Diagram (DFD) describes the processes that are involved in a system to transfer data from the input to the file storage and reports generation.
|
48 videos|32 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Programming Concept - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What is a programming language translator? |  |
| 2. What are the generations of programming languages? |  |
| 3. What is an algorithm in programming? |  |
| 4. How is a flow chart used in programming? |  |
| 5. How are errors handled in programming? |  |




















