Pronoun | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Pronouns? |

|
| 1. Personal Pronouns |

|
| 2. Possessive Pronouns |

|
| 5. Demonstrative Pronouns |

|
| 6. Interrogative Pronouns |

|
| 7. Relative Pronouns |

|
| 8. Indefinite Pronouns |

|
What are Pronouns?
When we speak or write, we often use different words instead of repeating the same noun. These words are called pronouns.
Pronouns are used to replace nouns and help avoid repetition.

1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are words used to replace specific people or things in a sentence.
- They help us avoid repeating nouns.
- Personal pronouns are categorised into three types based on who they refer to:
(a) First Person – the speaker
Singular: I (subject), me (object)
Example: I am going to the store. She saw me there.
Plural: we (subject), us (object)
Example: We are planning a trip. The teacher praised us.
(b) Second Person – the listener(s)
You (same form for singular and plural, subject or object)
Example: You are invited to the party. I will help you.
(c) Third Person – the person/thing spoken about
Singular:
(i) He (subject), him (object)
Example: He is reading a book. I saw him at the park.
(ii) She (subject), her (object)
Example: She likes to swim. I gave her a gift.
(iii) It (subject/object, for animals, objects, ideas)
Example: It is raining outside. I found it under the table.
Plural:
They (subject), them (object)
Example: They are going to the concert. I met them yesterday.
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are words that show ownership or possession. They replace nouns to avoid repeating the same noun in a sentence.
Here are the common possessive pronouns:
Mine (something belongs to me)
Example: This book is mine.Yours (something belongs to you)
Example: That bag is yours.His (something belongs to him)
Example: This coat is his.Hers (something belongs to her)
Example: The pencil is hers.Its (something belongs to an animal or thing – less common in usage)
Example: Every dog has its day; this victory is its.Ours (something belongs to us)
Example: This house is ours.Theirs (something belongs to them)
Example: The toys are theirs.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of the verb are the same person or thing. They show that the action of the verb is directed back to the subject.
Myself (I) → I made the cake myself.
Yourself (you, singular) → Did you hurt yourself?
Himself (he) → He dressed himself.
Herself (she) → She taught herself to play the piano.
Itself (it) → The cat washed itself.
Ourselves (we) → We enjoyed ourselves at the party.
Yourselves (you, plural) → Enjoy yourselves, boys.
Themselves (they) → They laughed at themselves.
4. Emphatic Pronouns
Emphatic pronouns use the same forms as reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself, etc.), but their function is different. They are used only to add emphasis to the subject, not as objects of the verb.
The mother herself visited the school.
We ourselves served the guests.
The town itself is not very large.
They themselves went there.
Note
Reflexive pronouns = subject and object are the same.
Example: She cut herself while cooking.Emphatic pronouns = add emphasis to the subject.
Example: She herself cooked the meal.
5. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point out specific objects or people and indicate their position relative to the speaker.
- This (singular, near)
Example: This is a present from my brother. - These (plural, near)
Example: These are her books. - That (singular, distant)
Example: That is my bike. - Those (plural, distant)
Example: Those are your books.
Using these pronouns helps clarify which specific objects or people are being referred to in a sentence.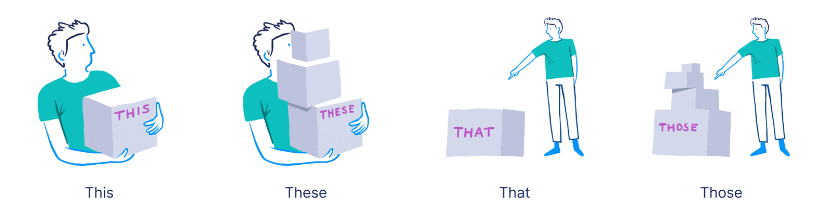
6. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They help gather information about people or things.
The main interrogative pronouns are:
- Who (asks about people)
Example: Who is coming to the party? - Which (asks about a specific choice from a group)
Example: Which book do you want to borrow? - What (asks about things or information)
Example: What are you doing?
Objective Case of 'Who': Whom?
When "who" is used as the object of a verb or preposition, it changes to "whom":
- Whom (object of a verb or preposition)
Example: Whom did you see at the store?
Possessive Case of 'Who': Whose?
When asking about possession, "who" changes to "whose":
- Whose (shows ownership)
Example: Whose bag is this?
7. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns link clauses or sentences and refer to nouns coming before them.
The common relative pronouns are:
- Who (refers to people)
Example: The teacher who helped me is very kind. - Whom (refers to people, used in formal contexts)
Example: The person with whom I was speaking is my neighbour. - Whose (shows possession)
Example: The student whose book was lost found it. - Which (refers to animals or things)
Example: The book which you lent me was interesting. - That (refers to people, animals, or things)
Example: The house that we visited was beautiful.
8. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to people or things in a general way, without specifying exact identities.
- Some (refers to an unspecified amount or number)
Example: Some of the cookies are missing. - Few (refers to a small number, but not none)
Example: Few escaped unhurt. - Many (refers to a large number)
Example: Many of these eggs are rotten. - All (refers to the entire amount or number)
Example: Not all are sick. - One (refers to a single item or person)
Example: One of the books is missing. - None (refers to not any)
Example: None of these apples is ripe.
|
49 videos|349 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Pronoun - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What are personal pronouns? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between possessive pronouns and reflexive pronouns? |  |
| 3. How do emphatic pronouns differ from personal pronouns? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a demonstrative pronoun? |  |
| 5. When should relative pronouns be used in a sentence? |  |





















