RD Sharma Solutions (Part - 2) - Ex-14.1, Lines and Angles, Class 7, Math | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 7 Mathematics PDF Download
Question 15:
One of the angles forming a linear pair is a right angle. What can you say about its other angle?
Answer 15:
One angle of a linear pair is the right angle, i.e., 90°.
∴ The other angle = 180° - 90° = 90°
Question 16:
One of the angles forming a linear pair is an obtuse angle. What kind of angle is the other?
Answer 16:
If one of the angles of a linear pair is obtuse, then the other angle should be acute; only then can their sum be 180°.
Question 17:
One of the angles forming a linear pair is an acute angle. What kind of angle is the other?
Answer 17:
In a linear pair, if one angle is acute, then the other angle should be obtuse. Only then their sum can be 180°.
Question 18:
Can two acute angles form a linear pair?
Answer 18:
No, two acute angles cannot form a linear pair because their sum is always less than 180°.
Question 19:
If the supplement of an angle is 65°; then find its complement.
Answer 19:
Let x be the required angle.
Then, we have:
x + 65° = 180°
⇒⇒x = 180° - 65° = 115°
The complement of angle x cannot be determined.
Question 20:
Find the value of x in each of the following figures.
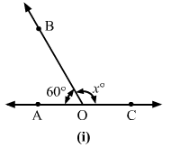
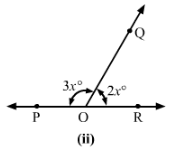
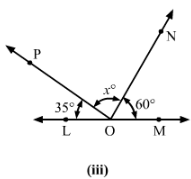
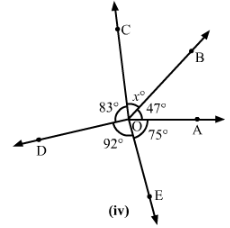
Answer 20:
(i)
Since ∠BOA+∠BOC=180° (Linear pair)
∴ ∠x=180°−∠BOA=180°−60°=120°
(ii)
Since ∠QOP+∠QOR=180° (Linear pair)
∴2x+3x=180°
⇒5x=180°
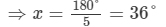
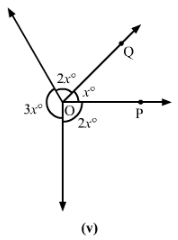
(v)
2x°+x°+2x°+3x°=180°⇒8x=180
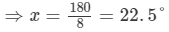
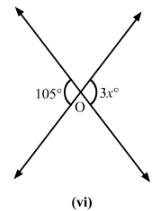
(vi)
3x°=105°
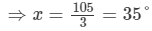
Question 21:
In Fig. 22, it being given that ∠1 = 65°, find all other angles.
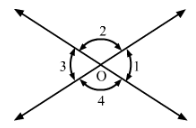
Answer 21:
∠1=∠3∠1=∠3 (Vertically opposite angles)
∴∠3=65°∴∠3=65°
Since ∠1+∠2=180° (Linear pair)
∴∠2=180°−65°=115°
∠2=∠4 (Vertically opposite angles)
∴∠4=∠2=115° and ∠3=65°
Question 22:
In Fig., OA and OB are opposite rays:
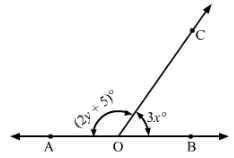
(i) If x = 25°, what is the value of y?
(ii) If y = 35°, what is the value of x?
Answer 22:
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒(2y+5)+3x=180°
⇒3x+2y=175°
i) If x = 25°, then
3×25°+2y=175°
⇒75°+2y=175°
⇒2y=175°−75°=100°
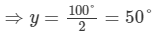
(ii) If y = 35°, then
3x+2×35°=175°
⇒3x+70°=175°
⇒3x=175°−70°=105°
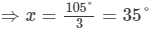
Question 23:
In Fig., write all pairs of adjacent angles and all the linear pairs.
Answer 23:
Adjacent angles:
∠DOA and ∠DOC
∠DOC and ∠BOC
∠AOD and ∠DOB
∠BOC and ∠AOC
Linear pairs of angles:
∠AOD and ∠DOB
∠BOC and ∠AOC
Question 24:
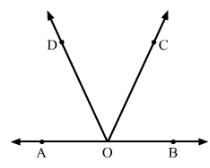
In Fig. 25, find ∠x. Further find ∠BOC, ∠COD and ∠AOD.
Answer 24:
∠AOD+∠DOC+∠COB=180°(Linear pair)
(x+10)°+x°+(x+20)°=180°
3x+30°=180°
3x=180°−30°
3x=150°
x=150°/3=50°
∠BOC=x+20°=50°+20°=70°
∠COD=x=50°
∠AOD=x+10°=50°+10°=60°
Question 25:
How many pairs of adjacent angles are formed when two lines intersect in a point?
Answer 25:
If two lines intersect at a point, then four adjacent pairs are formed, and those pairs are linear as well.
Question 26:
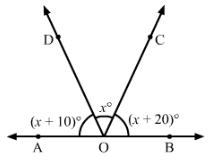
How many pairs of adjacent angles, in all, can you name in Fig.?
Answer 26:
There are 10 adjacent pairs in the given figure; they are:
∠EOD and ∠DOC
∠COD and ∠BOC
∠COB and ∠BOA
∠AOB and ∠BOD
∠BOC and ∠COE
∠COD and ∠COA
∠DOE and ∠DOB
∠EOD and ∠DOA
∠EOC and ∠AOC
∠AOB and ∠BOE
Question 27:
In Fig., determine the value of x.
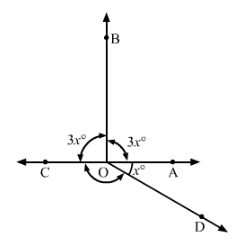
Answer 27:
∠AOB+∠BOC=180° (Linear pair)
⇒3x+3x=180°
⇒6x=180°
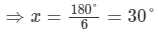
Question 28:
In Fig., AOC is a line, find x.
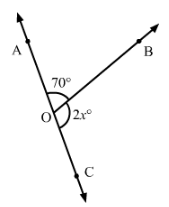
Answer 28:
∠AOB+∠BOC=180° (Linear pair)
⇒70°+2x=180°
⇒2x=180°−70°=110°
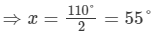
Question 29:
In Fig., POS is a line, find x.
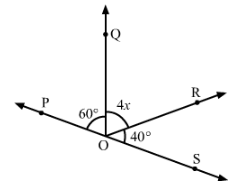
Answer 29:
∠QOP+∠QOR+∠ROS=180° (Angles on a straight line)
⇒60°+4x+40°=180°
⇒100°+4x=180°
⇒4x=180°−100°=80°
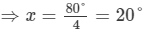
Question 30:
In Fig., lines l1 and l2 intersect at O, forming angles as shown in the figure. If x = 45°, find the values of y, zand u.
Answer 30:
∠z=∠x=45° (Vertically opposite angles)
Now,∠x+∠y=180° (Linear pair)
⇒∠y=180°−45°=135°
∠u=∠y=135° (Vertically opposite angles)
Question 31:
In Fig., three coplanar lines intersect at a point O, forming angles as shown in the figure. Find the values of x, y, z and u.
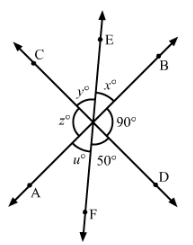
Answer 31:
∠BOD + ∠DOF + ∠FOA = 180° (Linear pair)
∴ ∠FOA = ∠u = 180°−90°−50°=40
∠FOA=∠x=40° (Vertically opposite angles)
∠BOD=∠z=90° (Vertically opposite angles)
∠EOC=∠y=50° (Vertically opposite angles)
Question 32:
In Fig., find the values of x, y and z.
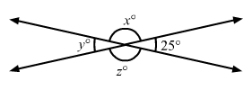
Answer 32:
∠y=25° (Vertically opposite angles)
Since ∠x+∠y=180° (Linear pair)
∴∠x=180°−25°=155°
∠z=∠x=155° (Vertically opposite angles)
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions (Part - 2) - Ex-14.1, Lines and Angles, Class 7, Math - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 7 Mathematics
| 1. What are the types of angles? |  |
| 2. How do you identify parallel lines? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of interior angles of a triangle? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between alternate interior angles and corresponding angles? |  |
| 5. How do you find the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle? |  |





















