RS Aggarwal Solutions: Factorisation of Polynomials- 2 | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3B - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Factorise: 9x2 – 16y2
Ans. 9x2−16y2
=(3x)2−(4y)2
=(3x+4y)(3x−3y)
[a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.2. Factorise: (25/4 x2−1/9 y2)
Ans. (25/4 x2−1/9 y2)
=(5/2 x)2−(1/3 y)2
=(5/2 x + 1/3 y)(5/2 x−1/3 y)
[a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.3. Factorise: 81 – 16x2
Ans. 81−16x2
=92−(4x)2
=(9+4x)(9−4x) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.4. Factorise: 5 – 20x2
Ans. 5−20x2
=5(1−4x2)
=5[12−(2x)2]
=5(1+2x)(1−2x) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.5. Factorise: 2x4 – 32
Ans. 2x4−32
=2(x4−16)
=2[(x2)2−42]
=2(x2+4)(x2−4) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=2(x2+4)(x2−22)
=2(x2+4)(x+2)(x−2) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.6. Factorize: 3a3b − 243ab3
Ans. 3a3b−243ab3=3ab(a2−81b2)
=3ab[a2−(9b)2]
=3ab(a−9b)(a+9b)
Q.7. Factorize: 3x3 − 48x
Ans. 3x3−48x=3x(x2−16)
=3x(x2−42)
=3x(x−4) (x+4)
Q.8. Factorize: 27a2 − 48b2
Ans. 27a2−48b2=3(9a2−16b2)
=3[(3a)2−(4b)2]
=3(3a−4b)(3a+4b)
Q.9. Factorize: x − 64x3
Ans. x−64x3=x(1−64x2)
=x[1−(8x)2]
=x(1−8x) (1+8x)
Q.10. Factorize: 8ab2 − 18a3
Ans. 8ab2−18a3=2a(4b2−9a2)
=2a[(2b)2−(3a)2]
=2a(2b−3a)(2b+3a)
Q.11. Factorize: 150 − 6x2
Ans. 150−6x2=6(25−x2)
=6(52−x2)
=6(5−x)(5+x)
Q.12. Factorise: 2 – 50x2
Ans. 2−50x2
=2(1−25x2)
=2[12−(5x)2]
=2(1+5x)(1−5x) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.13. Factorise: 20x2 – 45
Ans. 20x2−45
=5(4x2−9)
=5[(2x)2−32]
=5(2x+3)(2x−3) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.14. Factorise: (3a + 5b)2 – 4c2
Ans. (3a+5b)2−4c2
=(3a+5b)2−(2c)2
=(3a+5b+2c)(3a+5b−2c) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.15. Factorise: a2 – b2 – a – b
Ans. a2−b2−a−b
=(a+b)(a−b)−1(a+b) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(a+b)[(a−b)−1]
=(a+b)(a−b−1)
Q.16. Factorise: 4a2 – 9b2 – 2a – 3b
Ans. 4a2−9b2−2a−3b
=(2a)2−(3b)2−1(2a+3b)
=(2a+3b)(2a−3b)−1(2a+3b) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(2a+3b)[(2a−3b)−1]
=(2a+3b)(2a−3b−1)
Q.17. Factorise: a2 – b2 + 2bc – c2
Ans. a2−b2+2bc−c2
=a2−(b2−2bc+c2)
=a2−(b−c)2 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=[a+(b−c)][a−(b−c)] [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(a+b−c)(a−b+c)
Q.18. Factorise: 4a2 – 4b2 + 4a + 1
Ans. 4a2−4b2+4a+1
=(4a2+4a+1)−4b2
=[(2a)2+2×2a×1+12]−4b2
=(2a+1)2−(2b)2 [a2+2ab+b2=(a+b)2]
=[(2a+1)+2b] [(2a+1)−2b] [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(2a+1+2b)(2a+1−2b)
=(2a+2b+1)(2a−2b+1)
Q.19. Factorize: a2 + 2ab + b2 − 9c2
Ans. a2+2ab+b2−9c2=(a+b)2−(3c)2
=(a+b−3c)(a+b+3c)
Q.20. Factorize: 108a2 − 3(b − c)2
Ans. 108a2−3(b−c)2=3[36a2−(b−c)2]
=3[(6a)2−(b−c)2]
=3(6a−b+c)(6a+b−c)
Q.21. Factorize: (a + b)3 − a − b
Ans. (a+b)3−a−b=(a+b)3−(a+b)
=(a+b)[(a+b)2−1]
=(a+b)[(a+b)2−12]
=(a+b)(a+b−1)(a+b+1)
Q.22. Factorise: x2 + y2 – z2 – 2xy
Ans. x2+y2−z2−2xy
=(x2+y2−2xy)−z2
=(x−y)2−z2 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=(x−y+z)(x−y−z) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.23. Factorise: x2 + 2xy + y2 – a2 + 2ab – b2
Ans. x2+2xy+y2−a2+2ab−b2
=(x2+2xy+y2)−(a2−2ab+b2)
=(x+y)2−(a−b)2 [a2+2ab+b2=(a+b)2 and a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=[(x+y)+(a−b)][(x+y)−(a−b)] [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(x+y+a−b)(x+y−a+b)
Q.24. Factorise: 25x2 – 10x + 1 – 36y2
Ans. 25x2−10x +1−36y2
=[(5x)2−2×5x×1+12]−(6y)2
=(5x−1)2−(6y)2 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=[(5x−1+6y)][(5x−1−6y)] [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(5x+6y−1)(5x−6y−1)
Q.25. Factorize: a − b − a2 + b2
Ans. a−b−a2+b2=(a−b)−(a2−b2)
=(a−b)−(a−b)(a+b)
=(a−b)[1−(a+b)]
=(a−b)(1−a−b)
Q.26. Factorize: a2 − b2 − 4ac + 4c2
Ans. a2−b2−4ac+4c2
=(a2−4ac+4c2)−b2
=a2−2×2a×c +(2c)2−b2
=(a−2c)2−b2
=(a−2c+b)(a−2c−b)
Q.27. Factorize: 9 − a2 + 2ab − b2
Ans. 9−a2+2ab−b2=9−(a2−2ab+b2)
=32−(a−b)2
=[3−(a−b)][3+(a−b)]
=(3−a+b)(3+a−b)
Q.28. Factorize: x3 − 5x2 − x + 5
Ans. x3−5x2−x+5
=x2(x−5)−1(x−5)
=(x−5)(x2−1)
=(x−5)(x2−12)
=(x−5)(x−1)(x+1)
Q.29. Factorise: 1 + 2ab – (a2 + b2)
Ans. 1+2ab−(a2+b2)
=1+2ab−a2−b2
=1−a2+2ab−b2
=12−(a2−2ab+b2)
=12−(a−b)2 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=[1+(a−b)][1−(a−b)] [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(1+a−b)(1−a+b)
Q.30. Factorise: 9a2 + 6a + 1 – 36b2
Ans. 9a2+6a+1−36b2
=[(3a)2+2×3a×1+12]−(6b)2
=(3a+1)2−(6b)2 [a2+2ab+b2=(a+b)2]
=(3a+1−6b)(3a+1+6b) [a2−b2=(a−b)(a+b)]
=(3a−6b+1)(3a+6b+1)
Q.31. Factorize: x2 − y2 + 6y − 9
Ans. x2−y2+6y−9
=x2−(y2−6y+9)
=x2−(y2−2×y×3 +32)
=x2−(y−3)2
=[x+(y−3)][x−(y−3)]
=(x+y−3)(x−y+3)
Q.32. Factorize: 4x2 − 9y2 − 2x − 3y
Ans. 4x2−9y2−2x−3y
=(4x2−9y2)−(2x+3y)
=[(2x)2−(3y)2]−(2x+3y)
=(2x−3y)(2x+3y)−1(2x+3y)
=(2x+3y)(2x−3y−1)
Q.33. Factorize: 9a2 + 3a − 8b − 64b2
Ans. 9a2+3a−8b−64b2
=9a2−64b2+3a−8b
=(3a)2−(8b)2+(3a−8b)
=(3a−8b)(3a+8b)+1(3a−8b)
=(3a−8b)(3a+8b+1)
Q.34. Factorise: x2+1/x2−3
Ans. x2+1/x2−3
=x2+1/x2−2−1
=[x2+(1/x)2−2×x×1/x]−1
=(x−1/x)2−12 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=(x−1/x+1)(x−1/x−1) [a2−b2=(a−b)(a+b)]
Q.35. Factorise: x2−2+1/x2 y2
Ans. x2−2+1/x2−y2
=[x2−2×x×1/x+(1/x)2]−y2
=(x−1/x)2−y2 [a2−2ab+b2=(a−b)2]
=(x−1/x+y)(x−1/x−y) [a2−b2=(a−b)(a+b)]
Disclaimer: The expression of the question should be x2−2+1/x2−y2. The same has been done before solving the question.
Q.36. Factorise: x4+4/x4
Ans. x4+4/x4
=x4+4/x4+4−4
=[(x2)2+(2/x2)2+2×(x2)×(2/x2)]−22
=(x2+2/x2)2−22 [a2+2ab+b2=(a+b)2]
=(x2+2/x2+2)(x2+2/x2−2) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.37. Factorise: x8 – 1
Ans. x8−1=(x4)2−12
=(x4+1)(x4−1) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(x4+1)[(x2)2−12]
=(x4+1)(x2+1)(x2−1) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(x4+1)(x2+1)(x2−1)2
=(x4+1)(x2+1)(x+1)(x−1) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.38. Factorise: 16x4 – 1
Ans. 16x4−1
=(4x2)2−12
=(4x2+1)(4x2−1) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(4x2+1)[(2x)2−12]
=(4x2+1)(2x+1)(2x−1) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.39. 81x4 – y4
Ans. 81x4−y4
=(9x2)2−(y2)2
=(9x2+y2)(9x2−y2) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
=(9x2+y2)[(3x)2−y2]
=(9x2+y2)(3x+y)(3x−y) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
Q.40. x4 – 625
Ans. x4−625
=(x2)2−252
=(x2+25)(x2−25) [a2−b2=(a+b)(a−b)]
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3C - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Factorize: x2 + 11x + 30
Ans. We have:
x2+11x+30
We have to split 11 into two numbers such that their sum of is 11 and their product is 30.
Clearly, 5+6=11 and 5×6=30.
∴ x2+11x+30
= x2+5x+6x+30
= x(x+5)+6(x+5)
=(x+5)(x+6)
Q.2. Factorize: x2 + 18x + 32
Ans. We have:
x2+18x+32
We have to split 18 into two numbers such that their sum is 18 and their product is 32.
Clearly, 16+2=18 and 16×2=32.
∴x2+18x+32
=x2+16x+2x+32
=x(x+16)+2(x+16)
=(x+16)(x+2)
Q.3. Factorise: x2 + 20x – 69
Ans. x2+20x-69
=x2+23x-3x-69
=x(x+23)-3(x+23)
=(x+23)(x-3)
Q.4. x2 + 19x – 150
Ans. x2+19x-150
=x2+25x-6x-150
=x(x+25)-6(x+25)
=(x+25)(x-6)
Q.5. Factorise: x2 + 7x – 98
Ans. x2+7x-98
=x2+14x-7x-98
=x(x+14)-7(x+14)
=(x+14)(x-7)
Q.6. Factorise: x2+2√3x–24
Ans. x2+2√3x–24
= x2+4√3x-2√3x-24
= x(x+4√3)-2√3(x+4√3)
=(x+4√3)(x-2√3)
Q.7. Factorise: x2 – 21x + 90
Ans. x2-21x+90
=x2-15x-6x+90
=x(x-15)-6(x-15)
=(x-6)(x-15)
Q.8. Factorise: x2 – 22x + 120
Ans. x2-22x+120
=x2-12x-10x+120
=x(x-12)-10(x-12)
=(x-10)(x-12)
Q.9. Factorise: x2 – 4x + 3
Ans. x2-4x+3
=x2-3x-x+3
=x(x-3)-1(x-3)
=(x-1)(x-3)
Q.10. Factorise: x2+7√6x+60
Ans. x2+7√6x+60
=x2+5√6x+2√6x+60
=x(x+5√6)+2√6(x+5√6)=(x+5√6)(x+2√6)
Q.11. Factorise: x2+3√3x+6
Ans. x2+3√3x+6
=x2+2√3x+√3x+6
=x(x+2√3)+√3(x+2√3)
=(x+2√3)(x+√3)
Q.12. Factorise: x2+6√6x+48
Ans. x2+6√6x+48
=x2+4√6x+2√6x+48
=x(x+4√6)+2√6(x+4√6)
=(x+4√6)(x+2√6)
Q.13. Factorise: x2+5√5x+30
Ans. x2+5√5x+30
=x2+3√5x+2√5x+30
=x(x+3√5)+2√5(x+3√5)=(x+3√5)(x+2√5)
Q.14. Factorise: x2-24x-180
Ans. x2-24x-180
=x2-30x+6x-180
=x(x-30)+6(x-30)
=(x-30)(x+6)
Q.15. Factorise: x2 – 32x – 105
Ans. x2-32x-105
=x2-35x+3x-105
=x(x-35)+3(x-35)
=(x-35)(x+3)
Q.16. Factorise: x2 – 11x – 80
Ans. x2-11x-80
=x2-16x+5x-80
=x(x-16)+5(x-16)
=(x-16)(x+5)
Q.17. Factorise: 6 – x – x2
Ans. -x2-x+6
=-x2-3x+2x+6
=-x(x+3)+2(x+3)
=(x+3)(-x+2)
=(x+3)(2-x)
Q.18. Factorise: x2-√3x-6
Ans. x2-√3x-6
=x2-2√3x+√3x-6
=x(x-2√3)+√3(x-2√3)
=(x-2√3)(x+√3)
Q.19. Factorise: 40 + 3x – x2
Ans. -x2+3x+40
=-x2+8x-5x+40
=-x(x-8)-5(x-8)
=(x-8)(-x-5)
=(8-x)(x+5)
Q.20. Factorise: x2 – 26x + 133
Ans. x2-26x+133
=x2-19x-7x+133
=x(x-19)-7(x-19)
=(x-19)(x-7)
Q.21. Factorise: x2-2√3x-24
Ans. x2-2√3x-24
=x2-4√3x+2√3x-24
=x(x-4√3)+2√3(x-4√3)
=(x-4√3)(x+2√3)
Q.22. Factorise: x2-3√5x-20
Ans. x2-3√5x-20
=x2-4√5x+√5x-20
=x(x-4√5)+√5(x-4√5)
=(x-4√5)(x+√5)
Q.23. Factorise: x2+√2x-24
Ans. x2+√2x-24
=x2+4√2x-√2x-24
=x(x+4√2)-3√2(x+4√2)
=(x+4√2)(x-3√2)
Q.24. Factorise: x2-2√2x-30
Ans. x2-2√2x-30
=x2-5√2x+3√2x-30
=x(x-5√2)+3√2(x-5√2)
=(x-5√2)(x+3√2)
Q.25. Factorize: x2 − x − 156
Ans. We have: x2-x-156
We have to split (-1) into two numbers such that their sum is (-1) and their product is (-156).
Clearly, -13+12=-1 and -13×12=-156.
∴x2-x-156
=x2-13x+12x-156
=x(x-13)+12(x-13)
=(x-13)(x+12)
Q.26. Factorise: x2 – 32x – 105
Ans. x2-32x-105
=x2-35x+3x-105
=x(x-35)+3(x-35)
=(x-35)(x+3)
Q.27. Factorise: 9x2 + 18x + 8
Ans. 9x2+18x+8
=9x2+12x+6x+8
=3x(3x+4)+2(3x+4)
=(3x+4)(3x+2)
Q.28. Factorise: 6x2 + 17x + 12
Ans. 6x2+17x+12
=6x2+9x+8x+12
=3x(2x+3)+4(2x+3)
=(2x+3)(3x+4)
Q.29. Factorize: 18x2 + 3x − 10
Ans. We have: 18x2+3x-10
We have to split 3 into two numbers such that their sum is 3 and their product is (-180), i.e., 18×(-10).
Clearly, 15+(-12)=3 and 15×(-12)=-180.
∴18x2+3x-10
=18x2+15x-12x-10
=3x(6x+5)-2(6x+5)
=(6x+5)(3x-2)
Q.30. Factorize: 2x2 + 11x − 21
Ans. We have: 2x2+11x-21
We have to split 11 into two numbers such that their sum is 11 and their product is (-42),
i.e., 2×(-21).
Clearly, 14+(-3)
=11 and 14×(-3)
=-42.
∴2x2+11x-21
=2x2+14x-3x-21
=2x(x+7)-3(x+7)
=(x+7)(2x-3)
Q.31. Factorize: 15x2 + 2x − 8
Ans. We have: 15x2+2x-8
We have to split 2 into two numbers such that their sum is 2 and their product is (-120), i.e., 15×(-8).
Clearly, 12+(-10)=2
and 12×(-10)=-120.
∴15x2+2x-8
=15x2+12x-10x-8
=3x(5x+4)-2(5x+4)
=(5x+4)(3x-2)
Q.32. Factorise: 21x2 + 5x – 6
Ans. 21x2+5x-6
=21x2+14x-9x-6
=7x(3x+2)-3(3x+2)
=(3x+2)(7x-3)
Q.33. Factorize: 24x2 − 41x + 12
Ans. We have: 24x2-41x+12
We have to split (-41) into two numbers such that their sum is (-41) and their product is 288, i.e., 24×12.
Clearly, (-32)+(-9)=-41 and (-32)×(-9)=288.
∴24x2-41x+12
=24x2-32x-9x+12
=8x(3x-4)-3(3x-4)
=(3x-4)(8x-3)
Q.34. Factorise: 3x2 – 14x + 8
Ans. 3x2-14x+8
=3x2-12x-2x+8
=3x(x-4)-2(x-4)
=(x-4)(3x-2)
Hence, factorisation of 3x2 – 14x + 8 is (x-4)(3x-2).
Q.35. Factorize: 2x2 + 3x − 90
Ans. We have: 2x2+3x-90
We have to split 3 into two numbers such that their sum is 3 and their product is (-180), i.e., 2×(-90).
Clearly, -12 + 15 = 3 and -12×15 = -180.
∴2x2+3x-90
=2x2-12x+15x-90
=2x(x-6)+15(x-6)
=(x-6)(2x+15)
Q.36. Factorize: √5x2+2x-3√5
Ans. We have:√5x2+2x-3√5
We have to split 2 into two numbers such that their sum is 2 and product is (-15), i.e.,√5×(-3√5).
Clearly, 5+(-3)=2 and 5×(-3)=-15.
∴√5x2+2x-3√5
=√5x2+5x-3x-3√5
=√5x(x+√5)-3(x+√5)
=(x+√5)(√5x-3)
Q.37. Factorize: 2√3x2+x-5√3
Ans. We have: 2√3x2+x-5√3
We have to split 1 into two numbers such that their sum is 1 and product is 30, i.e.,2√3×(-5√3).
Clearly, 6+(-5)=1 and 6×(-5)=-30.
∴2√3x2+x-5√3
=2√3x2+6x-5x-5√3
=2√3x(x+√3)-5(x+√3)
=(x+√3)(2√3x-5)
Q.38. Factorize: 7x2+2√14x+2
Ans. We have: 7x2+2√14x+2
We have to split 2√14 into two numbers such that their sum is 2√14 and product is 14.
Clearly, √14+√14=2
√14 and √14×√14=14.
∴7x2+2√14x+2
=7x2+√14x+√14x+2
=√7x(√7x+√2)+√2(√7x+√2)
=(√7x+√2)(√7x+√2)
=(√7x+√2)2
Q.39. Factorize: 6√3x2-47x+5√3
Ans. We have: 6√3x2-47x+5√3
Now, we have to split (-47) into two numbers such that their sum is (-47) and their product is 90.
Clearly, (-45)+(-2)=-47 and (-45)×(-2)=90.
∴6√3x2-47x+5√3
=6√3x2-2x-45x+5√3
=2x(3√3x-1)-5√3(3√3x-1)
=(3√3x-1)(2x-5√3)
Q.40. Factorize: 5√5x2+20x+3√5
Ans. We have: 5√5x2+20x+3√5
We have to split 20 into two numbers such that their sum is 20 and their product is 75.
Clearly, 15+5=20 and 15×5=75
∴5√5x2+20x+3√5
=5√5x2+15x+5x+3√5
=5x(√5x+3)+√5(√5x+3)
=(√5x+3)(5x+√5)
Q.41. Factorise: √3x2+10x+8√3
Ans. √3x2+10x+8√3
=√3x2+6x+4x+8√3
=√3x(x+2√3)+4(x+2√3)
=(x+2√3)(√3x+4)
Hence, factorisation of √3x2+10x+8√3 is (x+2√3)(√3x+4).
Q.42. Factorize: √2x2+3x+√2
Ans. We have: √2x2+3x+√2
We have to split 3 into two numbers such that their sum is 3 and their product is 2, i.e.,
√2×√2.
Clearly, 2+1=3 and 2×1=2.
∴√2x2+3x+√2
=√2x2+2x+x+√2
=√2x(x+√2)+1(x+√2)
=(x+√2)(√2x+1)
Q.43. Factorize: 2x2+3√3x+3
Ans. We have: 2x2+3√3x+3
We have to split 3√3 into two numbers such that their sum is 3√3 and their product is 6, i.e.,2×3.
Clearly, 2√3+√3=3√3 and 2√3×√3=6.
∴2x2+3√3x+3=2x2+2√3x+√3x+3
=2x(x+√3)+√3(x+√3)
=(x+√3)(2x+√3)
Q.44. Factorize: 15x2 − x − 128
Ans. We have: 15x2-x-28
We have to split (-1) into two numbers such that their sum is (-1) and their product is (-420), i.e., 15×(-28).
Clearly, (-21)+20=-1 and (-21)×20=-420.
∴15x2-x-28
=15x2-21x+20x-28
=3x(5x-7)+4(5x-7)
=(5x-7)(3x+4)
Q.45. Factorize: 6x2 − 5x − 21
Ans. We have: 6x2-5x-21
We have to split (-5) into two numbers such that their sum is (-5) and their product is (-126), i.e., 6×(-21).
Clearly, 9+(-14)=-5 and 9×(-14)=-126.
∴6x2-5x-21
=6x2+9x-14x-21
=3x(2x+3)-7(2x+3)
=(2x+3)(3x-7)
Q.46. Factorize: 2x2 − 7x − 15
Ans. We have: 2x2-7x-15
We have to split (-7) into two numbers such that their sum is (-7) and their product is (-30), i.e., 2×(-15).
Clearly, (-10)+3=-7 and (-10)×3=-30.
∴2x2-7x-15
=2x2-10x+3x-15
=2x(x-5)+3(x-5)
=(x-5)(2x+3)
Q.47. Factorize: 5x2 − 16x − 21
Ans. We have: 5x2-16x-21
We have to split (-16) into two numbers such that their sum is (-16) and their product is (-105), i.e., 5×(-21).
Clearly, (-21)+5=-16 and (-21)×5=-105.
∴ 5x2-16x-21
=5x2+5x-21x-21
=5x(x+1)-21(x+1)
=(x+1)(5x-21)
Q.48. Factorise: 6x2 – 11x – 35
Ans. 6x2-11x-35
=6x2-21x+10x-35
=3x(2x-7)+5(2x-7)
=(2x-7)(3x+5)
Hence, factorisation of 6x2 – 11x – 35 is (2x-7)(3x+5).
Q.49. Factorise: 9x2 – 3x – 20
Ans. 9x2-3x-20
=9x2-15x+12x-20
=3x(3x-5)+4(3x-5)
=(3x-5)(3x+4)
Hence, factorisation of 9x2 – 3x – 20 is (3x-5)(3x+4).
Q.50. Factorize: 10x2 − 9x − 7
Ans. We have: 10x2-9x-7
We have to split (-9) into two numbers such that their sum is (-9) and their product is (-70), i.e., 10×(-7).
Clearly, (-14)+5=-9 and (-14)×5=-70.
∴10x2-9x-7
=10x2+5x-14x-7
=5x(2x+1)-7(2x+1)
=(2x+1)(5x-7)
Q.51. Factorize: x2-2x+7/16
Ans. We have:x2-2x+716
= (16x2-32x+7)/16
= 1/16 (16x2-32x+7)
Now, we have to split (-32) into two numbers such that their sum is (-32) and their product is 112, i.e., 16×7.
Clearly, (-4)+(-28)=-32 and (-4)×(-28)=112.
∴x2 - 2x + 7/16 = 1/16 (16x2-32x+7)
= 1/16 (16x2-4x-28x+7)
= 1/16 [4x(4x-1)-7(4x-1)]
= 1/16 (4x-1)(4x-7)
Q.52. Factorise: (1/3)x2-2x-9
Ans. (1/3)x2-2x-9 = (x2-6x-27)/3
= (x2-9x+3x-27)/3
= (x(x-9)+3(x-9))/3
= ((x-9)(x+3))/3
= (x-9)/3×(x+3)/1
=(1/3x-3)(x+3)
Hence, factorisation of (1/3) x2-2x-9 is (1/3x-3)(x+3).
Q.53. Factorise: x2+ 12/35 x+1/35
Ans. x2+ 12/35x+ 1/35
= (35x2+12x+1)/35
= (35x2+7x+5x+1)/35
= (7x(5x+1)+1(5x+1))/35= ((5x+1)(7x+1))/35
= (5x+1)/5 x (7x+1)/7
= (x+1/5) × (x+1/7)
Hence, factorisation of x2+12/35x+1/35is (x+1/5)(x+1/7).
Q.54. Factorise: 21x2-2x+ 1/21
Ans. 21x2-2x+1/21
=21x2-x-x+1/21
=21x(x-1/21)-1(x-1/21)
=(x-1/21)(21x-1)
Hence, factorisation of 21x2-2x+1/21 is (x-1/21)(21x-1).
Q.55. Factorise: 3/2 x2+16x+10
Ans. 3/2 x2+16x+10
Hence, factorisation of 3/2 x2+16x+10 is (x+10)(3/2x+1).
Q.56. Factorise: 2/3x2 - 17/3x-28
Ans. 2/3x2-17/3 x-28
Hence, factorisation of 2/3 x2- 17/3 x-28 is (1/3x-4)(2x+7).
Q.57. Factorise: 3/5 x2-19/5x+4
Ans. 3/5 x2-19/5 x+4
Hence, factorisation of 3/5 x2- 19/5 x+4 is (1/5 x-1)(3x-4).
Q.58. Factorise: 2x2-x+1/8
Ans. 2x2-x+1/8
Hence, factorisation of 2x2-x+1/8 is (x-1/4)(2x-1/2).
Q.59. Factorize: 2(x + y)2 − 9(x + y) − 5
Ans. We have: 2(x+y)2-9(x+y)-5
Let:(x+y)=u
Thus, the given expression becomes
2u2-9u-5
Now, we have to split (-9) into two numbers such that their sum is (-9) and their product is (-10).
Clearly, -10+1=-9 and -10×1=-10.
∴2u2-9u-5
=2u2-10u+u-5
=2u(u-5)+1(u-5)
=(u-5)(2u+1)
Putting u=(x+y), we get:
2(x+y)2 - 9(x+y) - 5
= (x+y-5)[2(x+y)+1]
= (x+y-5)(2x+2y+1)
Q.60. Factorize: 9(2a − b)2 − 4(2a − b) − 13
Ans. We have: 9(2a-b)2-4(2a-b)-13
Let:(2a-b)=p
Thus, the given expression becomes
9p2-4p-13
Now, we must split (-4) into two numbers such that their sum is (-4) and their product is (-117).
Clearly, -13+9=-4 and -13×9=-117.
∴ 9p2-4p-13
=9p2+9p-13p-13
=9p(p+1)-13(p+1)
=(p+1)(9p-13)
Putting p=(2a-b), we get: 9(2a-b)2-4(2a-b)-13
=[(2a-b)+1][9(2a-b)-13]
=(2a-b+1)[18a-9b-13]
Q. 61. Factorise: 7(x−2y)2−25(x−2y)+12
Ans. 7(x−2y)2−25(x−2y)+12
=7(x−2y)2−21(x−2y)−4(x−2y)+12
=[7(x−2y)](x−2y−3)−4(x−2y−3)
=[7(x−2y)−4](x−2y−3)
=(7x−14y−4)(x−2y−3)7x-2y2-25x-2y+12
=7x-2y2-21x-2y-4x-2y+12
=7x-2yx-2y-3-4x-2y-3
=7x-2y-4x-2y-3
=7x-14y-4x-2y-3
Hence, factorisation of 7(x−2y)2−25(x−2y)+12 is (7x−14y−4)(x−2y−3)
Q.62. Factorise: 10(3x+1/x)2−(3x+1/x)−3
Ans. 10(3x+1/x)2−(3x+1/x)−3
=10(3x+1/x)2−6(3x+1/x)+5(3x+1/x)−3
=[2(3x+1/x)][5(3x+1/x)−3]+1[5(3x+1/x)−3]
=[5(3x+1/x)−3][2(3x+1/x)+1]
=(15x+5/x−3)(6x+2/x+1)
Hence, factorisation of 10(3x+1/x)2−(3x+1/x)−3 is (15x+5/x−3)(6x+2/x+1)
Q.63. Factorise: 6(2x−3/x)2+7(2x−3/x)−20
Ans. 6(2x−3/x)2+7(2x−3/x)−20
=6(2x−3/x)2+15(2x−3x)−8(2x−3x)−20
=[3(2x−3/x)][2(2x−3/x)+5]−4[2(2x−3/x)+5]
=[2(2x−3/x)+5][3(2x−3/x)−4]
=(4x−6/x+5)(6x−9/x−4)
Hence, factorisation of 6(2x−3/x)2+7(2x−3/x)−20 is (4x−6/x+5)(6x−9/x−4)
Q.64. Factorise: (a+2b)2+101(a+2b)+100
Ans. (a+2b)2+101(a+2b)+100
=(a+2b)2+100(a+2b)+1(a+2b)+100
=(a+2b)[(a+2b)+100]+1[(a+2b)+100]
=[(a+2b)+1][(a+2b)+100]
=(a+2b+1)(a+2b+100)
Hence, factorisation of (a+2b)2+101(a+2b)+100 is (a+2b+1)(a+2b+100)
Q.65. Factorise: 4x4 + 7x2 – 2
Ans. 4x4+7x2−2
=4x4+8x2−x2−2
=4x2(x2+2)−1(x2+2)
=(4x2−1)(x2+2)
Hence, factorisation of 4x4 + 7x2 – 2 is (4x2−1)(x2+2)
Q.66. Evaluate {(999)2 – 1}.
Ans. {(999)2−1}
={(999)2−12}
=(999−1)(999+1)
=(998)(1000)
=998000
Hence, {(999)2 – 1} = 998000.
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3D - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Expand:
(i) (a + 2b + 5c)2
(ii) (2b − b + c)2
(iii) (a − 2b − 3c)2
Ans. (i) (a+2b+5c)2
=(a)2 + (2b)2 +(5c)2+2(a)(2b)+2(2b)(5c)+2(5c)(a) =a2+4b2+25c2+4ab+20bc+10ac
(ii) (2a−b+c)2=[(2a)+(−b)+(c)]2
=(2a)2+(−b)2+(c)2+2(2a)(−b)+2(−b)(c)+4(a)(c)
=4a2+b2+c2−4ab−2bc+4ac
(iii) (a−2b−3c)2=[a+(−2b)+(−3c)]2
=(a)2+(−2b)2+(−3c)2+2(a)(−2b)+2(−2b)(−3c)+2(a)(−3c)
=a2+4b2+9c2−4ab+12bc−6ac
Q.2. Expand:
(i) (2a − 5b − 7c)2
(ii) (−3a + 4b − 5c)2
(iii) (12a−14a+2)2
Ans. (i) (2a−5b−7c)2
=[(2a)+(−5b)+(−7c)]2
=(2a)2+(−5b)2+(−7c)2+2(2a)(−5b)+2(−5b)(−7c)+2(2a)(−7c)
=4a2+25b2+49c2−20ab+70bc−28ac
(ii) (−3a+4b−5c)2=[(−3a)+(4b)+(−5c)]2
=(−3a)2+(4b)2+(−5c)2+2(−3a)(4b)+2(4b)(−5c)+2(−3a)(−5c)
=9a2+16b2+25c2−24ab−40bc+30ac
(iii) (1/2a−1/4b+2)2=[(a/2)+(−b/4)+(2)]2
=(a2)2+(−b4)2+(2)2+2(a/2)(−b/4)+2(−b/4)(2)+2(a/2)(2)
=a2/4+b2/16+4−ab/4−b+2a
Q.3. Factorize: 4x2 + 9y2 + 16z2 + 12xy − 24yz − 16xz.
Ans. We have: 4x2+9y2+16z2+12xy−24yz−16xz
=(2x)2+(3y)2+(−4z)2+2(2x)(3y)+2(3y)(−4z)+2(−4z)(2x)
=[(2x)+(3y)+(−4z)]2
=(2x+3y−4z)2
Q. 4. Factorize: 9x2 + 16y2 + 4z2 − 24xy + 16yz − 12xz
Ans. We have: 9x2+16y2+4z2−24xy+16yz−12xz
=(−3x)2+(4y)2+(2z)2+2(−3x)(4y)+2(4y)(2z)+2(2z)(−3x)
=[(−3x)+(4y)+(2z)]2
=(−3x+4y+2z)2
Q.5. Factorize: 25x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 − 20xy − 12yz + 30xz.
Ans. We have: 25x2+4y2+9z2−20xy−12yz+30xz
=(5x)2+(−2y)2+(3z)2+2(5x)(−2y)+2(−2y)(3z)+2(3z)(5x)
=[(5x)+(−2y)+(3z)]2
=(5x−2y+3z)2
Q.6. 16x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 – 16xy – 12yz + 24xz
Ans. 16x2+4y2+9z2−16xy−12yz+24xz
=(4x)2+(−2y)2+(3z)2+2(4x)(−2y)+2(−2y)(3z)+2(3z)(4x)
=(4x−2y+3z)2 [using a2+b2+c2+2ab+2bc+2ca=(a+b+c)2]
Hence, 16x2 + 4y2 + 9z2 – 16xy – 12yz + 24xz = (4x−2y+3z)2
Q.7. Evaluate
(i) (99)2
(ii) (995)2
(iii) (107)2
Ans. (i) (99)2=(100−1)2
=[(100)+(−1)]2
= (100)2+2×(100)×(−1)+(−1)2
=10000−200+1
=9801
(ii) (995)2=(1000−5)2
=[(1000)+(−5)]2
=(1000)2+2×(1000)×(−5)+(−5)2
=1000000−10000+25
=990025
(iii) (107)2=(100+7)2
=(100)2+2×(100)×(7)+(7)2
=10000+1400+49
=11449
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3E - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Expand
(i) (3x + 2)3
(ii) (3a+1/4b)3
(iii) (1+2/3 a)3
Ans. (i) (3x+2)3=(3x)3+3×(3x)2x2+3×3x×(2)2+(2)3
=27x3+54x2+36x+8
(ii) (3a+1/4b)3=(3a)3+(1/4b)3+3(3a)2(1/4b)+3(3a)(14b)2 =27a3+1/64b3+27a2/4b+9a/16b2
(iii) (1+2/3a)3=(2/3a)3+3×(2/3a)2×1+3a2/3a×(1)2+(1)3 =827a3+43a2+2a+1iii 1+23a3=23a3+3×23a2×1+3a23a×12+13 =8/27a3+43a2+2a+1
Q.2. Expand
(i) (5a – 3b)3
(ii) (3x−5/x)3
(iii) (4/5a−2)3
Ans. (i) (5a−3b)3=(5a)3−(3b)3−3(5a)2(3b)+3(5a)(3b)2 =125a3−27b3−225a2b+135ab2
(ii) (3x−5/x)3=(3x)3−(5/x)3−3(3x)2(5/x)+3(3x)(5/x)2
=27x3−125/x3−135x+225/x
(iii) (4/5a−2)3=(4/5a)3−(2)3−3(4/5a)2(2)+3(4/5a)(2)2
=64/125a3−8−96/25a2+48/5a
Q.3. Factorise 8a3+27b3+36a2b+54ab2
Ans. 8a3+27b3+36a2b+54ab2
=(2a)3+(3b)3+3(2a)2(3b)+3(2a)(3b)2
=(2a+3b)3
Hence, factorisation of 8a3+27b3+36a2b+54ab2
Q.4. Factorise 64a3−27b3−144a2b+108ab2
Ans. 64a3−27b3−144a2b+108ab2
=(4a)3−(3b)3−3(4a)2(3b)+3(4a)(3b)2
=(4a-3b)3
Hence, factorisation of 64a3−27b3−144a2b+108ab2
Q.5. Factorise 1+27/125 a3+9a/5+27a2/24
Ans. 1+27/125 a3+9a/5+27a2/25
=(1)3+(3/5a)3+3(1)2(3/5 a)+3(1)(3/5a)2
Hence, factorisation of 1+27/125 a3+9a/5+27a2/25 is (1+3/5a)3
Q.6. Factorise 125x3−27y3−225x2y+135xy2
Ans. 125x3−27y3−225x2y+135xy2
=(5x)3−(3y)3−3(5x)2(3y)+3(5x)(3y)2
=(5x-3y)3
Hence, factorisation of 125x3−27y3−225x2y+135xy2 is (5x−3y)3
Q.7. Factorise: a3x3−3a2bx2+3ab2x−b3
Ans. a3x3−3a2bx2+3ab2x−b3
=(ax)3−(b)3−3(ax)2(b)+3(ax)(b)2
= (ax-b)3
Hence, factorisation of a3x3−3a2bx2+3ab2x−b3 is (ax−b)3.
Q.8. Factorise: 64/125a3−96/25a2+48/5a−8
Ans. 64/125 a3−96/25 a2+48/5 a−8
=(4/5 a)3−(2)3−3(4/5 a)2(2)+3(4/5 a)(2)2
=(4/5 a-2)3
Hence, factorisation of 64/125 a3−96/25 a2+48/5 a is (4/5a−2)3 is (4/5a-2)3.
Q.9. Factorise a3 – 12a(a – 4) – 64
Ans. a3−12a(a−4)−64
=a3−12a2+48a−64
=(a)3−(4)3−3(a)2(4)+3(a)(4)2
= (a-4)3
Hence, factorisation of a3 – 12a(a – 4) – 64 is (a−4)3.
Q.10. Evaluate
(i) (103)3
(ii) (99)3
Ans. (i) (103)3=(100+3)3
=(100)3+(3)3+3(100)2(3)+3(100)(3)2
=1000000+27+90000+2700
=1092727
(ii) (99)3=(100−1)3
=(100)3−(1)3−3(100)2(1)+3(100)(1)2
=1000000−1−30000+300
=1000300−30001
=970299
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3F - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Factorize: x3 + 27
Ans. x3+27=(x)3+(3)3
=(x+3)(x2−3x+32)
=(x+3)(x2−3x+9)
Q.2. Factorise: 27a3 + 64b3
Ans. We know that x3+y3
=(x+y)(x2+y2−xy)x3+y3
Given: 27a3 + 64b3
x = 3a, y = 4b
27a3 + 64b3=(3a+4b)(9a2+16b2−12ab)
Q.3. Factorize: 125a3+1/8
Ans. 125a3+1/8=(5a)3+(1/2)3
=(5a+1/2)[(5a)2−5a×1/2+(1/2)2]
=(5a+1/2)(25a2−5a/2+1/4)
Q.4. Factorize: 216x3+1/125
Ans. 216x3+1/125=(6x)3+(1/5)3
=(6x+1/5)[(6x)2−6x×1/5+(1/5)2]
=(6x+1/5)(36x2−6x/5+1/25)
Q.5. Factorize: 16x4 + 54x
Ans. 16x4+54x
=2x(8x3+27)
=2x[(2x)3+(3)3]
=2x(2x+3)[(2x)2−2x×3+32]
=2x(2x+3)(4x2−6x+9)
Q.6. Factorize: 7a3 + 56b3
Ans. 7a3+56b3=7(a3+8b3)
=7[(a)3+(2b)3]
=7(a+2b)[a2−a×2b+(2b)2]
=7(a+2b)(a2−2ab+4b2)
Q.7. Factorize: x5 + x2
Ans. x5+x2=x2(x3+1)
=x2(x3+13)
=x2(x+1)(x2−x×1+12)
=x2(x+1)(x2−x+1)
Q.8. Factorize: a3 + 0.008
Ans. a3+0.008=a3+(0.2)3
=(a+0.2)[a2−a×(0.2)+(0.2)2]
=(a+0.2)(a2−0.2a+0.04)
Q.9. Factorise: 1 – 27a3
Ans. 1−27a3=13−(3a)3
=(1−3a)[12+1×3x+(3a)2]
=(1−3a)(1+3a+9a2)
Q.10. Factorize: 64a3 − 343
Ans. 64a3−343=(4a)3−(7)3
=(4a−7)(16a2+4a×7+72)
=(4a−7)(16a2+28a+49)
Q.11. Factorize: x3 − 512
Ans. x3−512 =x3−83
=(x−8)(x2+8x+82)
=(x−8)(x2+8x+64)
Q.12. Factorize: a3 − 0.064
Ans. a3−0.064=(a)3−(0.4)3
=(a−0.4)[a2+a×(0.4)+(0.4)2]
=(a−0.4)(a2+0.4a+0.16)
Q.13. Factorize: 8x3−1/27y3
Ans. 8x3−127y3=(2x)3−(1/3y)3
=(2x−1/3y)[(2x)2+2x×1/3y+(1/3y)2]
=(2x−1/3y)(4x2+2x/3y+1/9y2)
Q.14. Factorise: x3/216−8y3
Ans. We know a3−b3=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)
We have,
x3/216−8y3=(x/6)3−(2y)3
So, a=x/6,b=2y
x3/216−8y3=(x/6−2y)((x/6)2+x/6×2y+(2y)2)
=(x/6−2y)(x2/36+xy/3+4y2)
Q.15. Factorize: x − 8xy3
Ans. x−8xy3=x(1−8y3)
=x[13−(2y)3]
=x(1−2y)(12+1×2y+(2y)2)
=x(1−2y)(1+2y+4y2)
Q.16. Factorise: 32x4 – 500x
Ans. 32x4 – 500x=4x(8x3−125)=4x((2x)3−53)
we know
a3−b3=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)
a=2x,b=5
32x4 – 500x=4x((2x)3−53)
=4x(2x−5)(4x2+25+10x)
Q.17. Factorize: 3a7b − 81a4b4
Ans. 3a7b−81a4b4=3a4b(a3−27b3)
=3a4b[a3−(3b)3]
=3a4b(a−3b)[a2+a×3b+(3b)2]
=3a4b(a−3b)(a2+3ab+9b2)
Q.18. Factorise: x4 y4 – xy
Ans. Using the identity
a3−b3=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)
x4 y4–xy=xy(x3y3−1)
=xy(xy−1)(x2y2+1+xy)
Q.19. Factorise: 8x2 y3 – x5
Ans. 8x2y3–x5=x2(8y3−x3)
=x2(2y−x)(4y2+x2+2xy)
Q.20. Factorise:1029 – 3x3
Ans. 1029–3x3
=3(343−x3)
=3(73−x3)
=3(7−x)(49+x2+7x)
Q.21. Factorize: x6 − 729
Ans. x6−729=(x2)3−(9)3
=[x2−9][(x2)2+x2×9+92]
=[x2−32](x4+9x2+81)
=(x+3)(x−3)(x4+18x2+81−9x2)
=(x+3)(x−3)[(x2)2+2×x2×9+92−9x2]
=(x+3)(x−3)[(x2+9)2−(3x)2]
=(x+3)(x−3)(x2+9+3x)(x2+9−3x)
=(x+3)(x−3)(x2+3x+9)(x2−3x+9)
Q.22. Factorise: x9 – y9
Ans. x9–y9=(x3)3−(y3)3
we know
a3−b3=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)
a=x3,b=y3
So,x9–y9=(x3)3−(y3)3
=(x3−y3)(x6+y6+x3y3)
=(x−y)(x2+y2+xy)(x6+y6+x3y3)
Q.23. Factorize: (a + b)3 − (a − b)3
Ans. (a + b)3−(a−b)3=[(a+b)−(a−b)][(a+b)2+(a+b)(a−b)+(a−b)2]
=(a+b−a+b)[a2+2ab+b2+a2−b2+a2−2ab+b2]
=2b(3a2+b2)
Q.24. Factorize: 8a3 − b3 − 4ax + 2bx
Ans. 8a3−b3−4ax+2bx=[(2a)3−(b)3]−2x(2a−b)
=(2a−b)[(2a)2+2ab+b2]−2x(2a−b)
=(2a−b)(4a2+2ab+b2)−2x(2a−b)
=(2a−b)(4a2+2ab+b2−2x)
Q.25. Factorize: a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3 − 8
Ans. a3+3a2b+3ab2+b3−8=(a3+b3+3a2b+3ab2)−8
=[a3+b3+3ab(a+b)]−8
=(a+b)3−23
=(a+b−2)[(a+b)2+2(a+b)+22]
=(a+b−2)[(a+b)2+2(a+b)+4]
Q.26. Factorize: a3−1/a3−2a+2/a
Ans. a3−1/a3−2a+2/a=(a3−1/a3)−2(a−1/a)
=[(a)3−(1/a)3]−2(a−1/a)
=(a−1/a)[a2+a×1/a+(1/a)2]−2(a−1/a)
=(a−1/a)(a2+1+1/a2)−2(a−1/a)
=(a−1/a)(a2+1+1/a2−2)
=(a−1/a)(a2−1+1/a2)
Q.27. Factorize: 2a3 + 16b3 − 5a − 10b
Ans. 2a3+16b3−5a−10b=2[a3+8b3]−5(a+2b)
=2[a3+(2b)3]−5(a+2b)
=2(a+2b)[a2−a×2b+(2b)2]−5(a+2b)
=2(a+2b)(a2−2ab+4b2)−5(a+2b)
=(a+2b)[2(a2−2ab+4b2)−5]
Q.28. Factorise: a6 + b6
Ans. a6+b6=(a2)3+(b2)3
=(a2+b2)[(a2)2−a2b2+(b2)2]
=(a2+b2)(a4−a2b2+b4)
Q.29. Factorise: a12 – b12
Ans. a12 – b12
=(a6+b6)(a6−b6)
=[(a2)3+(b2)3][(a3)2−(b3)2]
=[(a2+b2)(a4+b4−a2b2)][(a3−b3)(a3+b3)]
=[(a2+b2)(a4+b4−a2b2)][(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)(a+b)(a2+b2−ab)]
=(a−b)(a2+b2+ab)(a+b)(a2+b2−ab)(a2+b2)(a4+b4−a2b2)
Q.30. Factorise: x6 – 7x3 – 8
Ans. Let x3=y
So, the equation becomes
y2−7y−8=y2−8y+y−8
=y(y−8)+(y−8)
=(y−8)(y+1)
=(x3−8)(x3+1)
=(x−2)(x2+4+2x)(x+1)(x2+1−x)
Q.31. Factorise: x3 – 3x2 + 3x + 7
Ans. x3 – 3x2 + 3x + 7
=x3–3x2+3x+7
=x3–3x2+3x+8−1
=x3–3x2+3x−1+8
=(x3–3x2+3x−1)+8
=(x−1)3+23
=(x−1+2)[(x−1)2+4−2(x−1)]
=(x+1)[x2+1−2x+4−2x+2]
=(x+1)(x2−4x+7)
Q.32. Factorise: (x +1)3 + (x – 1)3
Ans. (x +1)3 + (x – 1)3
=(x+1+x−1)[(x+1)2+(x−1)2−(x−1)(x+1)]
=(2x)[(x+1)2+(x−1)2−(x2−1)]
=2x(x2+1+2x+x2+1−2x−x2+1)
=2x(x2+3)
Q.33. Factorise: (2a +1)3 + (a – 1)3
Ans. (2a +1)3 + (a – 1)3
=(2a+1+a−1)[(2a+1)2+(a−1)2−(2a+1)(a−1)]
=(3a)[4a2+1+4a+a2+1−2a−2a2+2a−a+1]
=3a[3a2+3a+3]
=9a(a2+a+1)
Q.34. Factorise: 8(x +y)3 – 27(x – y)3
Ans. 8(x +y)3 – 27(x – y)3
=[2(x+y)]3−[3(x−y)]3
=(2x+2y−3x+3y)[4(x+y)2+9(x−y)2+6(x2−y2)]
=(−x+5y)[4(x2+y2+2xy)+9(x2+y2−2xy)+6(x2−y2)]
=(−x+5y)[4x2+4y2+8xy+9x2+9y2−18xy+6x2−6y2]
=(−x+5y)(19x2+7y2−10xy)
Q.35. Factorise: (x +2)3 + (x – 2)3
Ans. (x +2)3 + (x – 2)3
=(x+2+x−2)[(x+2)2+(x−2)2−(x2−4)]
=2x(x2+4+4x+x2+4−4x−x2+4)
=2x(x2+12)
Q.36. Factorise: (x + 2)3 – (x – 2)3
Ans. (x + 2)3 – (x – 2)3
=(x+2−x+2)[(x+2)2+(x−2)2+(x2−4)]
=4[x2+4+4x+x2+4−4x+x2−4]
=4(3x2+4)
Q.37. Prove that (0.85×0.85×0.85+0.15×0.15×0.15)/(0.85×0.85−0.85×0.15+0.15×0.15)=1.
Ans. LHS: (0.85×0.85×0.85+0.15×0.15×0.15)/(0.85×0.85−0.85×0.15+0.15×0.15)
=(0.85)3+(0.15)3/(0.85)2−0.85×0.15+(0.15)2
We know a3+b3=(a+b)(a2+b2−ab)
Here a=0.85,b=0.15
(0.85)3+(0.15)3/(0.85)2−0.85×0.15+(0.15)2
=(0.85+0.15)((0.85)2−0.85×0.15+(0.15)2)(0.85)2−0.85×0.15+(0.15)2=0.85+0.15=1:RHS
Thus, LHS = RHS
Q.38. Prove that (59×59×59−9×9×9)/(59×59+59×9+9×9)=50.
Ans. (59×59×59−9×9×9)/(59×59+59×9+9×9)
=(59)3−93/592+59×9+92
We know a3+b3=(a+b)(a2+b2−ab)
Here a=59,b=9
So, ((59−9)(592+92+59×9))/(592+92+59×9)=59−9=50:RHS
Thus, LHS=RHS
RS Aggarwal Solutions: Exercise 3G - Factorisation of Polynomials
Q.1. Find the product: (x + y − z) (x2 + y2 + z2 − xy + yz + zx)
Ans. (x+y−z)(x2+y2+z2−xy+yz+zx)
=[x+y+(−z)][x2+y2+(−z)2−xy−y×(−z)−[−z]×x]
=x3+y3+(−z)3−3x×y×(−z)
=x3+y3−z3+3xyz
Q.2. Find the product: (x – y − z) (x2 + y2 + z2 + xy – yz + xz)
Ans. (x – y − z) (x2 + y2 + z2 + xy – yz + xz)
=(x+(−y)+(−z)) (x2+y2+z2+xy–yz+xz)
We know
(a+b+c)(a2+b2+c2−ab−bc−ca)
=a3+b3+c3−3abc
Here, a=x,b=−y,c=−z
(x+(−y)+(−z)) (x2+y2+z2+xy–yz+xz)
=x3−y3−z3−3xyz
Q.3. Find the product: (x − 2y + 3) (x2 + 4y2 + 2xy − 3x + 6y + 9)
Ans. (x − 2y + 3)(x2+4y2+2xy−3x+6y+9)
=(x − 2y + 3)(x2+4y2+9+2xy+6y−3x)
=[x+(−2y)+3][x2+(−2y)2+(3)2−x×(−2y)−(−2y)×3−3×x]
=(x)3+(−2y)3+(3)3−3(x)(−2y)(3)
=x3−8y3+27+18xy
Q.4. Find the product: (3x – 5y + 4) (9x2 + 25y2 + 15xy − 20y + 12x + 16)
Ans. (3x−5y+4)(9x2+25y2+15xy−20y+12x+16)
=(3x+(−5y)+4)(9x2+25y2+16+15xy−20y+12x)
(a+b+c)(a2+b2+c2−ab−bc−ca)
=a3+b3+c3−3abc
Here, a=3x,b=−5y,c=4
(3x+(−5y)+4)(9x2+25y2+16+15xy−20y+12x)
=(3x)3+(−5y)3+43−3×3x(−5y)(4)
=27x3−125y3+64+180xy
Q.5. Factorize: 125a3 + b3 + 64c3 − 60abc
Ans. 125a3+b3+64c3−60abc=(5a)3+(b)3+(4c)3−3×5a×b×4c
=(5a+b+4c)[(5a)2+(b)2+(4c)2−5a×b−b×4c−5a×4c]
=(5a+b+4c)(25a2+b2+16c2−5ab−4bc−20ac)
Q.6. Factorize: a3 + 8b3 + 64c3 − 24abc
Ans. a3+8b3+64c3−24abc=a3+(2b)3+(4c)3−3×a×2b×4c
=(a+2b+4c)[a2+(2b)2+(4c)2−a×2b−2b×4c−4c×a]
=(a+2b+4c) (a2+4b2+16c2-2ab-8bc-4ca)
Q.7. Factorize: 1 + b3 + 8c3 − 6bc
Ans. 1+b3+8c3−6bc=(1)3+(b)3+(2c)3−3×1×b×2c
=(1+b+2c)[12+b2+(2c)2−1×b−b×2c−1×2c]
=(1+b+2c)(1+b2+4c2−b−2bc−2c)
Q.8. Factorize: 216 + 27b3 + 8c3 − 108abc
Ans. 216+27b3+8c3−108abc
=(6)3+(3b)3+(2c)3−3×6×3b×2c
=(6+3b+2c)[62+(3b)2+(2c)2−6×3b−3b×2c−2c×6]
=(6+3b+2c)(36+9b2+4c2−18b−6bc−12c)
Q.9. Factorize: 27a3 − b3 + 8c3 + 18abc
Ans. 27a3−b3+8c3+18abc=(3a)3+(−b)3+(2c)3−3×(3a)×(−b)×(2c)
=[3a+(−b)+2c][(3a)2+(−b)2+(2c)2−3a(−b)−(−b)2c−3a×2c]
=(3a−b+2c)(9a2+b2+4c2+3ab+2bc−6ac)
Q.10. Factorize: 8a3 + 125b3 − 64c3 + 120abc
Ans. 8a3+125b3−64c3+120abc=(2a)3+(5b)3+(−4c)3−3×(2a)×(5b)×(−4c)
=(2a+5b−4c)[(2a)2+(5b)2+(−4c)2−(2a)(5b)−(5b)(−4c)−(2a)×(−4c)]
=(2a+5b−4c)(4a2+25b2+16c2−10ab+20bc+8ac)
Q.11. Factorize: 8 − 27b3 − 343c3 − 126bc
Ans. 8−27b3−343c3−126bc
=(2)3+(−3b)3+(−7c)3−3×(2)×(−3b)×(−7c)
=[2+(−3b)+(−7c)][(2)2+(−3b)2+(−7c)2−(2)(−3b)−(−3b)(−7c)−(2)(−7c)]
=(2−3b−7c)(4+9b2+49c2+6b−21bc+14c)
Q.12. Factorize: 125 − 8x3 − 27y3 − 90xy
Ans. 125−8x3−27y3−90xy=53+(−2x)3+(−3y)3−3×5×(−2x)×(−3y)
=[5+(−2x) +(−3y)][52+(−2x)2+(−3y)2−5×(−2x)−(−2x)(−3y)−5×(−3y)] =(5−2x−3y)(25+4x2+9y2+10x−6xy+15y)
Q.13. Factorize: 2√2a3 + 16√2b3+c3−12abc
Ans. 2√2a3+16√2b3+c3−12abc
=(√2a)3+(2√2b)3+c3−3×(√2a)×(2√2b)×(c)
=(√2a+2√2b+c)[(√2a)2+(2√2b)2+c2−(√2a)×(2√2b)−(2√2b)×(c)−(2√a)×(c)]
=(√2a+2√2b+c)(2a2+8b2+c2−4ab−2√2bc−√2ac)
Q.14. Factorise: 27x3 – y3 – z3 – 9xyz
Ans. 27x3−y3–z3–9xyz
=(3x)3−y3−z3−3×(3x)×(−y)×(−z)
We know,
a3+b3+c3−3abc
=(a+b+c)(a2+b2+c2−ab−bc−ca)
a=3x,b=−y,c=−z
(3x)3−y3−z3−3×(3x)×(−y)×(−z)
=(3x−y−z)(9x2+y2+z2+3xy−yz+3xz)
Q.15. Factorise: 2√2a3+3√3b3+c3−3√6abc
Ans. 2√2a3+3√3b3+c3−3√6abc
=(√2a)3+(√3b)3+c3−3(√2a)(√3b)c
We know
x3+y3+z3−3xyz=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)
x=√2a,y=√3b,z=c
(√2a)3+(√3b)3+c3−3(√2a)(√3b)c
=(√2a+√3b+c)(2a2+3b2+c2−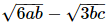 - √2ac)
- √2ac)
Q.16. Factorise: 3√3a3−b3−5√5c3−3√15abc
Ans. 3√3a3−b3−5√5c3−3√15abc
=(√3a)3+(−b)3+(−√5c)3−3(√3a)(−b)(−√5c)
We know
x3+y3+z3−3xyz=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)
Here, x=(√3a),y=(−b),z=(−√5c)
3√3a3−b3−5√5c3−3√15abc
=(√3a)3+(−b)3+(−√5c)3−3(√3a)(−b)(−√5c)
=(√3a−b−√5c)(3a2+b2+5c2+√3ab−√5bc+√15c)
Q.17. Factorize: (a − b)3 + (b − c)3 + (c − a)3
Ans. (a−b)3+(b−c)3+(c−a)3
Putting (a−b)=x, (b−c)=y and (c−a)=z, we get:
(a−b)3+(b−c)3+(c−a)3
=x3+y3+z3[Where (x+y+z)=(a−b)+(b−c)+(c−a)=0]
=3xyz [(x+y+z)=0 ⇒x3+y3+z3=3xyz]
=3(a−b)(b−c)(c−a)
Q.18. Factorise: (a−3b)3+(3b−c)3+(c−a)3
Ans. We know x3+y3+z3−3xyz=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)
x3+y3+z3=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)+3xyz
Here, x=(a−3b),y=(3b−c),z=(c−a)
(a−3b)3+(3b−c)3+(c−a)3
=(a−3b+3b−c+c−a)[(a−3b)2+(3b−c)2+(c−a)2−(a−3b)(3b−c)−(3b−c)(c−a)−(c−a)(a−3b)]+3(a−3b)(3b−c)(c−a)
=0+3(a−3b)(3b−c)(c−a)
=3(a−3b)(3b−c)(c−a)
Q.19. Factorize: (3a − 2b)3 + (2b − 5c)3 + (5c − 3a)3
Ans. Put (3a−2b)=x, (2b−5c)=y and (5c−3a)=z.
We have:
x+y+z = 3a−2b+2b−5c+5c−3a=0
Now,(3a−2b)3+(2b−5c)3+(5c−3a)3=x3+y3+z3
=3xyz [Here, x+y+z=0. So, x3 + y3 +z3 = 3xyz]
=3(3a−2b)(2b−5c)(5c−3a)
Q.20. Factorize: (5a − 7b)3 + (9c − 5a)3 + (7b − 9c)3
Ans. Put (5a−7b)=x, (9c−5a)=z and (7b−9c)=y.
Here, x+y+z = 5a − 7b + 9c−5a+7b−9c=0
Thus, we have:
(5a−7b)3+(9c−5a)3+(7b−9c)3=x3+z3+y3
=3xzy [When x+y+z=0, x3+y3+z3 = 3xyz.]
=3 (5a−7b)(9c−5a)(7b−9c)
Q.21. Factorize: a3(b − c)3 + b3(c − a)3 + c3(a − b)3
Ans. We have: a3(b−c)3+b3(c−a)3+c3(a−b)3 = [a(b−c)]3+[b(c−a)]3+[c(a−b)]3
Put a(b−c) = x
b(c−a) = y
c(a−b) = z
Here, x+y+z = a(b−c)+b(c−a)+c(a−b)
=ab − ac + bc − ab + ac − bc
=0
Thus, we have:
a3(b−c)3+b3(c−a)3+c3(a−b)3 =x3 + y3+ z3
=3xyz [When x+y+z =0, x3 + y3+ z3 =3xyz.]
=3 a(b−c)b(c−a)c(a−b)
=3abc(a−b)(b−c)(c−a)
Q.22. Evaluate
(i) (–12)3 + 73 + 53
(ii) (28)3 + (–15)3 + (–13)3
Ans. (i) (–12)3 + 73 + 53
We know
x3+y3+z3−3xyz=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)
x3+y3+z3=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)+3xyz
Here, x=(−12),y=7,z=5
(−12)3+73+53
=(−12+7+5)[(−12)2+72+52−7(−12)−35+60]+3(−12)×35
=0−1260
= -1260
(ii) (28)3 + (–15)3 + (–13)3
We know
x3+y3+z3−3xyz=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)
x3+y3+z3=(x+y+z)(x2+y2+z2−xy−yz−zx)+3xyz
Here, x=(−28),y=−15,z=−13
(28)3+(−15)3+(−13)3
=(28−15−13)[(28)2+(−15)2+(−13)2−28(−15)−(−15)(−13)−28(−13)]+3×28(−15)(−13)
=0+16380=16380
Q.23. Prove that (a+b+c)3−a3−b3−c3=3(a+b) (b+c) (c+a)
Ans. (a+b+c)3=[(a+b)+c]3
= (a+b)3+c3+3(a+b)c(a+b+c)
⇒(a+b+c)3=a3+b3+3ab(a+b)+c3+3(a+b)c(a+b+c)
⇒(a+b+c)3−a3+b3−c3=3ab(a+b)+3(a+b)c(a+b+c)
⇒(a+b+c)3−a3+b3−c3=3(a+b)[ab+ca+cb+c2]
⇒(a+b+c)3−a3+b3−c3=3(a+b)[a(b+c)+c(b+c)]
⇒(a+b+c)3−a3+b3−c3=3(a+b)(b+c)(a+c)
Q.24. If a, b, c are all nonzero and a + b + c = 0, prove that a2/bc+b2/ca+c2/ab=3.
Ans. a+b+c=0
⇒a3+b3+c3=3abc
Thus, we have:
(a2/bc+b2/ca+c2/ab)=(a3+b3+c3)/abc
=3abc/abc
=3
Q.25. If a + b + c = 9 and a2 + b2 + c2 = 35, find the value of (a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc).
Ans. a + b + c = 9
⇒(a+b+c)2=92=81
⇒a2+b2+c2+2(ab+bc+ca)=81
⇒35+2(ab+bc+ca)=81
⇒(ab+bc+ca)=23
We know,
(a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc)
= (a+b+c)(a2+b2+c2−ab−bc−ca)
=(9)(35−23)
=108
|
40 videos|420 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on RS Aggarwal Solutions: Factorisation of Polynomials- 2 - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What is the importance of factorisation of polynomials? |  |
| 2. How can I factorise a polynomial expression? |  |
| 3. Can all polynomials be factorised? |  |
| 4. What is the role of factorisation in solving quadratic equations? |  |
| 5. Can factorisation be used to simplify fractions with polynomial expressions? |  |






















