Rashtrakuta Dynasty | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
≫ Origin
- The Rashtrakutas considered themselves descendants of Satyaki.
- Historians differ on the question of their origins.
- It is evident from a few Chalukya kings’ inscriptions that they were vassals of the Chalukyas.
- Rashtrakutas were of Kannada origin and their mother tongue was Kannada.
≫ The Rashtrakuta Empire
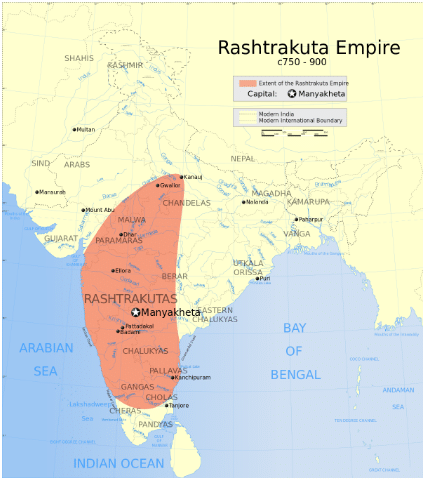
≫ The Rashtrakuta Emperors
Rashtrakuta Emperors (753-982)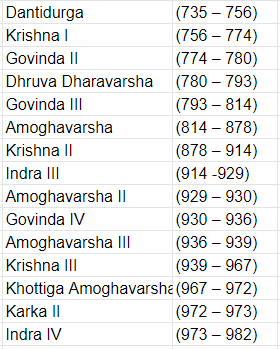
≫ Founder
Dantivarman or Dantidurga (735 - 756)
Dantivarman or Dantidurga (735 – 756) was the founder of the Rashtrakutas dynasty.
Dantidurga occupied all territories between the Godavari and Vima.
He is said to have conquered Kalinga, Kosala, Kanchi, Srisril, Malava, Lata etc. and occupied Maharashtra by defeating Chalukya King Kirtivarma.
≫ Rulers
(i) Krishna I (756 - 774)
- Krishna I succeeded Dantidurga.
- He conquered the territories that were still under the Chalukyas
- He also occupied Konkan.
- Krishna I also defeated Vishnuvardhana of Vengi and the Ganga king of Mysore.
- He was a great patron of art and architecture.
- The Kailash Temple at Ellora was built by the Rashtrakuta King Krishna I.
(ii) Govinda II (774 - 780)
- Govinda II son of Krishna I succeeded.
(iii) Dhruva (780 - 793)
- He defeated Gurjara-Pratihara King Vatsyaraja, the Pallavas of Kanchi and the Pala King Dharmapala of Bengal.
(iv) Govinda III (793 - 814)
- Dhruva son of Govinda III succeeded the throne.
- He defeated the great Gurjara King Nagabhatta II.
- Pala King Dharmapala and his protégé Charayudh sought the help of Govinda III.
- His kingdom spread up to the Vindhyas and Malava in the north and the river Tungabhadra to the south.
(v) Amoghavarsha I (814- 878 A.D.)
- The greatest king of the Rashtrakuta dynasty was Amoghavarsha I son of Govinda III.
- Amoghavarsha I set up a new capital at Manyakheta (now Malkhed in Karnataka State) and Broach became the best port of the kingdom during his reign
- Amoghavarsha I was a great patron of education and literature.
- Amoghavarsha was converted into Jainism by Jinasena, a Jaina monk.
- Suleman, an Arab merchant, in his account called Amoghavarsha I as one of the four greatest kings of the world, the other three being the Caliph of Bagdad, the king of Constantinople and the emperor of China.
- Amoghavarsha ruled for 63 years.
(vi) Krishna II (878 - 914)
- Son of Amoghavarsha, succeeded the throne.
(vii) Indra III (914 -929)
- Indra III was a powerful king.
- He defeated and deposed Mahipala
(viii) Krishna III (939 – 967)
- The last powerful and efficient king of the Rashtrakutas.
- He also succeeded in conquering Tanjore and Kanchi.
- He succeeded in defeating the Tamil kings of Chola kingdom.
(ix) Karka (972 – 973)
- The Rashtrakuta King Karka was defeated and deposed by Taila or Tailapa, the Chalukya king of Kalyani.
≫ Rasjtrakutas Administration
- divided rashtras (provinces) -contolled by rashtrapatis
- Rashtras divided into vishayas or districts governed by vishayapatis
- subdivision was bhukti consisting of 50 to 70 villages under the controlof bhogapatis
(i) Village headmen carried on village administration.
(ii) Village assemblies played a significant role in the village administration.
≫ Literature under Rashtrakutas
- Rashtrakutas widely patronized the Sanskrit literature.
- Trivikrama wrote Halayudha and composed Kavirahasya during the reign of Krishna III.
- Jinasena composed Parsvabhudaya, a biography of Parsva in verses.
- Jinasena wrote the Adipurana, the life stories of various Jain saints.
- Sakatayana wrote Amogavritti a grammar work.
- Viracharya – a Great mathematician of this period wrote Ganitasaram.
- During the period of the Rashtrakutas, the Kannada literature saw its beginning.
- Kavirajamarga composed by Amogavarsha’s was the first poetic work in the Kannada language.
- Pampa was the greatest of the Kannada poets and Vikramasenavijaya is his famous work.
- Santipurana was another great work wrote by Ponna another famous Kannada poet.
≫ Rashtrakutas Art and Architecture
(i) Art and Architecture
- The art and architecture of the Rashtrakutas can be found at Ellora and Elephanta.
- The most remarkable temple Kailasanatha temple at Ellora was built by Krishna.
(ii) Kailasanatha Temple
- The temple is carved out of a massive block of rock measuring 200 feet long, and 100 feet in breadth and height.
- The central face of the plinth has imposing figures of elephants and lions which give an impression that the entire structure rests on their back.
- It has three-tiered shikhara or tower which resembles the sikhara of the Mamallapuram rathas.
- There is a pillared hall with 16 square pillars in the interior of the temple.
- A sculpture of the Goddess Durga is engraved as slaying the Buffalo demon.
- In the interior of the temple, there is a pillared hall which has sixteen square pillars.
- The sculpture of the Goddess Durga is shown as slaying the Buffalo demon.
- In another sculpture Ravana was making attempts to lift Mount Kailasa, the abode of Siva.
(iii) Elephanta
- Originally called as Sripuri, Elephanta is an island near Bombay.
- The Portuguese named it as Elephanta after seeing the huge figure of an elephant.
- The sculptures in Ellora and Elephanta have close similarities.
- There are huge figures of dwara–palakas at the entrance to the sanctum.
- Trimurthi is the most magnificent figure of this temple. The sculpture is six metres high and said to represent the three aspects of Shiva as Creator, Preserver and Destroyer.
≫ Other facts of Rashtrakutas
- Vaishnavism and Saivism flourished during their period.
- Active commerce witnessed between the Deccan and the Arabs.
- They stimulated the Arab trade by maintaining a friendship with them.
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|
FAQs on Rashtrakuta Dynasty - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What is the significance of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty in Indian history? |  |
| 2. Who were the prominent rulers of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty? |  |
| 3. What were the major achievements of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty? |  |
| 4. What was the religious inclination of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty? |  |
| 5. How did the decline of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty occur? |  |
|
1365 videos|1312 docs|1010 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for SSC CGL exam
|

|


















