Representation on Number Line | Advance Learner Course: Mathematics (Maths) Class 5 PDF Download
Below are the steps the whole numbers to represent on the number line:
- Draw a straight line.
- Mark a point at the extreme left as 0.
Mark another points to the right of 0. Label them as 1, 2, 3,… The distance between these marks must be uniform. They are said to be at a unit distance from one another.
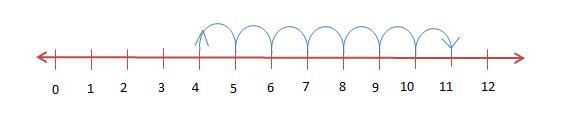
Addition to Represent on Number Line
We can add whole numbers to it. Let us see how to add 4 and 7. We start with 4 and make 7 jumps to the right of 4. The jumps are from 4 to 5, 5 to 6, …, 10 to 11. With the seventh jump, we reach 11. Thus, 4 + 7 = 11.
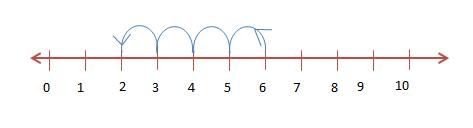
 Subtraction to Represent on Number Line
Subtraction to Represent on Number Line
Subtracting a whole number from another is just like addition. But the way of jumping is backward instead of forward. We jump to the left. Suppose we have to subtract 4 from 6. We start with 6 and make 4 jumps to the left of 6. The jumps are from 6 to 5, 5 to 4, …, 3 to 2. With the fourth jump, we reach 2. Thus, 6 − 4 = 2.
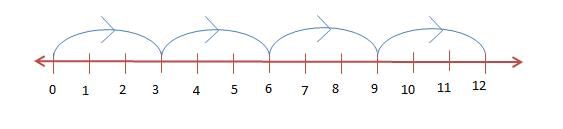
 Multiplication to Represent on Number Line
Multiplication to Represent on Number Line
To find the product of two whole numbers say, 4 × 3, we start from 0 and move 3 points forward at a time. After the fourth jump, we reach at 12. Also, we can move 4 points forward and with the third jump, we get the same result.
 Division to Represent on Number Line
Division to Represent on Number Line
Division on it is like the iterated or the repeated subtraction. If we have to divide 10 by 2, we start at 10. With an interval of 2 points, we move backwards one at a time till we reach 0. The number of jumps made is the solution. Here, it is 5. So, 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
Solved Examples
Ques 1: Fill in the blank:
On a number line, the greater whole number lies to the ___ of the smaller whole number.
Sol: The greater whole number lies to the right of the smaller number.
Ques 2: Solve 12 ÷ 6 using a number line.
Sol: We start from 12 make jumps of an interval of 6 points. There are two jumps. So, 12 ÷ 6 = 2.
Natural Numbers
The natural numbers are the counting numbers. It goes like 1, 2, 3, 4, …, and so on. It is interesting to know that if we subtract 1 from any natural number, we get its predecessor (previous number). If we add 1 to any natural numbers, it gives its successor (next number).
The predecessor of 5 is 5 − 1 = 4. The successor of 5 is 5 + 1 = 6. Is there any natural number that has no predecessor? The predecessor of 2 is 1. What is the predecessor of 1? Does that predecessor is also a natural number? No, no natural number is the predecessor of 1.
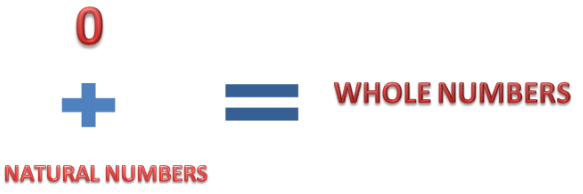
Whole Numbers
Suppose you have 5 chocolates and you distribute them among your friends. How many chocolates do you have? Zero. Zero is denoted by the symbol 0. When we add 0 to the group of natural numbers, we get whole numbers. The predecessor of 1 is 1 − 1 = 0. 1 has the predecessor which is a whole number and not a natural number.
Properties of Zero
- Any number, when multiplied by 0, gives 0.
- When 0 is added to any number, nothing changes.
- When 0 is subtracted from any number, it remains the same.
- 0 is the smallest whole number.
The whole numbers are said to consist of two types of numbers – even numbers and odd numbers.
Even Numbers
The numbers which are divisible by 2 are even numbers. Even numbers leave 0 as a remainder when divided by 2. Even numbers have 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8 as their unit digit. 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22 etc. are even numbers. The sets of even number are expressed as Even = {2n: n ∈ integer (number)}.
Is 0 an even number? Zero is an even number as it is a multiple of 2. It can be expressed as {2n = 2 × 0}.
Odd Numbers
Odd numbers are numbers that are not completely divisible by 2. The odd numbers leave 1 as a remainder when divided by 2. They have 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 as their unit digit. 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, etc. are odd numbers. The sets of odd number are expressed as Odd = {2n + 1: n ∈ integer (number)}.
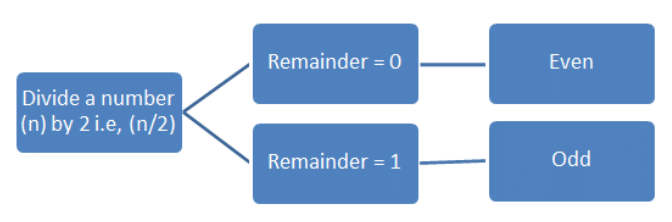
Steps to Check for Odd and Even Numbers
- Divide the number by 2.
- Check the remainder.
- If the remainder is 0, it is an even number else if the remainder is 1, it is an odd number.
Think of any two odd numbers. Subtract the two odd numbers. What do you get? An even number? Multiply the two odd numbers? What is the product? An odd number. Repeat this with any other odd numbers. The result will be the same. This shows that the product of any two odds is an odd number. When we subtract any two odd numbers, we get an even number.
Solved Examples
Ques 1: Is 134256791 an even number?
Sol: The unit digit of the given number is 1 which is odd. The above number will leave 1 as a remainder when divided by 2. The number 134256791 is odd.
Ques 2: What is the sum of two even numbers? What is the sum of two odd numbers?
Sol: The sum of two even numbers is always an even number. Two odd numbers add up to give an even number.
|
37 videos|22 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Representation on Number Line - Advance Learner Course: Mathematics (Maths) Class 5
| 1. What are natural numbers? |  |
| 2. What are whole numbers? |  |
| 3. How are natural numbers represented on a number line? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between natural numbers and whole numbers? |  |
| 5. Can we find negative natural numbers on a number line? |  |

















