Reproductive Health: Problems & Strategies | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is Reproductive Health?
Reproductive health refers to the complete physical, mental and social well-being and not simply the absence of a disease in an individual capable of reproducing.
Maintaining reproductive health is significant for both individuals and society as a whole. It includes various aspects of physical, emotional, behavioral, and social well-being related to reproduction

- As per the WHO -World Health Organization, reproductive health can be defined as the total well-being and proper functioning of reproductive organs in all phases of reproduction. This includes a complete state of mental, physical, and social well-being.
- There are a number of programs that are directed for maintaining reproductive health.
- These programs include both small ads and few entertainment shows telecasted on the television for promoting safe sexual habits and awareness about various sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). All these efforts by the government and NGOs aim at achieving a reproductively healthy society.
Objectives of Reproductive Health
Maintaining reproductive health is significant for both individuals and society as a whole. It encompasses various aspects of physical, emotional, behavioral, and social well-being related to reproduction, and here are some of the reasons why it is essential:
- Individual Well-being: Reproductive health is crucial for the overall health and well-being of individuals. When individuals have access to information, services, and support for their reproductive needs, they can make informed decisions about their sexual and reproductive health, leading to healthier lives and better outcomes.
- Gender Equality: Promoting reproductive health is linked to gender equality. It ensures that both men and women have equal access to reproductive healthcare and the ability to make decisions about their bodies and reproductive choices. This can help reduce gender-based disparities and empower individuals to make choices based on their own preferences and needs.
- Preventing Health Issues: Good reproductive health care can help prevent and manage various health issues. For instance, access to family planning services can reduce unintended pregnancies and the associated health risks. Regular check-ups can detect and treat reproductive health problems early, which can have long-term health benefits.
- Reducing Maternal Mortality: Adequate reproductive health services, including safe and hygienic childbirth, can significantly reduce maternal mortality rates. Ensuring women have access to skilled healthcare during pregnancy and childbirth is crucial for preventing maternal deaths.
- Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Promoting safe sexual practices and providing information on preventing STIs is a key part of reproductive health. This can help reduce the spread of STIs, including HIV, and their associated health consequences.
Components of Reproductive Health
There are three essential components of sexual and reproductive health care:
- Family planning: It has a significant impact on the well-being of families and especially women. With better family planning and the use of contraceptives, one can avoid unwanted pregnancies, space births and also protect themselves from STDs.
- Sexual health: It refers to a respectful and positive approach towards sexual relationships. It is a very important prerequisite for good reproductive health.
- Maternal health: It refers to the maintenance of a woman’s health during pregnancy and after childbirth
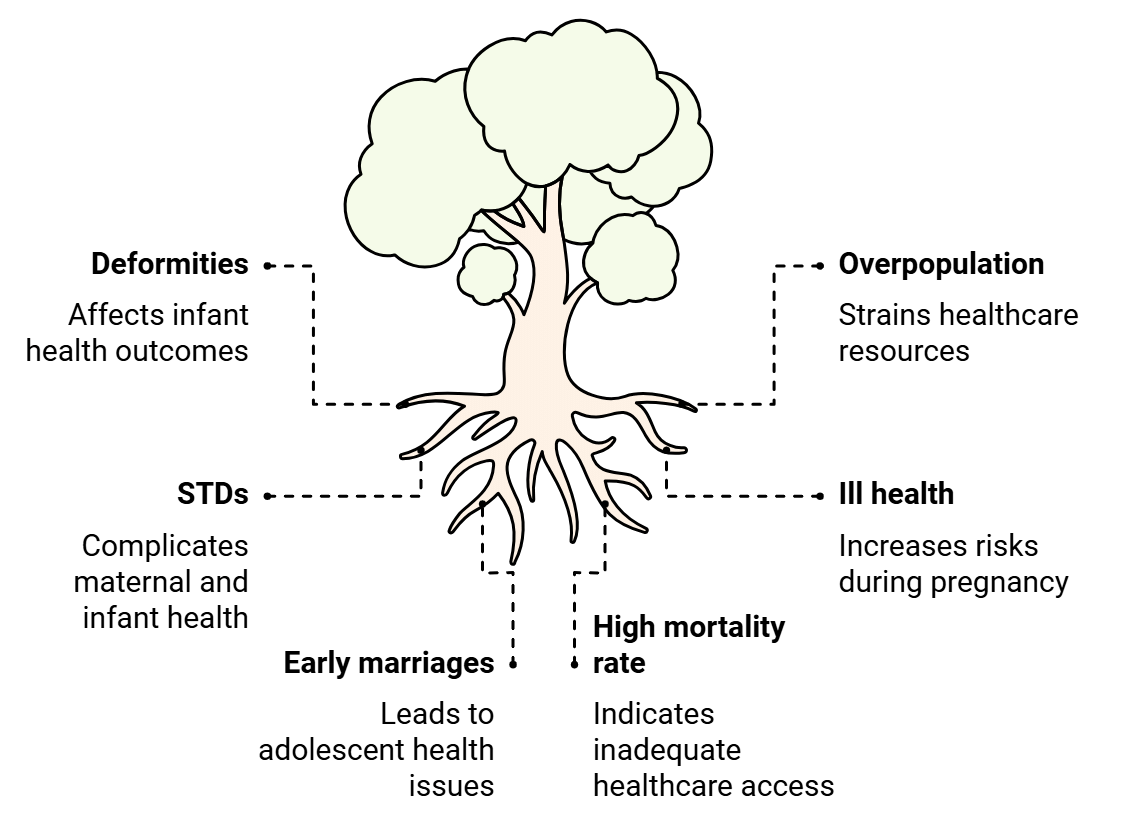
Reproductive Health Problems
The common problems or concerns associated with reproductive health are:
Strategies to Improve Reproductive Health
Listed below are a few strategies followed to improve reproductive health:
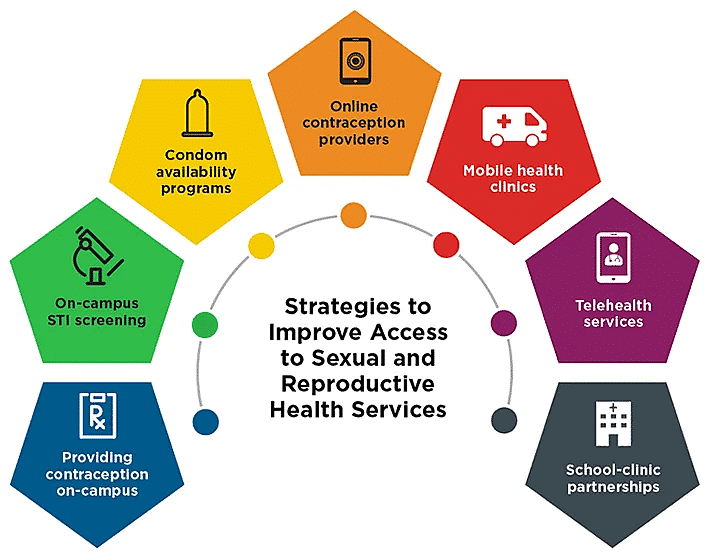
(i) Early Initiatives in Family Planning: India was one of the early countries to launch national-level action plans and programs aimed at achieving total reproductive health as a social goal. These programs, commonly referred to as 'family planning,' were initiated in 1951. Family planning programs focus on regulating birth rates through various means, including contraception and reproductive health education.
(ii) Evolution to Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) Programs: Over the decades, these family planning programs have evolved into more comprehensive initiatives known as 'Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH) programs.' These programs encompass a wider range of reproductive health-related areas and are designed to create awareness and provide support for building a reproductively healthy society.
(iii) Awareness and Education: Governmental and non-governmental agencies have used audio-visual and print media to create awareness among the public about various aspects of reproduction. Parents, relatives, teachers, and friends also play a crucial role in disseminating information. Encouraging sex education in schools is emphasized to provide accurate information to young individuals, dispelling myths and misconceptions.
(iv) Reproductive Health Education: Proper information is crucial in educating individuals about reproductive organs, adolescence, safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), AIDS, and more. This education is particularly important for adolescents, as it helps them lead reproductively healthy lives.
(v) Family Planning and Birth Control: Fertile couples and those of marriageable age are educated about available birth control options. This includes care for pregnant mothers, post-natal care for mothers and children, and the importance of breastfeeding. The goal is to help individuals make informed decisions about family size and promote equal opportunities for male and female children.
(vi) Addressing Social Issues: The programs aim to create awareness about problems associated with uncontrolled population growth, such as social evils like sex abuse and sex-related crimes. These issues are highlighted to encourage individuals to take necessary steps to prevent them and build a socially responsible and healthy society.
(vii) Infrastructure and Professional Support: Successful implementation of these initiatives requires strong infrastructural facilities, professional expertise, and material support. These are essential to provide medical assistance and care for various reproduction-related issues, including pregnancy, delivery, STDs, abortions, contraception, menstrual problems, infertility, etc.
(viii) Research and Innovation: Research on reproduction-related areas is encouraged and supported by governmental and non-governmental agencies to develop new methods and improve existing ones. The passage mentions the development of 'Saheli,' a new oral contraceptive for females, by scientists at the Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow, India.
(ix) Positive Outcomes: The passage notes several positive outcomes of these initiatives, including increased awareness about sex-related matters, medically assisted deliveries, reduced maternal and infant mortality rates, smaller family sizes, better detection and cure of STDs, and overall improved medical facilities for reproductive health-related issues.
Importance of Reproductive Health
- It is essential to know the importance of reproductive health as it checks the spread of many sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, AIDS, etc.
- The well-being of the reproductive system also ensures the production of better offspring which have better chances at surviving.
- Spreading awareness about sex education helps keep a check on the population, thereby preventing a population explosion.
- Teen pregnancies are usually unwanted and can hence be avoided, thereby keeping a check on their overall health.
- Through awareness alone, reproductive health has improved tremendously in India, in the past 50 years.
- Knowledge of the benefits of smaller families through the use of contraceptives has proven to result in the economic growth of the family.
- Various schemes and programmes are being implemented by the government to ensure and provide proper health care services with a vision of reducing the mortality rate and promoting a better standard of living in the country.
Obstacles and Approaches
The commonly related concerns of reproductive health are:
- Population explosion
- Disfigurements
- Poor health of the pregnant mother and hence the baby’s ill health
- Marriage before adolescence
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- The increased death rate of pregnant mothers and the fetus
Population Explosion
- Population growth is one of the major concerns of the present world as the human population is not a static factor. Rather, it is growing at a very alarming rate.
- In spite of the increasing world population, the resources of the earth remain constant. Thus, the ability to maintain sustainable development is becoming a major challenge to mankind today.
- The tremendous increase in size and growth rate of population is called population explosion. It occurs due to increased health facilities and better living conditions.
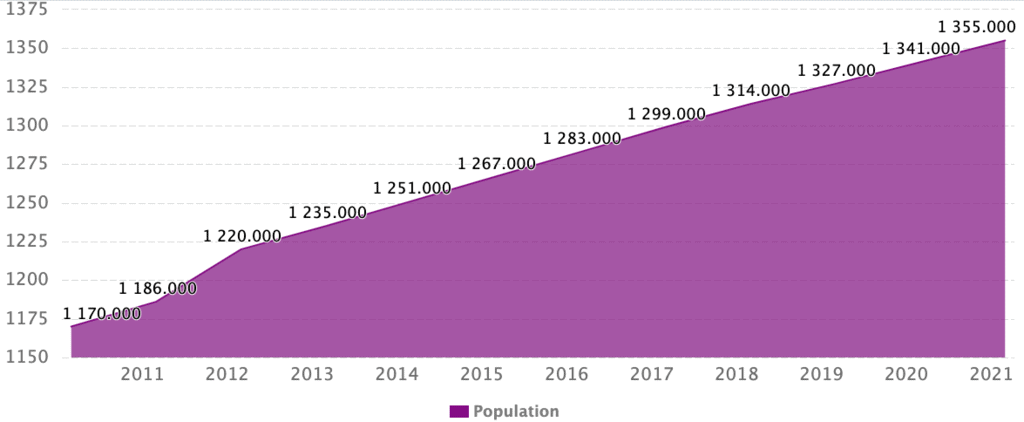 Increase in India's Population
Increase in India's Population
Reasons for population explosion:
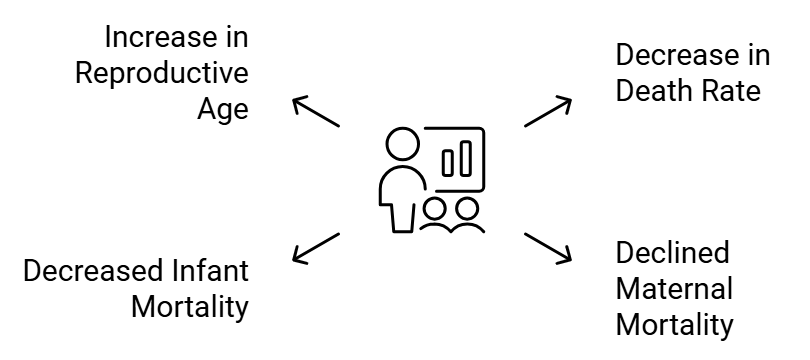 Reasons for Population Explosion
Reasons for Population Explosion
According to the 2001 census report, the population growth rate was around 1.7%, i.e. 17/1000/year. By this rate, our population could alarmingly double in the next 33 years.
Methods to prevent population explosion:
- Raising the marriageable age to 18 years for females and 21 years for males.
- Couples with small families should be given some incentives.
- Birth control is an important step to control population growth by motivating smaller families to use contraceptive methods.
What is Amniocentesis Test?
- The amniocentesis test is mainly used for the determination of the sex of unborn baby through analyzing the chromosomal content of the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus.
- All these efforts being put forward to achieve a reproductively healthy society would be worthless if we do not cooperate.
- Thus, with the cooperation of the society, government and other NGOs, a reproductively healthy society can be achieved.
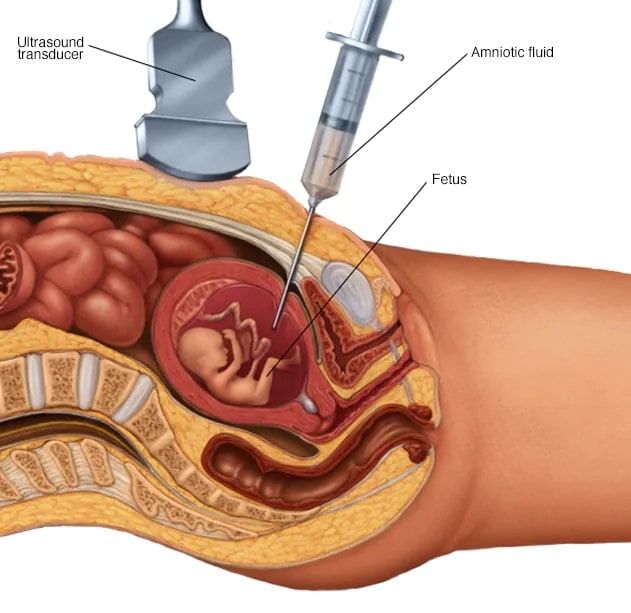 Aminocentesis Test
Aminocentesis Test
Why is Amniocentesis performed?
The amniocentesis is performed to check:
- If the karyotype (the chromosomes) of the baby is (are) normal
- If there is evidence of a neural tube defect (spina bifida or open spine)
- If there is evidence that the baby might have had an infection
- If the lungs of the baby are ready to breathe
Risks Involved In Amniocentesis
The risks involved in amniocentesis include:
- Risk of Miscarriages
- Risk of Injuries.
- Cramping
- Leaking of amniotic fluid from the puncture site or vagina
- Preterm labour
- Risk of Injuries
- Injuries to the baby by the needle are exceedingly rare now since the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.
Ban on Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis had been banned in India in 1994, under the Preconception and Prenatal Diagnostic Techniques Act. This was because amniocentesis could reveal the sex of the foetus. Since a girl child is not accepted in many parts of the country, the female foetus is aborted in most of the cases. To stop this, amniocentesis was banned in India.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Reproductive Health: Problems & Strategies - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is reproductive health? |  |
| 2. What are the objectives of reproductive health? |  |
| 3. What are the components of reproductive health? |  |
| 4. What are some common reproductive health problems? |  |
| 5. What strategies can be implemented to improve reproductive health? |  |






















