Social Structure, Stratification and Social Processes Class 11 Sociology
Introduction
- In Introducing Sociology (refer to pages 28-35), it is highlighted that each individual holds a unique position in the social structure and system of social stratification.
- As a result, their access to social resources may vary both in terms of type and degree, which is often determined by their socioeconomic class.
- This underscores the importance of understanding the dialectical relationship between the individual and society, which has been a key objective of the sociological approach.
- To comprehend this dynamic interaction, we need to discuss the three essential concepts of structure, stratification, and social processes in this chapter.
Social Structure and Stratification
Social Structure
- The term "social structure" pertains to the general organization or structure of society.
- Social structure often refers to the consistent patterns or regularities found in human behavior and relationships.
- Underlying patterns and regularities are present in the way people interact with each other, as seen through repeated behaviors across different times and spaces.
- The concepts of social reproduction and social structure are intertwined in sociology due to this repetition of patterns, as seen in the establishment of institutions such as schools, where processes like admissions, dress codes, annual events, daily assemblies, uniforms, and anthems are observed and repeated over time.
As a result, modifications are made to the social institutions' structure. Either cooperative behaviour or major conflict brought on by rivalry results in a change.
The pattern of human behaviour connected to cooperation and conflict is explained by two main elements.
- Emile Durkheim emphasized that societies exercise social control over the actions of their members. He believed that society has a solidity similar to physical structures, and that it exists independently of individual actions. Durkheim's perspective places society before the individual.
- While Karl Marx and other social theorists acknowledge the constraints of social structure, they also recognize the capacity of human agency and creativity to both maintain and transform social structures.
Social Stratification
- Social stratification is the systematic inequalities between social classes in terms of access to physical and symbolic rewards.
- Modern societies are characterized by stark differences in income and power.
- While class is the most apparent form of stratification in contemporary societies, other factors such as race, caste, location, community, tribe, and gender still play a significant role as the foundation of social stratification.
- Inequality within social stratification is not randomly spread among people in society but is systematically linked to participation in various social groups.
- Members of higher-ranked groups tend to pass on their privileged status to their offspring.
- Thus, the term "stratification" refers to the idea that society is divided into a consistent pattern of unequal groups, which tend to endure across generations.
- Social stratification serves to meet the needs of different strata, as no one can fulfill all their demands alone.
- A social structure consists of social units and patterned relationships that form a unique set of relationships between different units.
- Social structure is what makes the external, relatively permanent, and abstract form of society apparent.
- The most apparent types of stratification in contemporary societies are those based on class, race, caste, religion, community, tribe, and gender.
A form of social stratification known as the caste system includes the following characteristics:
- Social and religious disadvantages faced by different groups.
- Coexistence and dietary limitations.
- Constraints on marital relationships.
- Limitations on career options.
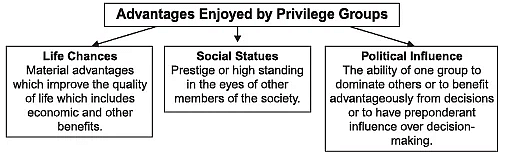
Some of the fundamental benefits that advantaged groups may enjoy are:
- Life chances refer to the tangible benefits that enhance a person's quality of life, including wealth, income, health insurance, job stability, and leisure time.
- Social status is the level of respect or importance a person holds in society.
- Political influence involves one group's ability to exert power and control over another group based on their decision-making capabilities.
- Social structure and stratification impact the opportunities and resources available to individuals and groups, shaping their ability to compete, collaborate, and engage in conflict.
Two Ways of Understanding Social Processes in Sociology
Sociology seeks to understand the processes of collaboration, rivalry, and conflict within the social structure of society. Both the conflict and functionalist perspectives recognize the importance of cooperation in fulfilling fundamental human needs and reproducing society and its environment- The conflict perspective focuses on how cooperation differs across historical societies and how the system of production relations can create conflict and rivalry between groups. It recognizes the potential for hidden conflicts of interest in daily interactions between groups, such as between factory owners and workers. Additionally, it highlights how society is divided along caste, class, or patriarchal lines, with some groups experiencing discrimination and disadvantage.
- The functionalist perspective emphasizes the specific functional requirements of society, such as integrating new members, communication mechanisms, and assigning responsibilities to people. It assumes that various components or organs of society have a role or function to play in maintaining and operating society. The functional approach acknowledges that collaboration, competition, and conflict are universal characteristics of all societies, with complex and interrelated relationships between them.
Social Processes
- Social processes refer to the various actions individuals undertake while operating within the confines of a particular social organization.
- Sociologists seek to elucidate social processes by utilizing the existing social structure and society, as well as adopting a pluralistic understanding of society.
- MacIver and Page describe social process as "the continuous change that takes place in a specific manner within the social structure."
- Consequently, social processes, or the process of social interaction, result from social contact.
- Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim both assert that humans must collaborate to meet their basic needs and to produce and reproduce themselves and their environment.
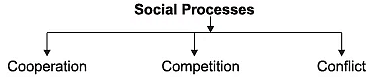
Cooperation
- The act of two or more people working together voluntarily and equally towards a common objective is referred to as cooperation, which is critical for human society's survival.
- Cooperation is based on several assumptions about human behavior.
- Cooperation is a universal and ongoing process that involves both sympathy and empathy for others. Its nature is selfless, and it is essential both on a psychological and social level.
- Human life would face significant challenges without cooperation, and to meet basic social needs, cooperation is essential, facilitated by the division of labor in society.
- Associative thinking is a fundamental aspect of cooperation.
Competition
- Competition can be described as a struggle between individuals or groups vying for a limited resource.
- It is a widespread and inherent social process present in all human societies, and in modern society, it is a pervasive norm and practice.
- In contemporary times, competition serves as a driving force for societal functioning.
- The prevalence of competition in modern capitalist societies fosters individualism as a result.
- In capitalist societies, the emphasis on trade expansion necessitates mass production in factories with multiple workers.
- The ideology of competition is the prevailing belief system in capitalism.
Conflict
- Conflict and cooperation are distinct social processes, with conflict being characterized by dissociation.
- While conflict is typically a conscious process, cooperation can sometimes be unconscious.
- Conflict arises from groups competing for access to scarce resources and control over them within society.
- Conflicts can have various roots, including caste, class, tribe, gender, ethnicity, or religion.
- Competition and conflict are distinct processes, with conflict being primarily conscious and competition sometimes being unconscious.
- Personal ambitions tend to drive conflicts, while goal achievement is the main motivation behind competition.
- Conflict may not be apparent until it is publicly expressed, and lack of movement does not necessarily mean an absence of conflict.
- Conflict can coexist with cooperation and may even be necessary for it, with forced and voluntary cooperation having different implications. An example of this is daughters' property rights in Indian society, where asking for those rights may be seen as greedy, while giving them up may be viewed as cooperative. Therefore, cooperative behavior may result from intense social strife.
- Emile Durkheim argued that collaboration is necessary to achieve certain societal objectives, with the division of labor serving that purpose, while Karl Marx believed that people both cooperate and change society through their interactions.
Cooperation and Labor Division
- Cooperation is essential for human survival as it simplifies goal achievement and brings individuals together, leading to expanded learning opportunities, especially in the economic sphere.
- Understanding Durkheim's solidarity is crucial for knowledge cooperation, which involves both organic and mechanical solidarity as examples of social collaboration.
- Labor division requires cooperation to satisfy particular societal needs.
- Although Karl Marx and Durkheim both emphasize cooperation, they have differences. Marx argues that collaboration in a class-based society is not voluntary and arises spontaneously from class conflict. This is significantly different from a worker in a factory who may find satisfaction and pleasure in creative work, such as a weaver, potter, or iron smith, and requires cooperation.
Organic Solidarity
- Cohesiveness can be based on various factors such as age, sex, division of labor, specialization, and lifestyle.
- Social cohesion can be achieved through interdependence and division of labor.
- A sense of unity can arise among individuals who share common values, attitudes, and awareness, like members of a farming family.
- With increasing specialization, individuals become more reliant on each other, as can be observed in corporations that specialize in clothing or automobile manufacturing.
Mechanical Solidarity
- Cohesion can take the form of shared lifestyle, specialization, division of labor, age, and sex.
- It may be based on a common interdependence and division of labor, as well as shared values, attitudes, and awareness. For example, a farming family may share a common lifestyle and belief system.
Competition as an Idea and Practice
- Competition is the pursuit of scarce goods or services through conflict between two or more parties, and it is a ubiquitous and organic social process found in every human society. Although it is a natural process, the social explanation for competition differs from naturalistic explanations.
- In modern culture, competition is a widely accepted belief, social norm, and behavior, and it is impossible to imagine a society where competition does not serve as a driving force.
- The expansion of trade and large-scale manufacturing in factories, which employ many people, is the primary goal of contemporary capitalism, and both Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim observed the rise of individuality and competition in modern civilization, both of which are fundamental to contemporary capitalism's operation.
- The prevailing ideology of capitalism is that of competitiveness, which assumes that everyone competes on an equal footing, and the market operates in a way that maximizes efficiency, such as through competitions for resources, jobs, or education. However, stratification and inequality reveal that people are positioned differently in society, leading to conflict.
- Hidden conflict and open cooperation are common coping mechanisms employed by marginalized groups like women or peasants to deal with conflict and promote collaboration. Sociological research has shown that both hidden conflict and open cooperation are widespread in cultures.
Conflicts and Cooperation
Nature of Conflicts:
- Conflicts vary by scale and nature, existing between nations and within them.
- Conflicts are not new; they evolve with societal development and become more visible with social change and democratic assertions by marginalized groups.
- Conflicts stem from clashes of interests, often due to resource scarcity, and can be based on class, caste, tribe, gender, ethnicity, or religion.
Developing Societies and Conflicts:
- In developing countries, conflicts arise between traditional systems and modern forces, often leading to discord and sometimes violence.
- These conflicts highlight the struggles between maintaining the old order and accommodating new societal demands.
Conflict Expression:
- Conflict may not always be overt; absence of overt conflict does not imply absence of underlying issues.
- Examples include covert conflicts within families or among peasants over land resources, where overt cooperation masks underlying disagreements.
Family and Household Conflicts:
- Families and households, traditionally seen as harmonious, often harbor covert conflicts with overt cooperation.
- Conflicts within families can involve gendered distribution processes and decision-making hierarchies, with women often adopting covert strategies to cope with and resist male dominance.
Strategies of Subaltern Groups:
- Subordinate groups develop covert strategies to handle conflicts and maintain cooperation, such as secret economic activities or subtle negotiations of societal norms.
- Women in patriarchal societies may engage in maternal altruism biased towards sons as a strategy for future security.
Sociological Perspective:
- Sociology challenges the naturalization of competition, cooperation, and conflict, relating them to broader social and economic contexts.
- Sociological studies explore how societal cooperation is intertwined with technological and economic arrangements.
|
41 videos|94 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Social Structure, Stratification and Social Processes Class 11 Sociology
| 1. What is social structure and how does it relate to social processes in society? |  |
| 2. How does labor division contribute to cooperation in society? |  |
| 3. In what ways does competition influence social processes in society? |  |
| 4. How do conflicts arise in social structures and what impact do they have on society? |  |
| 5. How do social processes such as cooperation, competition, and conflict shape social stratification in society? |  |




















