Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Mathematics Class 9 ICSE > Revision Notes: Circle
Revision Notes: Circle | Mathematics Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Related Terms
- A circle is a locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point is always constant. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle.
- The line segment joining any two points on a circle is called a chord of the circle.
- A chord of a circle passing through its centre is called a diameter of the circle.
It is the largest chord of a circle.
Also, Diameter = 2 x Radius - A circle divides the plane region into three parts:
Circumference: A point P lies on the circle if and only if its distance from the centre of the circle is equal to the radius of the circle.
Interior of a circle: A point P lies inside a circle if and only if its distance from the centre of the circle is less than the radius of the circle.
Exterior of a circle: A point P lies outside a circle if and only if its distance from the centre of the circle is greater than the radius of the circle. - Circles having the same centre but with different radii are said to be concentric circles.
- Two circles are said to be equal or congruent if they have equal radii.
- A circle passing through all the vertices of a polygon is called circumscribed circle of the polygon and its centre is called circumcentre.
The polygon is called inscribed polygon. - A circle touching all the sides of a polygon is called an inscribed circle of the polygon and its centre is called incentre.
Arc, Segment and Sector
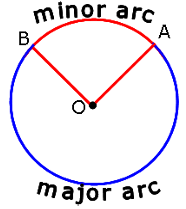
Arc
- An arc is a part of the circumference of a circle.
- An arc less than one-half of the whole arc of a circle is called a minor arc of the circle, and an arc greater than one-half of the whole arc of a circle is called a major arc of the circle.
Segment
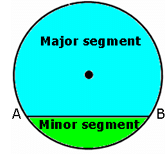
- A chord of a circle divides it into two parts. Each part is called a segment.
- The part containing the minor arc is called the minor segment, and the part containing the major arc is called the major segment.
Sector
- The region bounded by an arc and two radii, joining the centre to the end points of the arc, is called a sector.
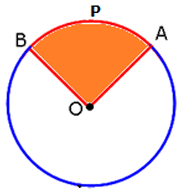
- The region bounded by an arc APB and radii OA and OB is a sector.
Chord Properties
- A straight line drawn from the centre of a circle to bisect a chord which is not a diameter is at right angles to chord.
- Perpendicular drawn to a chord from the centre of a circle bisects the chord.
- Equal chords of a circle are equidistant from centre.
- Chords which are equidistant from the centre are equal in lengths.
- There is one and only circle which passes through three given points not in a straight line.
- The perpendicular bisector of a chord of a circle always passes through its centre.
- Perpendicular bisectors of two chords of a circle intersect at its centre.
Arc Properties
- In equal circles, if two arcs subtend equal angles at the centre then they are equal.
- In equal circles, if two arcs are equal then they subtend equal angles at the centre.
- In equal circles, equal chords cut off equal arcs.
- In equal circles, if two arcs are equal then their chords are equal.
- Equal chords of the same circle subtend equal angles at the centre of the circle.
- Equal angles at the centre make equal chords.
- Equal arcs of the same circle subtend equal angles at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
The document Revision Notes: Circle | Mathematics Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course Mathematics Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
64 videos|165 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Circle - Mathematics Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What is the definition of a circle in geometry? |  |
Ans. A circle is a two-dimensional shape consisting of all points that are equidistant from a fixed point called the center. The distance from the center to any point on the circle is known as the radius.
| 2. How do you calculate the circumference of a circle? |  |
Ans. The circumference of a circle can be calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where C represents the circumference and r is the radius of the circle. Alternatively, if the diameter (d) is known, it can also be calculated using C = πd.
| 3. What is the area of a circle and how is it calculated? |  |
Ans. The area of a circle is the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries. It is calculated using the formula A = πr², where A represents the area and r is the radius of the circle.
| 4. What is the relationship between the radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle? |  |
Ans. The diameter of a circle is twice the length of the radius (d = 2r). The circumference is directly proportional to the diameter and can be expressed as C = πd. Therefore, knowing any one of these measurements allows you to calculate the others.
| 5. How do you find the length of an arc in a circle? |  |
Ans. The length of an arc can be calculated using the formula L = (θ/360) × C, where L is the arc length, θ is the central angle in degrees, and C is the circumference of the circle. If the angle is in radians, the formula simplifies to L = rθ, where r is the radius.
Related Searches
















