Revision Notes: Elasticity of Demand | Economics for Grade 9 PDF Download
Meaning of Elasticity of Demand
The elasticity of demand assesses how responsive the quantity demanded of a good is to changes in its price, the price of other goods, and changes in the consumer's income. This concept was first introduced by Alfred Marshall, who defined price elasticity of demand as the ratio of relative change in quantity demanded to relative change in price.
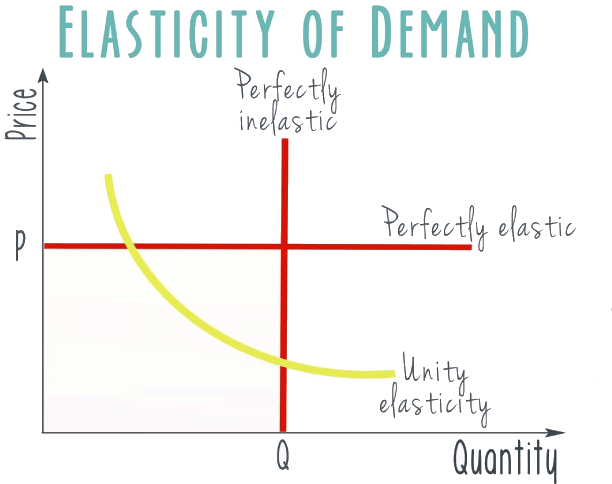
Degrees of Price Elasticity of Demand
- Perfectly Inelastic Demand: In this case, the demand curve is vertical, indicating that quantity demanded remains constant regardless of price changes. Here, the price elasticity of demand (ed) is equal to 0.
- Inelastic Demand: The demand curve for inelastic demand is steep. This means that a large change in price results in only a small change in quantity demanded. In this scenario, ed is less than 1.
- Unit Elastic Demand: The demand curve in this case is a rectangular hyperbola, extending towards both axes. This indicates that the percentage change in quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price, i.e., ed = 1.
- Elastic Demand: The demand curve for elastic demand is relatively flat. This suggests that a percentage change in quantity demanded is much greater than the percentage change in price, with ed greater than 1.
- Perfectly Elastic Demand: In this scenario, the demand curve is horizontal. A small change in price leads to an infinitely large change in quantity demanded, indicating that ed is infinite.
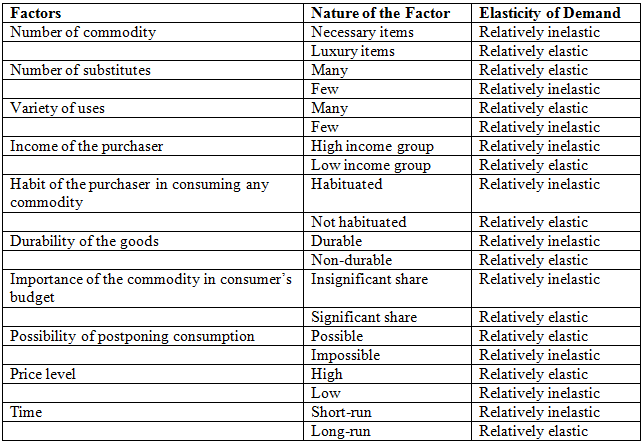
Factors Influencing Demand Elasticity
Method of Measurement
There are three methods to measure the price elasticity of demand: Total Expenditure Method, Proportionate Method and Geometric Method.
Price elasticity of demand refers to the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good to changes in its price. It is calculated by dividing the percentage change in demand by the percentage change in price. This measure is unitless, meaning it does not depend on the specific units used for price and quantity. However, it is typically a negative number because demand usually falls when prices rise.
The formula for price elasticity of demand is: e p = Percentage change in demand/Percentage change in price
e p = ( Δ Q/Q ) × 100 / ( Δ P/P ) × 100
Where: e p = Price elasticity of demand Δ Q = Change in demand Δ P = Change in price Q = Original demand P = Original price
Total Expenditure Method
- Unit Elasticity: When a change in price does not affect total expenditure, the elasticity of demand is unitary.
- Greater than Unitary Elasticity: If a decrease in price leads to an increase in total expenditure, or if an increase in price leads to a decrease in total expenditure, demand is greater than unitary elastic.
- Less than Unitary Elasticity: If a decrease in price leads to a decrease in total expenditure, or if an increase in price leads to an increase in total expenditure, demand is less than unitary elastic.
Significance of Elasticity of Demand
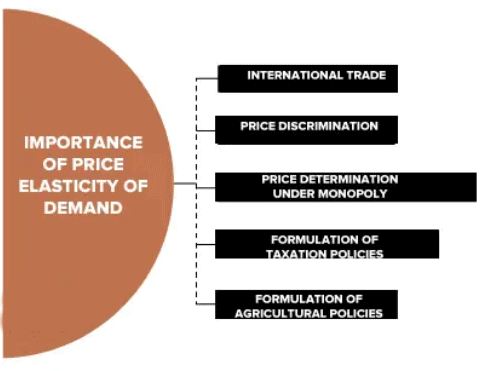
Elasticity of demand is a crucial concept in economics with applications in various fields such as:
- Price Setting: Businesses use elasticity to determine how much they can change prices without significantly affecting demand.
- Wage Bargaining: Understanding how demand for labor changes with wage variations helps in negotiating salaries.
- International Terms of Trade: Countries assess elasticity to set favorable trade terms based on how demand for goods changes with price shifts.
- Indirect Taxation: Governments consider elasticity to predict the impact of taxes on goods and services and to set tax rates accordingly.
- Devaluation Policy: Elasticity informs decisions on currency devaluation by predicting its impact on demand for exports and imports.
Different Types of Elasticity of Demand
1. Price Elasticity of Demand
- It measures how much the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in its price.
- Formula: ep = Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in price
2. Income Elasticity of Demand
- This measures how the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in consumer income.
- Formula: ed = Percentage change in quantity demanded / Percentage change in income
3. Geometric Method (Point Method)
- This method assesses elasticity at different points on the demand curve.
- Formula: eg = Lower segment of the demand curve / Upper segment of the demand curve
4. Cross Elasticity of Demand
- This measures how the quantity demanded of one good changes in response to a change in the price of another related good.
- Formula: ec = Percentage change in quantity demanded of good X / Percentage change in price of good Y
|
34 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Elasticity of Demand - Economics for Grade 9
| 1. What is the definition of elasticity of demand? |  |
| 2. How is elasticity of demand measured? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of elasticity of demand? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the elasticity of demand for a product? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding elasticity of demand important for businesses? |  |





















