Revision Notes: Inflation | Economics for SSS 2 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Inflation |

|
| Types of Inflation |

|
| Effects of Inflation |

|
| Control of Inflation |

|
Inflation
Inflation refers to a sustained increase in the overall price levels within an economy. It signifies a scenario where prices are continuously rising, rather than just being high at a given point in time.
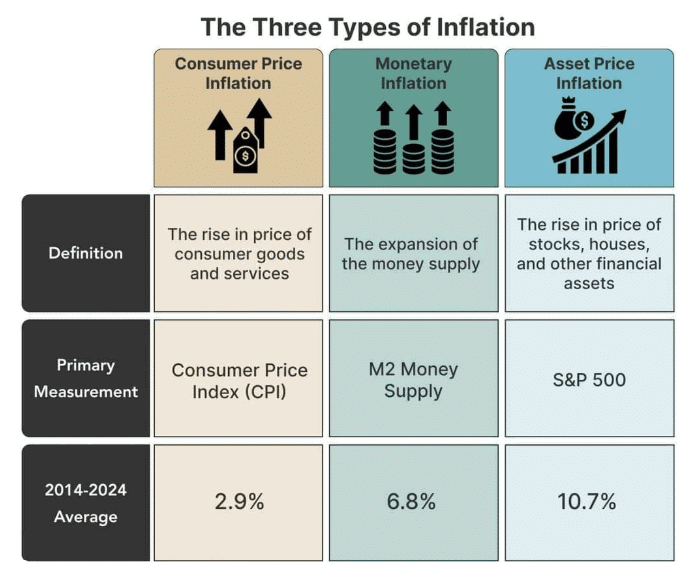
Types of Inflation
There are various types of inflation, each characterized by the rate at which prices are increasing.
- Creeping Inflation: This type of inflation occurs when the price level rises at a very slow rate, typically between 2% to 2.5% per annum.
- Walking Inflation: In this case, the general price level increases at a moderate rate of 5% to 6% per annum.
- Running Inflation: This refers to a situation where the price level is increasing rapidly, at a rate of about 10% per annum, indicating a shift to double-digit inflation.
- Hyperinflation: This is an extreme form of inflation where the price level soars by 200% or more per month, leading to astronomical price increases, sometimes ten or a hundredfold within a month.
Demand-Pull Inflation
- This type of inflation is caused by excessive demand in relation to supply. When aggregate demand exceeds aggregate supply, prices tend to rise, leading to inflation.
- Factors contributing to demand-pull inflation include:
- Population Pressure: An increasing population drives up the demand for essential goods such as food, contributing to price increases.
- Growing Government Expenditure: Increased government spending on infrastructure and development projects boosts employment and income, leading to higher demand for goods and services.
- Growing Supply of Money: Expansionary government policies increase the money supply, enhancing purchasing power and demand for goods and services.
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation occurs when the overall price level rises due to increased costs of production and inputs. This type of inflation is driven by factors that increase the cost of production, leading producers to pass on these costs to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Key factors that contribute to cost-push inflation include:
- Rising Wages: When wages increase significantly, labor costs for businesses rise. If companies face higher labor costs, they may raise the prices of their goods and services to maintain profit margins.
- Increased Raw Material Costs: If the prices of essential raw materials and inputs, such as oil, metals, or agricultural products, rise sharply, production becomes more expensive. Businesses often pass these increased costs on to consumers, leading to higher prices across various sectors.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events that disrupt supply chains, such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics, can lead to shortages of key inputs. These shortages can drive up costs for manufacturers, contributing to cost-push inflation.
Factors Leading to Cost-Push Inflation
- Rise in Wages: A rise in wages is a key factor in cost-push inflation. Trade unions often advocate for higher wages, and when labor costs increase, producers are likely to pass on these costs to consumers in the form of higher prices. This creates a cycle where increased prices lead to further demands for higher wages.
- Increase in the Price of Basic Materials: Basic materials such as steel, chemicals, and oil are essential inputs for various industries. When the prices of these materials rise, it impacts production costs across the economy, leading to an overall increase in prices.
- Higher Taxes: Increases in taxes such as excise duties, sales tax, and value-added tax can also contribute to cost-push inflation. When businesses can pass on these tax increases to consumers, it results in higher prices for various commodities.
Effects of Inflation

Effects on Purchasing Power of Money
- Purchasing power of money refers to the quantity of goods and services that a unit of money can buy. During inflation, people find themselves able to purchase fewer goods and services than before, leading to a decline in real income.
Effects on Production
- Hyperinflation can have a detrimental impact on production due to the resulting uncertainty. It disrupts the price system and encourages hoarding behavior. Additionally, hyperinflation diminishes savings and capital accumulation, both of which are essential for production.
Effects on Distribution
- Fixed Income Groups: People on fixed incomes are severely affected during periods of rising prices because their incomes do not increase. This situation is particularly challenging for the middle class, who strive to provide for their children's education through hard work. They find it increasingly difficult to make ends meet during times of significant inflation.
- Borrowers: During inflation, as prices rise and the real value of money decreases, debtors repay less in real terms than what they borrowed, making them, to some extent, beneficiaries of inflation. Conversely, creditors receive less in terms of goods and services than what they lent, leading to their loss in this context.
- Investors: When prices rise, returns on equities increase due to higher profits. However, bond and debenture holders do not benefit in the same way because their income remains fixed. Conversely, during a depression, bond and debenture holders may gain while equity holders suffer losses.
Control of Inflation
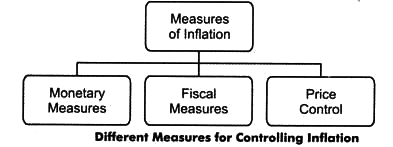
Monetary Measures
- Bank Rate Policy: When the bank rate increases, it raises the cost of borrowing for commercial banks. This leads to a decrease in the amount banks borrow from the Central Bank, which in turn reduces the flow of money from banks to the public. As a result, inflation caused by bank credit is controlled.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): To control inflation, the Central Bank may raise the CRR, which limits the lending capacity of commercial banks. This decrease in lending reduces the flow of money from banks to the public, helping to curb inflation driven by bank credit.
- Open Market Operations: In efforts to control inflation, the Central Bank sells government securities to the public through banks. This process transfers a portion of bank deposits to the Central Bank, reducing the credit creation capacity of commercial banks and helping to manage inflation.
Fiscal Measures
- Government Expenditure: When excess demand arises from government expenditure exceeding real output, cutting public expenditure is an effective measure. Reducing public spending lowers the government’s demand for goods and services, which in turn decreases private consumption expenditure. This leads to a greater reduction in excess demand compared to a cut in public expenditure alone.
- Taxation: When excess demand is driven by private expenditure, such as household and firm spending, increasing income taxes is a suitable measure to control inflation. Higher income taxes reduce disposable income, leading to a decrease in consumer demand since it is a function of disposable income. A well-designed taxation policy helps lower aggregate demand and brings inflation under control.
- Public Borrowing: Government borrowing to finance budget deficits utilizes idle money from banks and financial institutions, directing it towards productive functions through investments. When the government borrows from the market, it reduces the purchasing power of the public, contributing to inflation control.
Other Measures
- Price Control: When the government implements price control, it sets a maximum retail price for goods and services. The main goal is to prevent the price increase of scarce items and to ration their use. This measure is typically used to combat hyperinflation.
- Wage Control: Wage control is employed to fight inflation when wages are rising much faster than productivity. The government intervenes by imposing a ceiling on wage increases in both the private and public sectors.
- Increase in Output: Boosting the level of output helps maintain low prices for essential consumer goods. Additionally, the government may adopt a liberal import policy to address shortages of goods in the market.
|
46 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Inflation - Economics for SSS 2
| 1. What are the different types of inflation? |  |
| 2. What are the effects of inflation on the economy? |  |
| 3. How can inflation be controlled? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between hyperinflation and stagflation? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to monitor inflation rates? |  |














