SSS 1 Exam > SSS 1 Notes > Basic Electronics for SSS 1 > Revision Notes: Magnetism
Revision Notes: Magnetism | Basic Electronics for SSS 1 PDF Download
Magnets
- Natural : found in nature (ex. Lodestone) – composed of oxides of iron (Fe3O4)-Attracts iron
- Magnetism – property of attracting iron
- Magnetic force- the force that a magnet exerts on iron
- Artificial : magnetized piece of iron or magnetic materials.
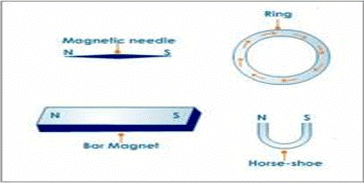
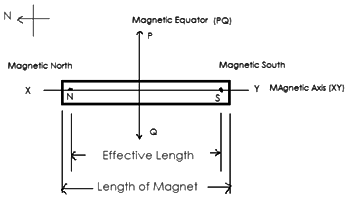
Parts of bar magnet
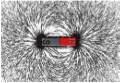
Magnetism
Properties of Magnets
- Attractive property
- Directive property
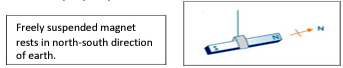
- Poles exist in pairs ( No Monopoles exist)

- Like poles repel and Unlike poles repel each other
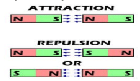
Repulsion is the Surer test for a Magnet
Making Magnets
- Magnetic Induction: Magnetism acquired by a magnetic material when it is kept near or in contact with a magnet.
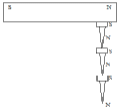
- Single Touch method:
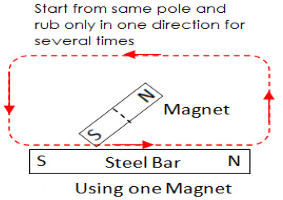
- Double Touch method:
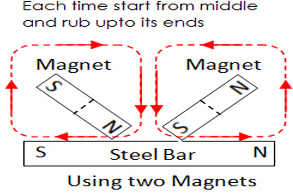
- Demagnetizing a Magnet :
- By hammering the magnet repeatedly
- By rough handling
- By heating and keeping in east west direction
- By passing AC current
- Self-demagnetization.
- Storing of Magnets : Magnet keepers
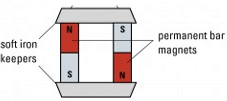
- Uses of Magnet :
- Magnetic compass
- Door bells
- Dynamos
- Motors
- Loudspeaker , etc.,
- Demagnetizing a Magnet :
- Electrical method: It is a temporary strong magnet made from a piece of soft iron when current flows in the coil wound around it. It is an artificial magnet. The polarity and magnetic field strength can be changed. Demagnetized by switching off the current.
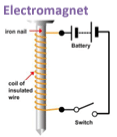 Strength depends on:
Strength depends on: - Number of turns in coil
- Amount of current flowing
- Uses: lifting and transporting huge mass of iron scrap, loading furnaces with iron, electric bell, electric fans, electric motors , etc.
- Electric Bell: Advantages of electromagnet :
- Can be easily magnetized and demagnetized by turning the current on or off in the coil.
- They can be made stronger than any other permanent magnet.
- Poles of an electromagnet can be interchanged by reversing the direction of current.
The document Revision Notes: Magnetism | Basic Electronics for SSS 1 is a part of the SSS 1 Course Basic Electronics for SSS 1.
All you need of SSS 1 at this link: SSS 1
|
40 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Magnetism - Basic Electronics for SSS 1
| 1. What is magnetism? |  |
Ans. Magnetism is a physical phenomenon produced by the motion of electric charge, which results in attractive and repulsive forces between objects. It is primarily associated with magnets, which can attract or repel certain materials, especially metals like iron, nickel, and cobalt.
| 2. How do magnets work? |  |
Ans. Magnets work due to the alignment of their atomic structure. In a magnet, the electrons' spins are aligned in the same direction, creating a magnetic field. This field extends around the magnet and can exert forces on other magnetic materials or other magnets.
| 3. What are the types of magnets? |  |
Ans. There are mainly three types of magnets: permanent magnets, which retain their magnetic properties over time; temporary magnets, which act as magnets only when in the presence of a magnetic field; and electromagnets, which are magnets created by electric current flowing through wire coils.
| 4. What are some common uses of magnets? |  |
Ans. Magnets have various applications in everyday life. They are used in refrigerator doors to keep them closed, in electric motors to convert electricity into motion, in speakers to produce sound, and in medical devices like MRI machines for imaging.
| 5. How can we demagnetize a magnet? |  |
Ans. A magnet can be demagnetized by exposing it to high temperatures, hitting it hard, or placing it in a strong opposing magnetic field. These actions disrupt the alignment of the atoms within the magnet, causing it to lose its magnetic properties.
Related Searches
















