Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Chemistry for Year 11 > Revision Notes: Pure Substances and Mixtures - Separation
Revision Notes: Pure Substances and Mixtures - Separation | Chemistry for Year 11 PDF Download
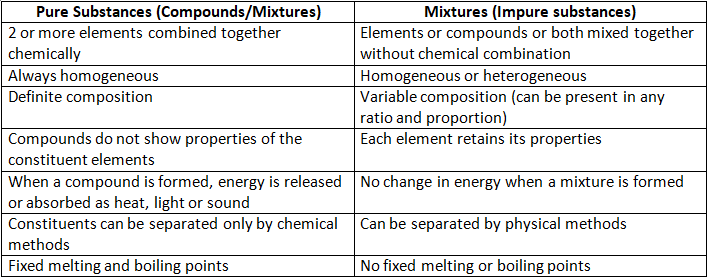
Methods of Separation of Mixtures
Separating components of solid- solid mixtures
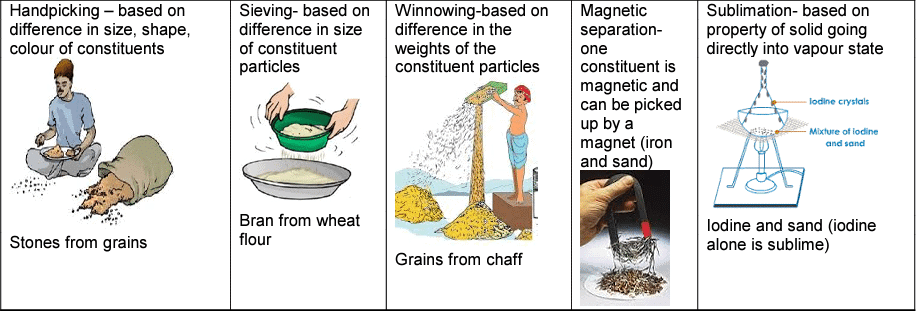 Separation of solid-liquid mixtures
Separation of solid-liquid mixtures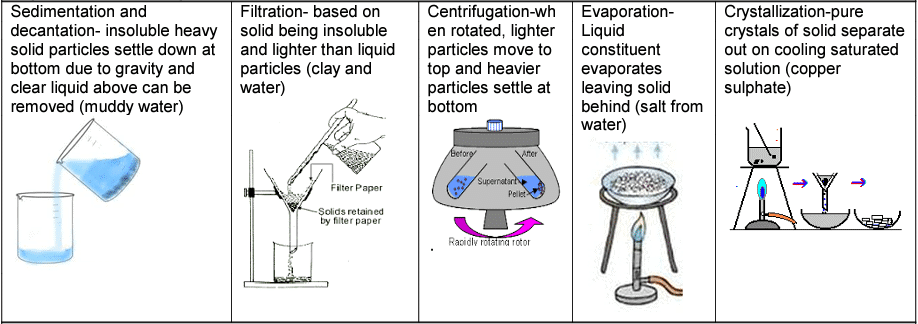 Separation of liquid -liquid mixture
Separation of liquid -liquid mixture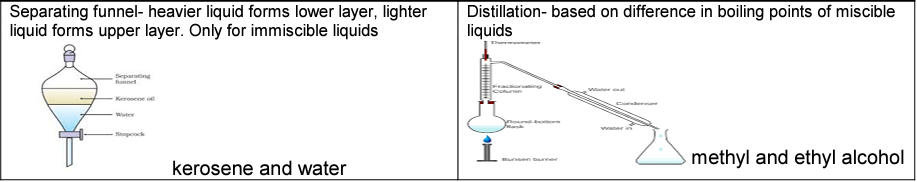
The document Revision Notes: Pure Substances and Mixtures - Separation | Chemistry for Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Chemistry for Year 11.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
2 videos|64 docs|20 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Pure Substances and Mixtures - Separation - Chemistry for Year 11
| 1. What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture? |  |
Ans. A pure substance is a material that has a uniform and definite composition, meaning it contains only one type of particle. Examples include elements like gold and compounds like water. In contrast, a mixture is made up of two or more different substances that are physically combined but not chemically bonded. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (distinct parts, like a salad).
| 2. How can we separate mixtures into their components? |  |
Ans. Mixtures can be separated using various physical methods, depending on the properties of the components. Common methods include filtration (separating solids from liquids), evaporation (removing liquids to leave solids), distillation (separating liquids based on boiling points), and magnetic separation (using magnets to remove magnetic materials).
| 3. What are some examples of pure substances and mixtures found in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Examples of pure substances include distilled water, table salt (sodium chloride), and oxygen gas. Common mixtures include air (a mixture of gases), salad (a mix of various vegetables), and concrete (a mixture of cement, sand, and gravel). Understanding these examples helps us identify the materials we encounter daily.
| 4. Why is it important to understand the difference between pure substances and mixtures? |  |
Ans. Understanding the difference is crucial because it influences how we interact with materials in science, cooking, and industry. For instance, knowing that a mixture can be separated allows us to purify substances or tailor materials for specific uses. This knowledge is important in fields such as chemistry, environmental science, and food technology.
| 5. What are some common methods of separation used in laboratories? |  |
Ans. In laboratories, common separation techniques include centrifugation (spinning mixtures to separate components based on density), chromatography (separating substances based on their movement through a medium), and recrystallization (purifying solids by dissolving and re-forming crystals). These methods are essential in chemical analysis and research.
Related Searches
















