Revision Notes: Some Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
Points to be Remembered
1. I.U.P.A.C. Nomenclature:
The following points should be remembered during I.U.P.A.C. (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) nomenclature of an organic compound.
- Find out the principal functional group first.
- Find out the longest carbon chain.
- During the numbering that path will be followed which involves lower sum for the substituents.
- During the naming of the substituents alphabetical order should be followed.
- During the naming, if more than one functional groups are present the suffix of the principal functional group should only be used. For the other functional groups, prefixes should be used.
- If one substituent is present two, three, four, ..... times then di, tri, tetra.... terms should be used before their naming.
2. Priority Table of Functional Group :
(Priority decrease down the group)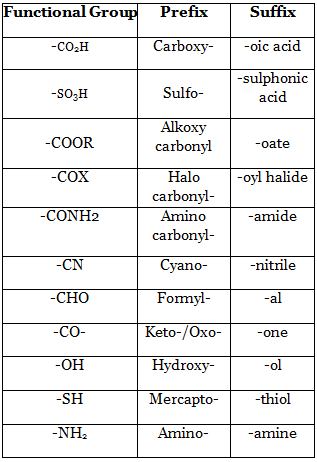
3. R/S Nomenclature:
- First assign priority of the groups as 1, 2, 3 and 4 on the basis of C.I.P. (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) rule.
- C.I.P. Rule: Higher is the atomic no. of the directly attached atom, higher will be its priority.
- If the 4-th group is at vertical position : 1 → 2 → 3 ⇛ Clockwise rotation ⇛ R and 1 → 2 → 3 ⇛ Anticlockwise rotation ⇛ S
- If the 4-th group is at horizontal position : 1 → 2 → 3 ⇛ Clockwise rotation ⇛ S and 1 → 2 → 3 ⇛ Anti-clockwise rotation ⇛ R
4. Dipole moment is expressed as the product of charge separation and distance i.e. μ = e x d.
5. The unit of dipole moment is Debye. 1 Debye = 10-18 e.s.u. cm.
6. If the group moments of some of the groups are exactly equal and opposite to the group moments of the rest groups, the molecule will be non-polar.
But, if the group moments of some of the groups are not exactly equal and opposite to the group moments of the rest groups, the molecule will be polar.
7. If μ1 and μ2 are the bond moments of two bonds with an angle of separation of θ, the resultant dipole moment will be : μres = √[μ12 + μ22 + 2μ1μ2Cos0]
8. Rules for determining Hybridization of an atom
- If (l.p. + σ b.p.) around an atom are equal to 4, 3 and 2 respectively, the hybridization of the atom will be sp3, sp2 and sp respectively.
- If the no. of π bonds presents around an atom are 0, 1 and 2 respectively, the hybridization of the atom will be sp3, sp2 and sp respectively.
9. For showing tautomerization, the presence of at least one acidic ∝-H is the necessary condition.
10. In general, the keto form is energetically more stable than the enol form. But, the % of enol form can be higher than the % of keto form due to the mainly following two reasons :
- Enol form can be stabilised through the formation of intra-molecular H-bond.
- Enol form can also get stabilised through resonance.
11. Boiling point/Melting point of a compound depends on the intermolecular force present in the compound. Greater is the intermolecular force of the compound, higher will be the B.P./M.P. Intermolecular force in turn depends on the effective molecular weight of the compound.
12. Intermolecular Forces : The strength of various types of intermolecular force : Ionic force > Ion-Dipole force > H-bonding > Keesom force > Debye force > London force.
- Ionic Force : It is the strongest intermolecular force. It occurs when two oppositely charged species will interact with each other. This force is mainly responsible for the very high BP/MP of ionic compounds like NaCl, KCl etc.
- Ion-Dipole Interaction : It occurs when an ion interacts with a molecule having a permanent dipole moment. Such type of force is responsible for the stability of alkali metal ions in solution.
- H-bonding :
(a) Types : It can be of two types. - Intra-molecular H-bonding : When the H- bonding occurs within the same molecule. This force is responsible for the higher BP/MP of compounds like salicylic acid.
- Inter-molecular H-bonding : When the Hbonding occurs between two molecules of same type or, of different types. This force is mainly responsible for the higher BP/MP of aliphatic carboxylic acids than the hydrocarbons/ethers/carbonyl compounds of comparable molecular weight.
(b) Conditions : The two basic conditions for stronger H-bonding are :
- The H-atom which is going to form H-bond should remain attach with a highly electronegative atom (N, O and F).
- Another highly electronegative atom (N, O and F) should be present closer to the H-atom which is already attached to an electronegative atom.
- Keesom Force : It is also known as dipole-dipole interaction. It occurs when a molecule with permanent dipole moment will interact with another molecule of same or, different type with permanent dipole moment. Such type of force is responsible for the very high BP/MP of carbonyl compounds compared to hydrocarbons/ethers compounds of comparable molecular weight.
- Debye Force : It is also known as dipole-induced dipole interaction. It occurs when a molecule having permanent dipole moment will interact with another molecule having no net dipole moment. The interaction of HCl with methane belongs to this category.
- London Force : It is also known as induced dipole-induced dipole interaction. Molecules like methane have no net dipole moment as the centre of positive charge and the centre of negative charge coincide. But, at a particular moment the electron cloud may stay one side resulting to the generation of partial positive and negative charges at the opposite sides of the molecules. Hence, the molecule will have instantaneous dipole moment. When such two molecules will interact with each other, London forces will occur. This force is responsible for the liquefaction of gases like methane.
13. SN2 Reaction:
- It is susceptible towards steric crowding at the reaction centre. Greater is the steric crowding at the reaction centre, lower will be the chance for the nucleophile to attack the electrophilic centre. Hence, slower will be the rate of the reaction. As the steric crowding increase from 1° to 3° alkyl halides, the SN2 reaction rate will decrease from 1° to 3° alkyl halide.
- SN2 reaction involves inversion of configuration at the reaction centre i.e. a centre with R configuration will convert to S configuration after SN2 reaction and vice versa.
- In case of SN2 reaction no new charge is created only the existing charge is dispersed. Hence, on increasing the solvent polarity will stabilize the starting material more than the T.S. Hence, the reaction rate will decrease. Hence, aprotic solvent favours the SN2 reaction.
14. SN1 Reaction :
- SN1 reaction is susceptible towards the stability of the intermediate carbocation. Greater is the stability of the carbocation, faster will be the rate of the reaction. As the stability of the carbocations increase from 1° to 3°, the rate of the reaction will also increase from 1° to 3° alkyl halides.
- SN1 reaction involves racemisation of configuration at the reaction centre i.e. 100 % pure R reactant will generate 50 % R and 50 % S products.
- In case of SN1 reaction separation of opposite charges will occur. Hence, on increasing the solvent polarity will stabilize the intermediate more than the starting material. Hence, the reaction rate will increase. Hence, protic solvent favours the SN1 reaction
15. Inductive effect arises due the difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Its effect decreases as the distance from the source increases. It is a permanent effect. It can be of two types - Electron donating inductive effect (+1 effect) and Electron withdrawing inductive effect (-1 effect). Many phenomena such as stability of reactive intermediates, acidity-basicity etc. can be explained by this effect.
16. Rules for finding out the most stable resonating structure
- Greater is the no. of covalent bonds, more will be the stability of the canonical.
- Negative charge on more electronegative atom and positive charge on more electropositive atom is more stable than the reverse.
- Structure having less charge separation is more stable than the structure having more charge separation.
- Structure involving opposite charges on closer atoms is more stable than the structure involving same charges on adjacent atoms.
17. Functional Group List :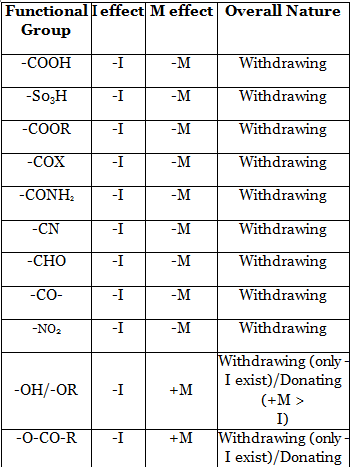

18. Carbocations are electron deficient species. Hence, any factor (Inductive, Hyperconjugative or, Mesomeric) that will increase the electron density on the carbocationic carbon will increase the stability of the carbocation. Mostly these are sp2 hybridized species. Sometimes these may also be sp hybridized also.
19. Carbanions are electron rich species. Hence, any factor (Inductive or, Mesomeric) that will decrease the electron density on the carbanionic carbon will increase the stability of the carbanion. Mostly these are sp2 hybridized species. Sometimes these may also be sp/sp3 hybridized.
20. Radicals are odd electron species. These are stabilised by both the electron donating as well as electron withdrawing groups. Mostly these are sp2 hybridized species. These may also be sp3 hybridized.
21. According to Huckel a system will be aromatic if it is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains (4n+2)π e" [n = 0 , 1 , 2 ....]. Similarly, a system will be antiaromatic if it is cyclic, planar, fully-conjugated and contains 4nπ e- [n = 1, 2 ....]. But, if a species does not maintain any of the first three conditions, it will be non-aromatic.
22. Stability order of aromatic, non-aromatic and antiaromatic species are : Aromatic > Non-aromatic > Anti-aromatic.
23. Acidity of a compound depends on the stability of the conjugate base. Greater is the stability of the conjugate base, higher will be the acidity of the compound. As conjugate base is anionic in nature, EWG will increase the acidity of an acid while EDG will decrease the acidity of the acid.
24. Basicity of a nitrogenous compound depends on the availability of lone pair on nitrogen atom. Greater is the availability of lone pair on nitrogen atom, higher will be the basicity. Any EDG will increase electron density on nitrogen atom and thereby increase basicity while any EWG will decrease the electron density on nitrogen atom and thereby decrease basicity.
|
44 videos|102 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Some Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What are the basic concepts of organic chemistry? |  |
| 2. Why is organic chemistry important? |  |
| 3. How do you name organic compounds? |  |
| 4. What are functional groups in organic chemistry? |  |
| 5. What are some common organic reactions? |  |

















