The Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1
| Table of contents |

|
| Building Blocks of Life And Their Functions |

|
| Systematics |

|
| Nomenclature |

|
| ICBN -“International Code of Botanical Nomenclature” |

|
| Taxonomic Categories |

|
| Taxonomic Aids |

|
Building Blocks of Life And Their Functions
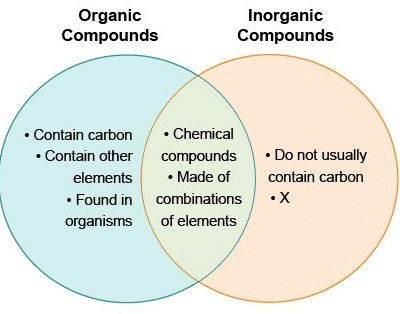
- Living organisms are formed of many types of Inorganic as well as Organic biomolecules.
- Inorganic compounds include water, minerals etc. and are always micro-biomolecules (small-sized, low molecular weight, readily soluble in water and diffusible) while organic molecules may be micro (Example - mono sugars, amino acids etc.) or macro-biomolecules (large-sized, high molecular weight, insoluble or slightly soluble and non-diffusible, e.g., proteins, fats, nucleic acids, etc.).

- These both types of biomolecules play important roles in metabolism.
 Living Organisms are made up of chemical building blocks
Living Organisms are made up of chemical building blocks
Role of Water
- Water forms 70-90% of the cellular pool. It forms 65% (about two-thirds) of the human body.
- It is formed of H and O in the ratio of 2:1.
- 95% of water is found in the free state and 5% in combined form in the cell.
- Water helps in sustaining life processes. So water is called elixir or cradle of the lip as life is not possible in the absence of water.
Role of Oxygen
- Oxygen is mainly utilized in aerobic cell respiration of the nutrients inside the mitochondria to produce energy-rich ATP molecules, so is essential for life.
- In the absence of oxygen, only 5% of the energy available is released.
Role of Sodium Chloride (common salt)
- Sodium chloride plays an important role in metabolic functions of the body, especially when in ionic form.
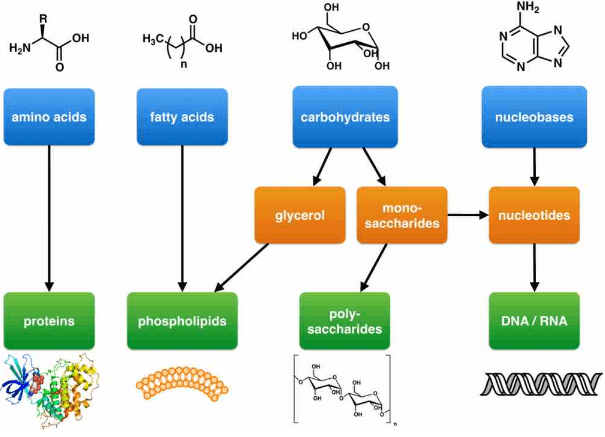
Role of Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are organic compounds formed of C, H and O generally in the ratio of 1:2:1. These are commonly called saccharides (Gk. saccharin = sugar).
- Carbohydrates are the main storage molecules, and most organisms use carbohydrates as an important fuel, breaking these bonds and releasing energy to sustain life.
Role of Proteins
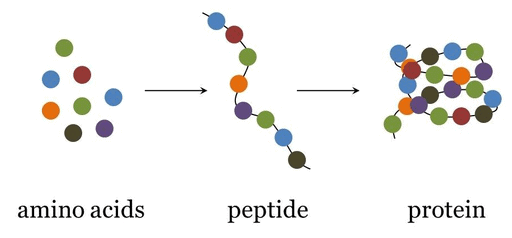
- Proteins are polymeric compounds formed by interlinking amino acids (monomers) by peptide bonds. Out of about 100 types of amino acids, only 20 types of amino acids are of biological importance, so are called Magic 20.

- Proteins play a vital role in the formation of structures in living organisms. Like carbohydrate and fat protein can be broken down with the release of energy. Protein is not stored as such in the body, and it is normally only used as a substantial source of energy in conditions of starvation.
Role of Lipids
- Lipids comprise a major group of insoluble hydrocarbons having many functions. These are polymers of alcohols (e.g. glycerol) and fatty acids interlinked by ester bonds. Complex lipids such as true fats are important organic molecules that are used to provide energy. Fats in animals also provide protection from heat loss.
Role of Nucleic Acid
- These are polymers of nucleotides interlinked by phosphodiester bonds called polynucleotides. Each nucleotide is formed of 3 components: a pentose sugar (e.g. ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a phosphate group and an inorganic nitrogen-base (a purine or a pyrimidine).
- DNA acts as genetic material in most organisms and controls the synthesis of structural and functional proteins. RNA also act as genetic material in all plant viruses, e.g. TMV and helps in protein synthesis.
Systematics
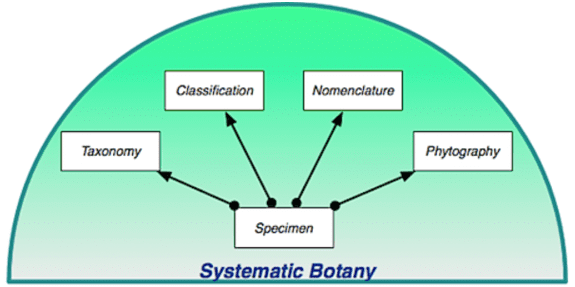
- The term ‘Systematics’ was proposed by Linnaeus in 1735.
- It includes a description of external morphological characters of plants or living organisms.
Example: Morphological characters of root, stem, leave flowers.
New systematics or Neo systematics or Biosystematics is a new branch. Its name was given by Julian Huxley (1940).
The term 'taxonomy' was coined by A. P. de Candolle.
- Carolus Linnaeus is called the father of taxonomy.
- H. Santapau is called the father of Indian taxonomy.
Taxonomy is of 6 types:
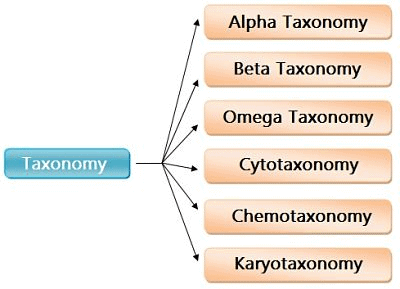 Taxonomic Categories(i) Alpha taxonomy: Only morphological characters are used for the identification and classification of plants.
Taxonomic Categories(i) Alpha taxonomy: Only morphological characters are used for the identification and classification of plants.
(ii) Beta taxonomy: Involves genetical, anatomical, cytological, palynological, physiological and other characters.
(iii) Omega taxonomy: Analysis and synthesis of all information and types of data to develop a classification system based on the phylogenetic relationship.
(iv) Cytotaxonomy: The use of cytological characters of plants in classification or in solving taxonomic problems is called Cytotaxonomy.
(v) Chemotaxonomy: The use of chemical compounds present in plants for classification or in solving taxonomic problems is called Chemotaxonomy or chemical taxonomy. The basic chemical compounds used in chemotaxonomy are alkaloids, carotenoids, tannins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, fatty acids, aromatic compounds etc.
(vi) Karyotaxonomy: It is based on the characters of the nucleus and chromosomes. The pattern of chromosome bands (dark bands and light bands) is the most specific character for classification of organisms.
Nomenclature
- Nomenclature is giving distinct scientific names to various structures, including living organisms for their identification.
- The names are of two types:
(i) Vernacular (common name)
(ii) Scientific Names - Types of Nomenclature:
(i) Polynomial Nomenclature
(ii) Binomial Nomenclature
(iii) Trinomial Nomenclature - Carolus Linnaeus is the founder of the binomial system.
- Linnaeus proposed scientific name in his book “Species Plantarum”.
- In binomial nomenclature, each scientific name has 2 components:
(i) Generic name (genus)
(ii) Specific name (species)
Example: Solanum tuberosum (potato).
ICBN -“International Code of Botanical Nomenclature”
- Collection of rules regarding scientific nomenclature of plants.
- ICBN was first proposed by Sprague, Hitchcock, Green (1930).
- ICBN was first accepted in 1961.
Main Rules of ICBN
- Name of any species consists of two names:
(i) Generic name
(ii) Specific name - In plant nomenclature, tautonyms are not valid, i.e. generic name and specific name cannot be the same, e.g., Mangifera indica. But tautonyms are valid for animal nomenclature, e.g., Naja naja (Indian cobra).
- Length of genus or species should not be less than 3 letters and not more than 12 letters, e.g., Mangifera indica.
Exception: Riccia pathankotensis - The first letter of the genus should be in capital letters, and the first letter of specific name should be in small letter.
- Name of the scientist (who proposed nomenclature) should be written in roman in short after the specific name, e.g., Mangifera indica Lin.
- If any scientist has proposed the wrong name, then his name should be written in the bracket, and the scientist who corrected the name should be written after the bracket, e.g., Tsuga canadensis (Lin.) Salisbury.
 |
Download the notes
Revision Notes: The Living World
|
Download as PDF |
Type Specimen (herbarium sheet) are of Different Types
- Holotype: Herbarium sheet on which the first description of the plant is based.
- Isotype: Isotype is any duplicate specimen of the holotype.
- Lectotype: In case holotype is lost, second herbarium sheet prepared from the original plant is called lectotype.
- Isolectotype: Isolectotype is any duplicate specimen of the lectotype.
- Syntype: If holotype and original plant are lost then many herbarium sheets prepared from many plants of the same species are called syntypes.
- Isosyntype: It is a duplicate specimen of a syntype.
- Neotype: In case holotype and original plant are lost then herbarium sheet prepared from other plants of same species is called neotype.
- Isoneotype: Any duplicate specimen of the neotype.
- Paratype: Additional description sheet used in the first description of the plant is called paratype. It is prepared from some other plant of same species having some variations.
Taxonomic Categories
- The term taxonomy was coined by - A.P. Candolle
- Father of taxonomy - Carolus Linnaeus
- Father of Indian taxonomy - H. Santapau
- They are also known as the Linnaean hierarchy.
- There are 7 main taxonomic categories. It is defined as the sequence of categories in a decreasing or increasing, which is from the highest kingdom to the lowest species.
- The hierarchy has two categories, i.e., obligate and intermediate.
- Obligate is the one which is followed strictly and range from kingdom to species.
- Intermediate is not followed strictly and they. Also, they are added in the obligate list like subdivision, superfamily, superclass, suborder, subspecies etc.
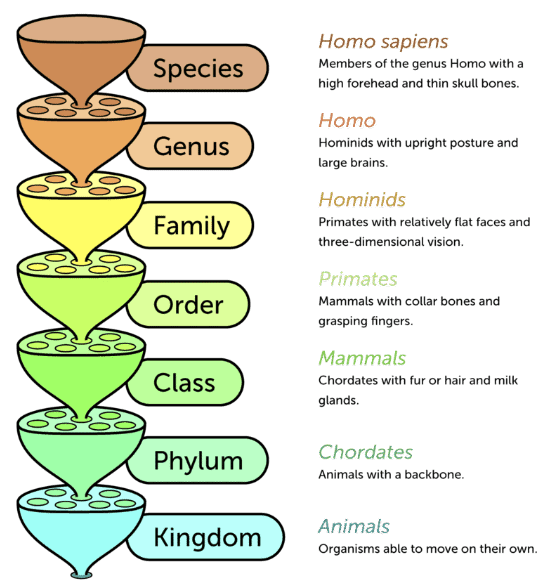 Linnaean Classification System
Linnaean Classification System
(i) Species: It is the smallest taxonomic category. It is the basic unit of classification. It is the group of population which is similar in shape, form and reproductive features. Due to the same reproductive features, the fertile sibling can be produced.
(ii) Genus: It is an assembly of a group of similar species which involved from a common ancestor and have certain common characters called correlated characters. But it is not mandatory to have many species. Monotypic genera have only one species. Polytypic genera have more than one species.
Example: Cat and leopard are put in the genus Panthera.
(iii) Family: It is the collection of similar genera. Families are characterised on the basis of reproductive and vegetative features. For example, the lion and tiger are included in the family Felidae.
(iv) Order: Being a higher category is the assembly of one or more than one similar families. Family Felidae is included in the order Carnivora.
(v) Class: A class is a subdivision within a phylum made of one or more than one order. Class Mammalia includes all mammals which are monkey, gorilla, gibbon and man.
(vi) Phylum: It comprises of a collection of similar classes. Phylum Chordata of animals has class Mammalia along with fishes, reptiles, birds, and amphibians.
(vii) Kingdom: All animals belonging to various phyla are assigned to the topmost taxonomic category called kingdom. Example all animals are included in Kingdom Animalia. All plants are included in kingdom Plantae. The unit that denotes grouping of the organism based on observable features is known as Taxon.
Kingdom → Phylum → [A] → Order → [B]
Taxonomic Aids
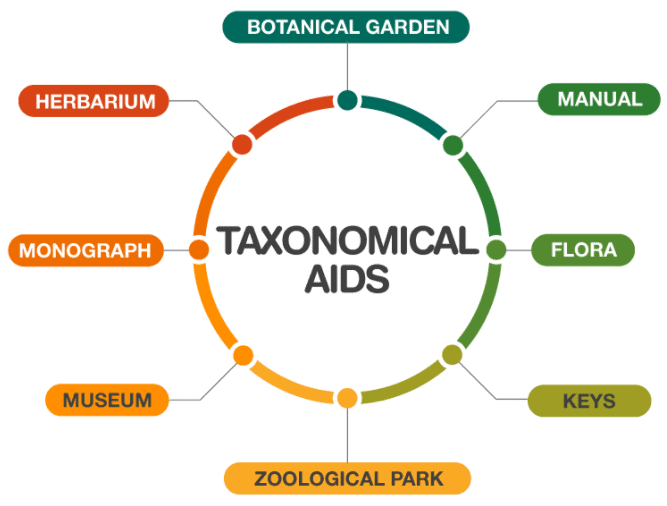
- The different methods which are being used to identify and classify organisms are referred to as Taxonomic aids. Identification of organisms is a tedious process.
- Keys are used for identification and are based on contrasting characters. These are referred to as Taxonomic key.
- Biologists use herbarium, botanical garden, museums, zoological parks and keys in taxonomical studies.
- The herbarium is a collection of plant parts that usually have been dried, presses and preserved on sheets.
- Museums have a collection of preserved plants and animal specimens for the study and reference.

Major Botanical Gardens
- The Royal Botanic Garden – Largest Botanical Garden
- The oldest botanical garden is ‘Padua Botanical Garden’, Italy.
- Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden, Shibpur, Kolkata
- Agri Horticultural Society of India, Alipore, Kolkata
- Assam State Zoo-cum-Botanical Garden, Guwahati
- Botanical Garden, Near Sarangpur, Chandigarh
- Empress Garden, Pune
- Garden of Medicinal Plants, North Bengal University, West Bengal
FAQs on The Living World Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 1
| 1. What are the building blocks of life and their functions? |  |
| 2. What is the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature? |  |
| 3. What are taxonomic categories? |  |
| 4. What are some taxonomic aids? |  |
| 5. What is systematics? |  |